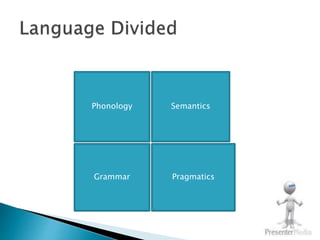
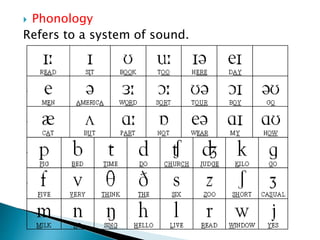
1. Language forms the core of culture and includes speech, writing, numerals, and symbols used to convey all aspects of a culture.
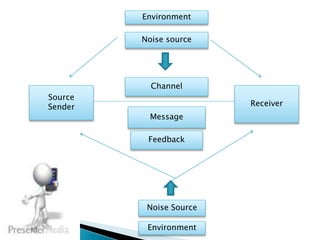
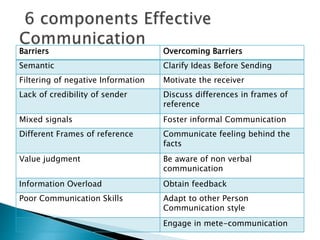
2. Communication is the exchange of ideas, feelings, and information through verbal and nonverbal means like speech, gestures, and writing.
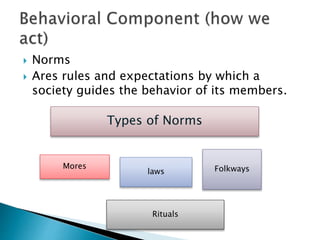
3. Culture is learned and shared by a group, and encompasses norms, values, knowledge, artifacts, and symbols that are communicated among its members.