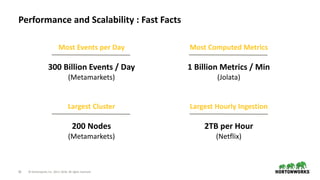
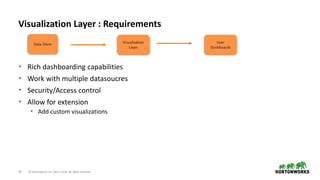
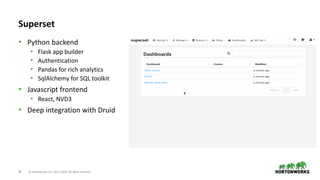
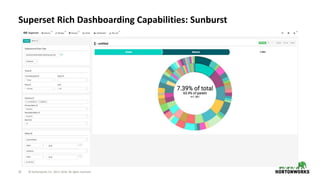
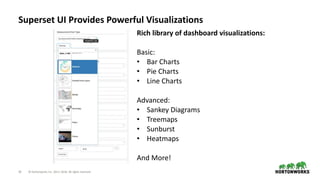
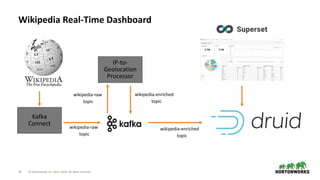
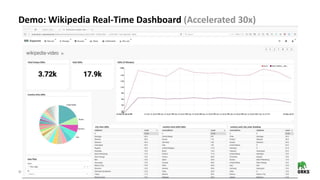
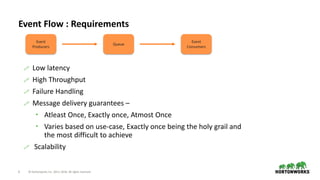
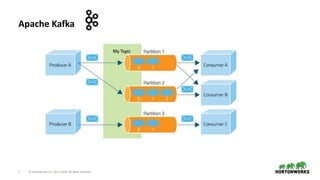
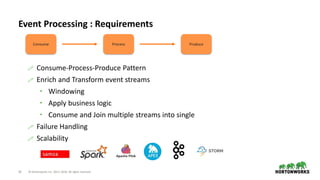
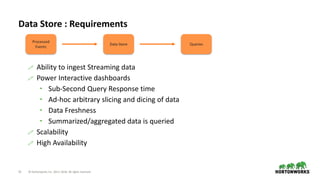
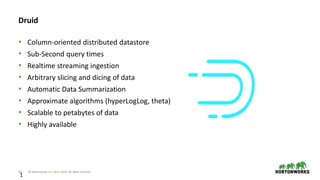
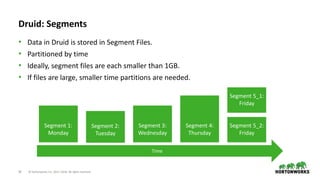
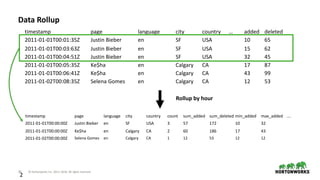
The document discusses the architecture and requirements for building interactive real-time dashboards using data streams, specifically focusing on components like Apache Kafka for event processing and Druid for data storage and visualization. Key features include low latency, high throughput, scalability, and the ability to ingest streaming data for creating actionable insights. It also emphasizes the importance of tools like Superset for visualization, enhancing user interaction with data analytics.


![3 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011–2018. All rights reserved
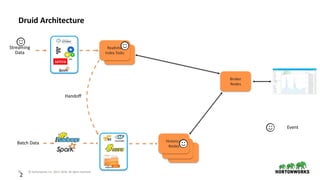
Step by Step Breakdown
Consume Events
Enrich / Transform
(Add Geolocation
from IP Address)
Store Events
Visualize Events
Sample Event : [[Eoghan Harris]] https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?diff=792474242&oldid=787592607 * 7.114.169.238 * (+167) Added fact](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interactiverealtimedashboards-180426224043/85/Interactive-real-time-dashboards-on-data-streams-using-Kafka-Druid-and-Superset-3-320.jpg)









![21 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011–2018. All rights reserved
2
Dictionary Encoding
• Create and store Ids for each value
• e.g. page column
⬢ Values - Justin Bieber, Ke$ha, Selena Gomes
⬢ Encoding - Justin Bieber : 0, Ke$ha: 1, Selena Gomes: 2
⬢ Column Data - [0 0 0 1 1 2]
• city column - [0 0 0 1 1 1]
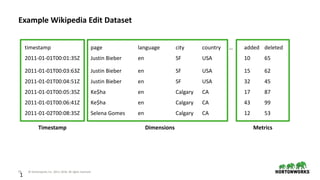
timestamp page language city country … added deleted
2011-01-01T00:01:35Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 10 65
2011-01-01T00:03:63Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 15 62
2011-01-01T00:04:51Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 32 45
2011-01-01T00:05:35Z Ke$ha en Calgary CA 17 87
2011-01-01T00:06:41Z Ke$ha en Calgary CA 43 99
2011-01-02T00:08:35Z Selena Gomes en Calgary CA 12 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interactiverealtimedashboards-180426224043/85/Interactive-real-time-dashboards-on-data-streams-using-Kafka-Druid-and-Superset-21-320.jpg)
![22 © Hortonworks Inc. 2011–2018. All rights reserved
2
Bitmap Indices
• Store Bitmap Indices for each value
⬢ Justin Bieber -> [0, 1, 2] -> [1 1 1 0 0 0]
⬢ Ke$ha -> [3, 4] -> [0 0 0 1 1 0]
⬢ Selena Gomes -> [5] -> [0 0 0 0 0 1]
• Queries
⬢ Justin Bieber or Ke$ha -> [1 1 1 0 0 0] OR [0 0 0 1 1 0] -> [1 1 1 1 1 0]
⬢ language = en and country = CA -> [1 1 1 1 1 1] AND [0 0 0 1 1 1] -> [0 0 0 1 1 1]
• Indexes compressed with Concise or Roaring encoding
timestamp page language city country … added deleted
2011-01-01T00:01:35Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 10 65
2011-01-01T00:03:63Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 15 62
2011-01-01T00:04:51Z Justin Bieber en SF USA 32 45
2011-01-01T00:01:35Z Ke$ha en Calgary CA 17 87
2011-01-01T00:01:35Z Ke$ha en Calgary CA 43 99
2011-01-01T00:01:35Z Selena Gomes en Calgary CA 12 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interactiverealtimedashboards-180426224043/85/Interactive-real-time-dashboards-on-data-streams-using-Kafka-Druid-and-Superset-22-320.jpg)