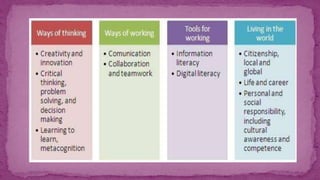
This document discusses the skills needed for students and teachers in the 21st century. It identifies key skills such as creativity, critical thinking, communication, collaboration, information literacy, media literacy, technology literacy, and cultural awareness. It emphasizes integrating these skills with core academic content through connecting learning to real-world problems, collaboration, project-based learning, and technology use. The 21st century teacher needs to be an adaptor who can adjust curriculum and tools to meet student needs, and a visionary who sees potential in emerging technologies and manipulates them for educational purposes.