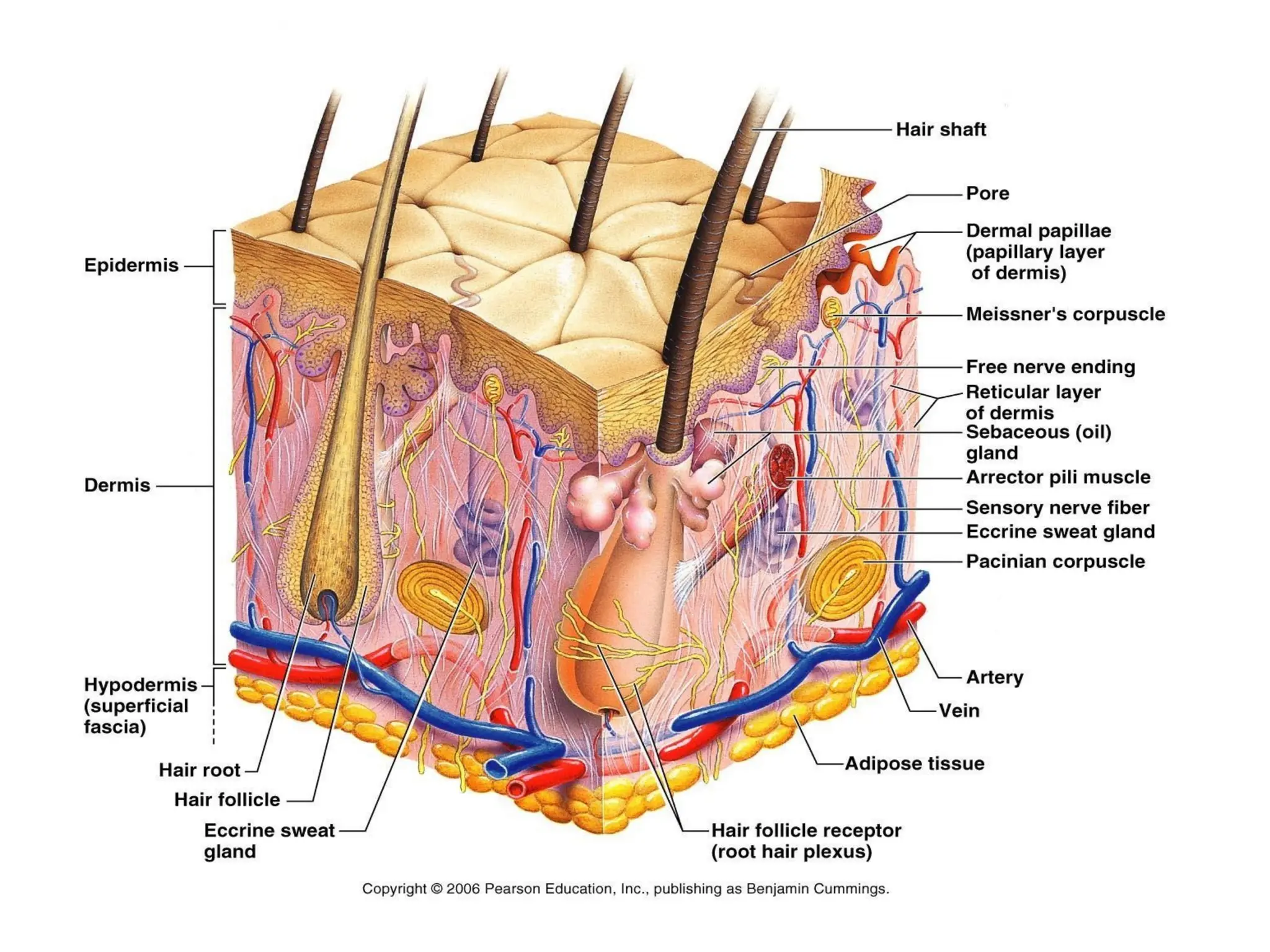
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory organs, including hair, nails, and glands, comprising three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. It performs essential functions such as protection from pathogens, excretion of waste, temperature regulation, cutaneous sensation, and vitamin D synthesis. Skin structure and health can be affected by burns and skin cancers, with preventative measures advised against excessive sun exposure.