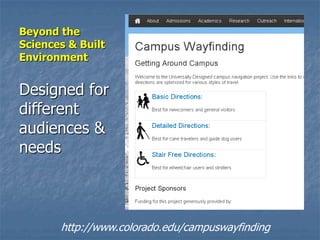
This document discusses integrating universal design content into university curriculum. It provides examples of courses that have incorporated universal design principles, such as a human-computer interaction class that teaches web accessibility and a digital media course on universal design. Strategies are suggested for promoting universal design in course content, such as sharing resources and replicating successful models at other campuses. Resources for teaching universal design are also presented, including textbooks, websites, and a conference for discussing universal design in curriculum.






![Campus & Faculty Conceptions of
Universal Design
“[F]ew postsecondary administrators, faculty, and staff
are even marginally acquainted with Universal Design or
Universal Instructional Design” (Higbee & Goff, eds.
2008)
Faculty at CU – may not have the definitive definition or
understanding of UD
Confusion on the distinction of “UD content”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ud-in-curriculum-csun2014-140321121351-phpapp02/85/Integrating-Universal-Design-Content-into-University-Curriculum-7-320.jpg)





![UD Defined – variations on a theme
…[T]he practice of designing products or
environments that can be effectively and
efficiently used by people with a wide range of
abilities operating in a wide range of situations
(Vanderheiden, 1997, p. 2014).
A framework for the design of buildings,
products and information technology to be
useable by the widest range of users.
(Valerie Fletcher, The Institute for Human
Centered Design)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ud-in-curriculum-csun2014-140321121351-phpapp02/85/Integrating-Universal-Design-Content-into-University-Curriculum-13-320.jpg)