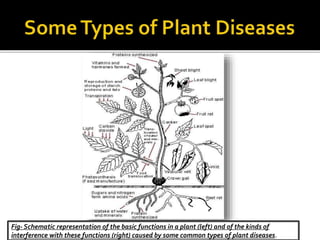
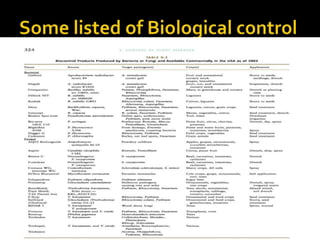
This document discusses the importance of biological control over chemical control for managing plant diseases. It notes that plant pathogens can infect most crop types and reduce yields. While chemicals are widely used to control bacteria, fungi and nematodes, there are concerns about pathogen resistance, environmental contamination, and human/animal toxicity. Biological control uses organisms like beneficial bacteria, fungi and insects to naturally reduce pathogens through competition, antibiotics or predation. It has benefits like lower impact on other organisms, compatibility with natural enemies, and no toxic residues. The document concludes that biological products are a more sustainable approach to pest control as chemicals are phased out due to resistance or commercial viability issues.