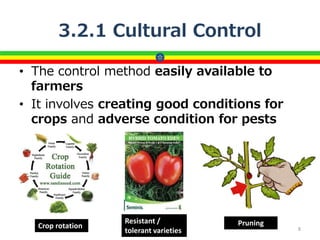
The document presents a training session on pest and disease control aimed at farmers, covering integrated pest management (IPM) techniques such as cultural, biological, mechanical, and chemical control methods. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining healthy crops, using appropriate strategies to minimize pest damage, and the careful application of pesticides while ensuring environmental safety. The training also includes a discussion of natural pest enemies and the significance of pest scouting for effective management.