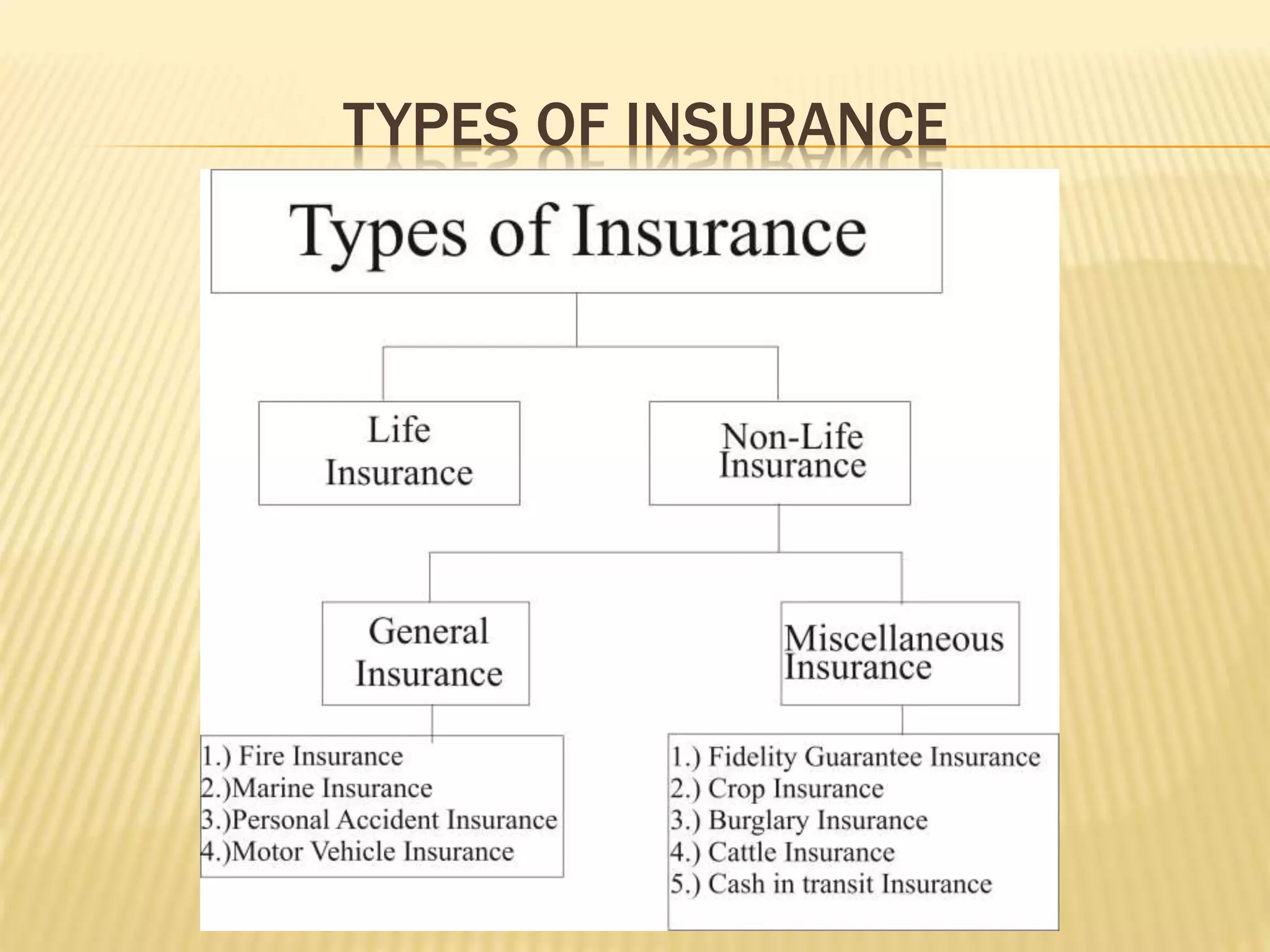
The document provides an overview of insurance law and regulations in India. It defines key terms like life insurance and general insurance. Insurance is described as a means of protecting against financial loss from uncertain events and sharing risks. The key principles of insurance like insurable interest and indemnity are outlined. The major acts governing insurance in India are the Insurance Act of 1938, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act of 1999, and Actuaries Act of 2006. The roles of regulatory bodies like IRDA in overseeing the insurance industry are also summarized.