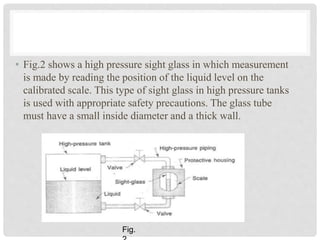
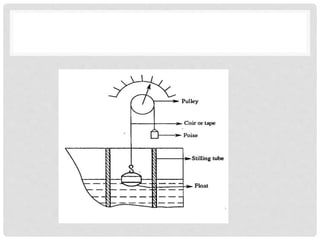
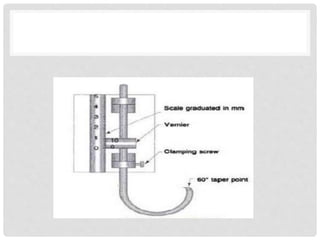
Accurate liquid level measurement is crucial in manufacturing and power plants, utilizing direct and indirect methods. The document details direct methods such as sight glasses, float-type indicators, and hook-type level indicators, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Various technologies for measuring liquid levels accommodate different operational requirements and conditions.