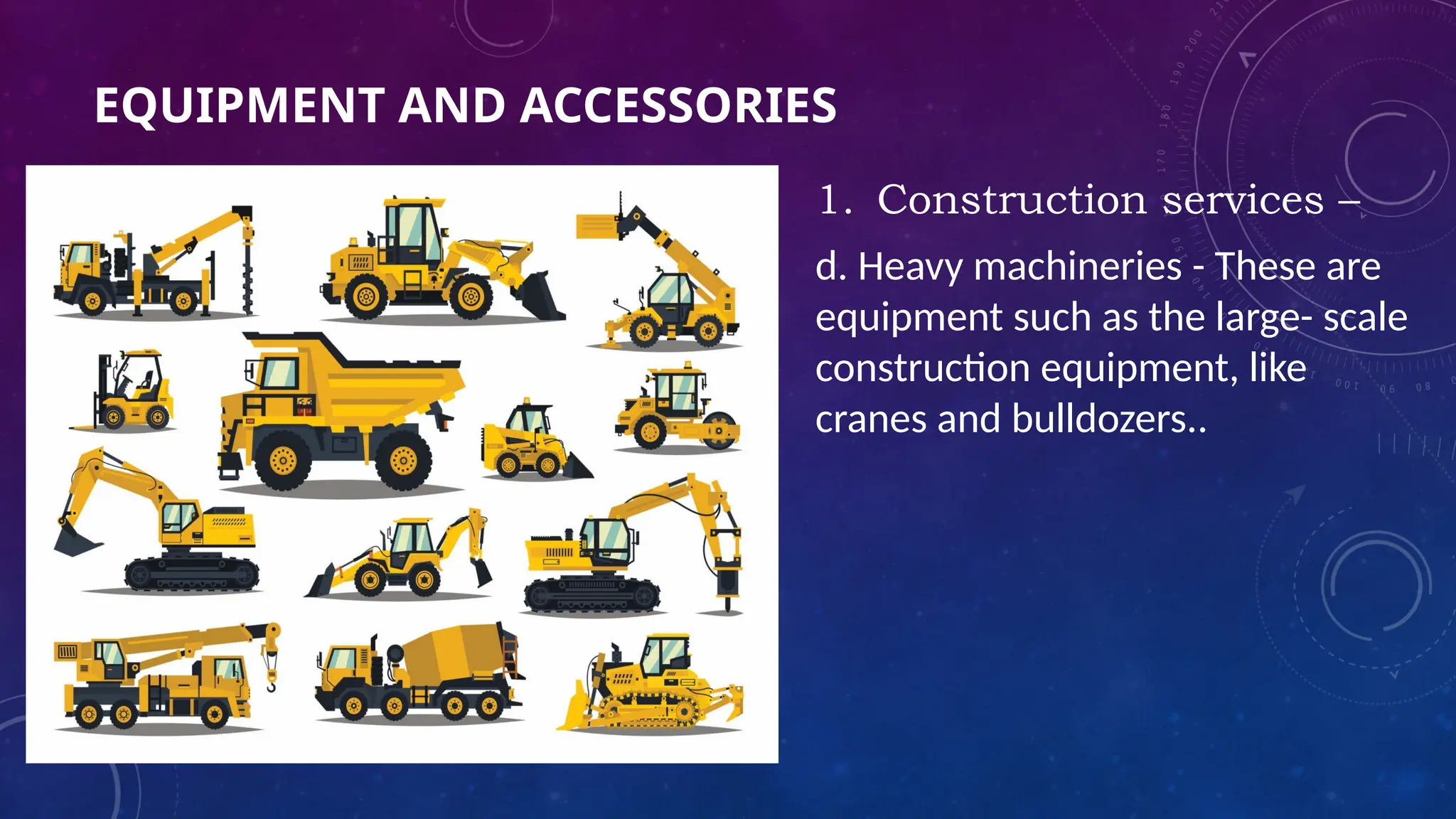
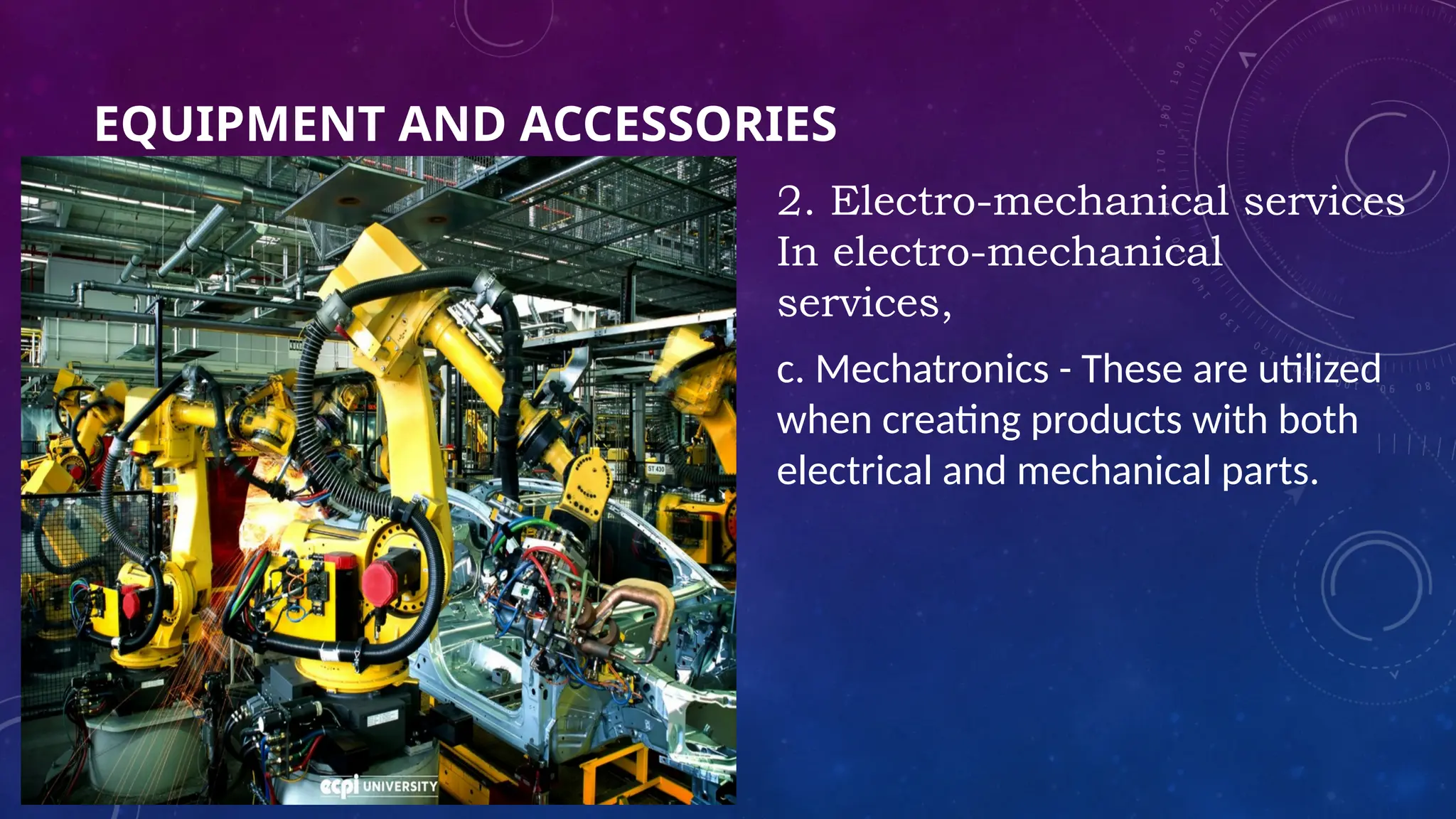
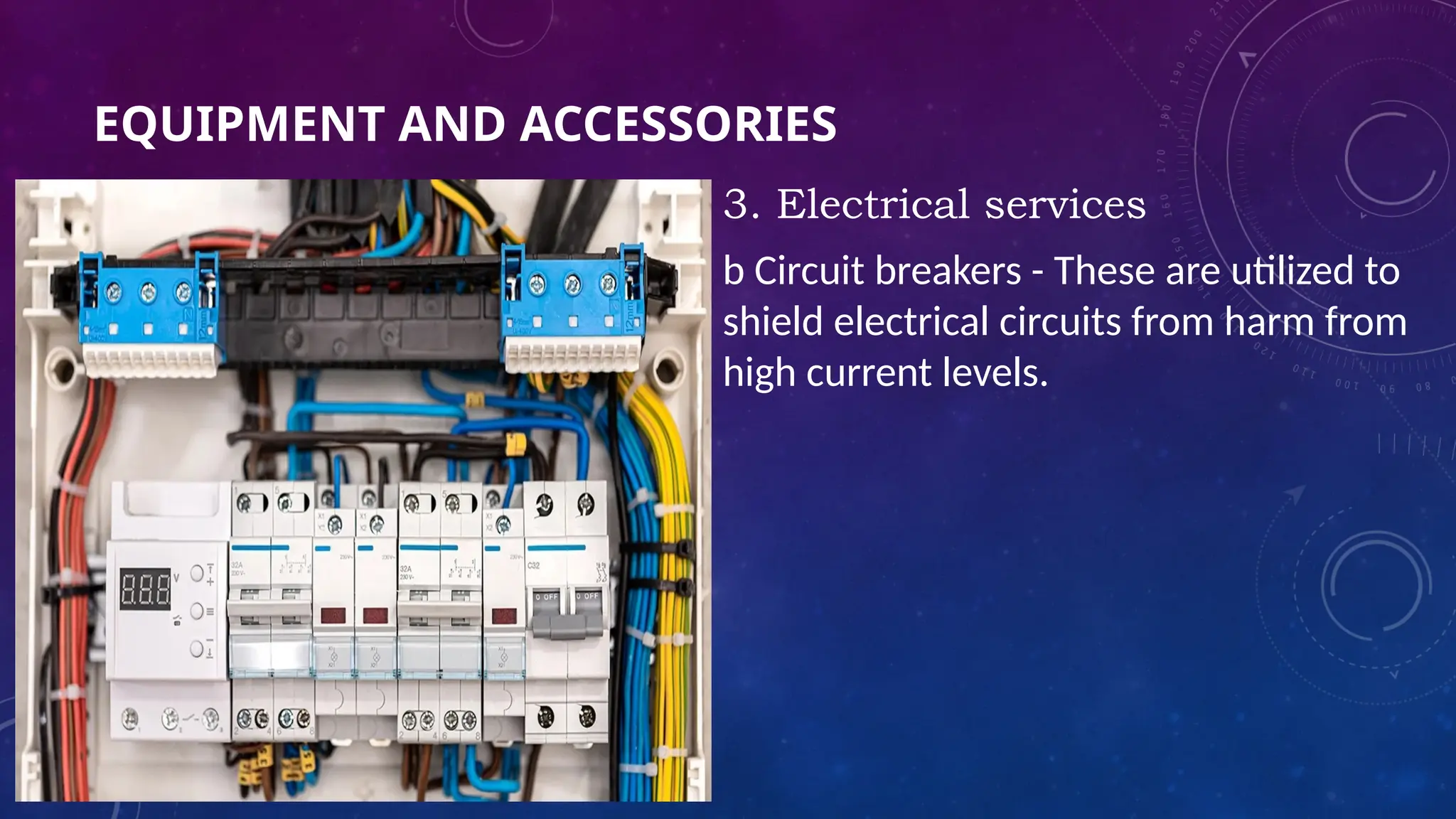
The document provides an overview of three types of instruments: analog, digital, and computer-based, detailing their principles and examples. Analog instruments function using electromagnetic induction, digital instruments display results in digits, and computer-based instruments connect to computers for enhanced measurement functionality. It also outlines various equipment and accessories used across construction, electro-mechanical, electrical, and automotive services, encouraging students to identify and present tools from each category.