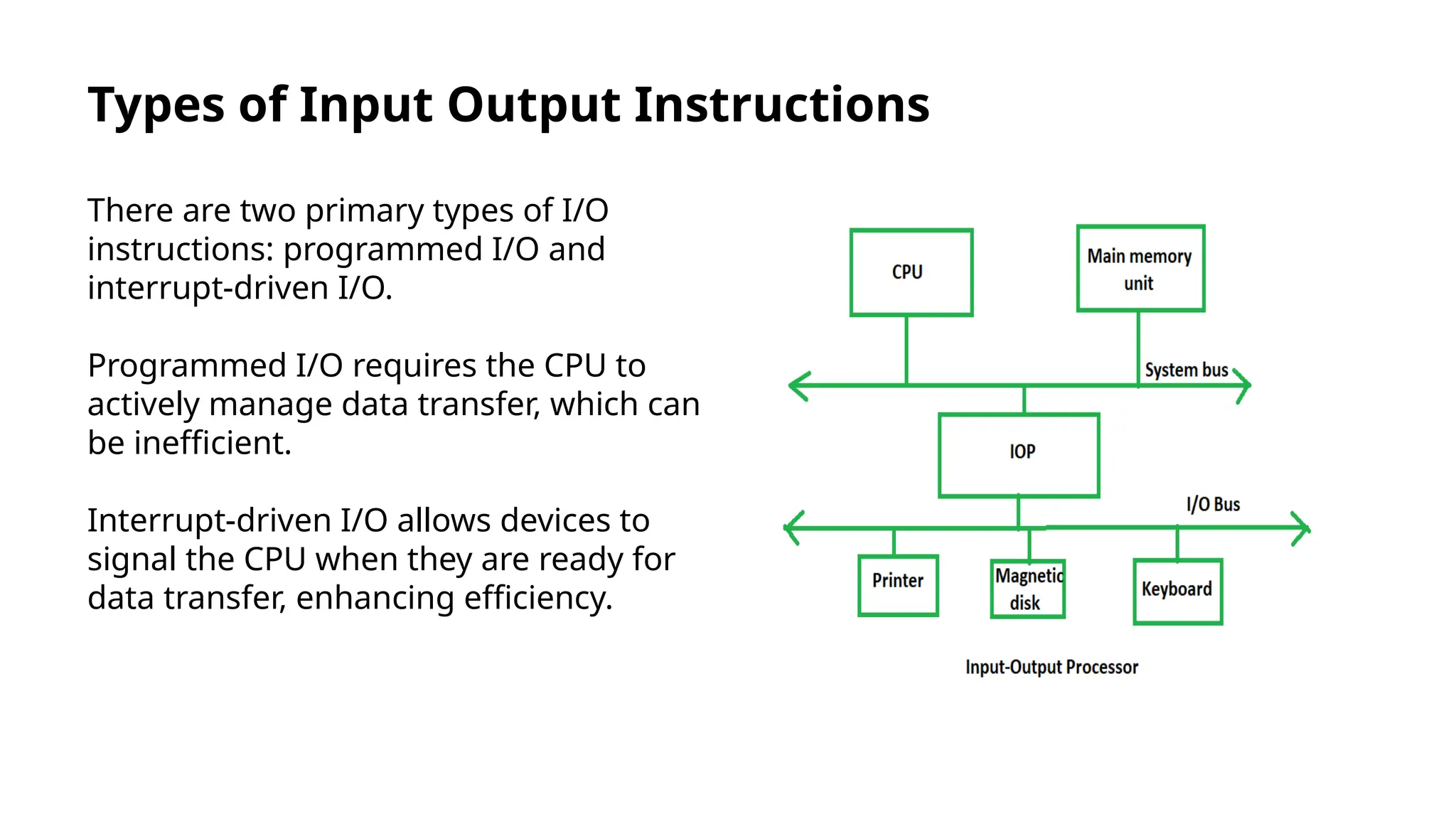
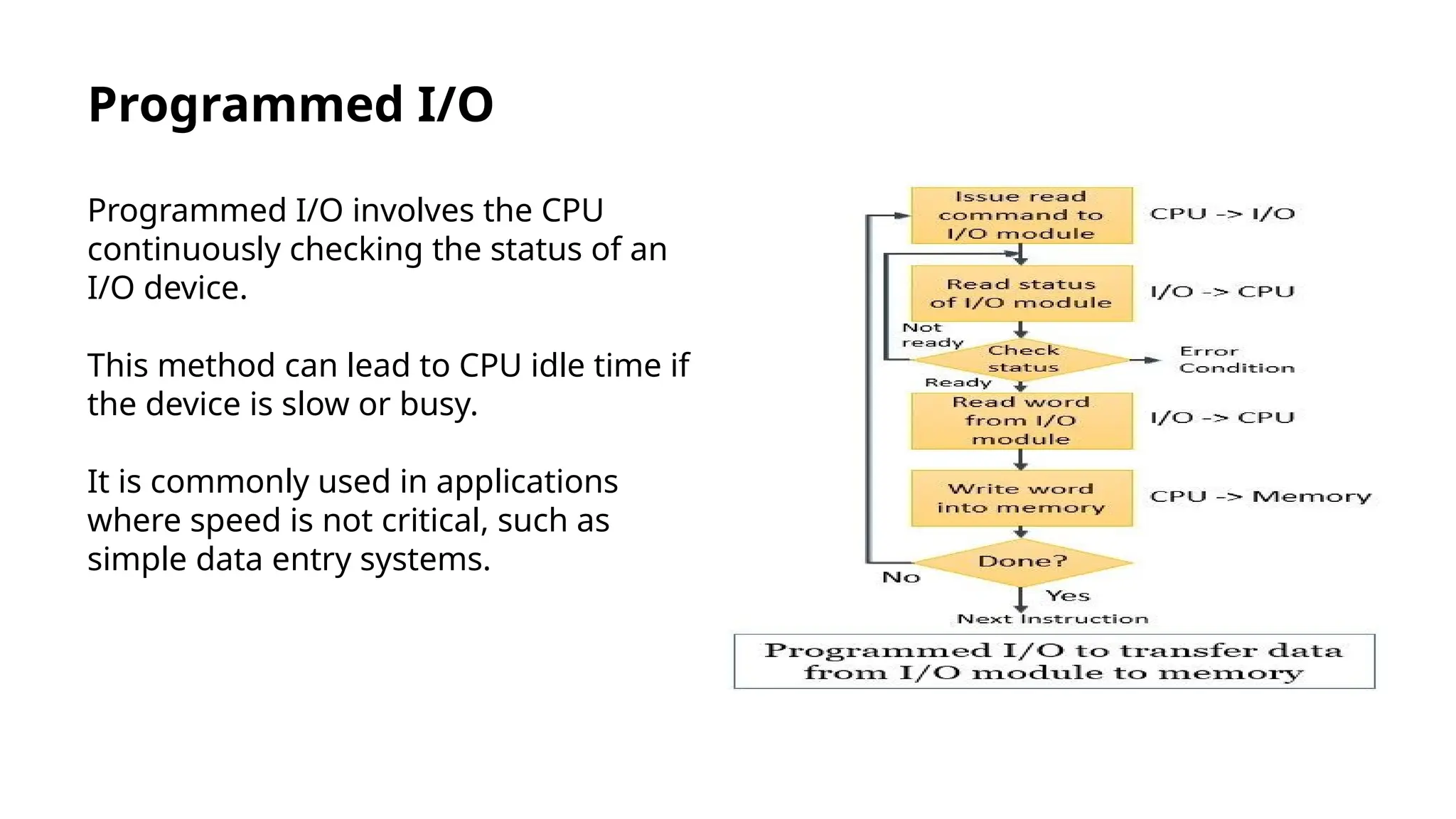
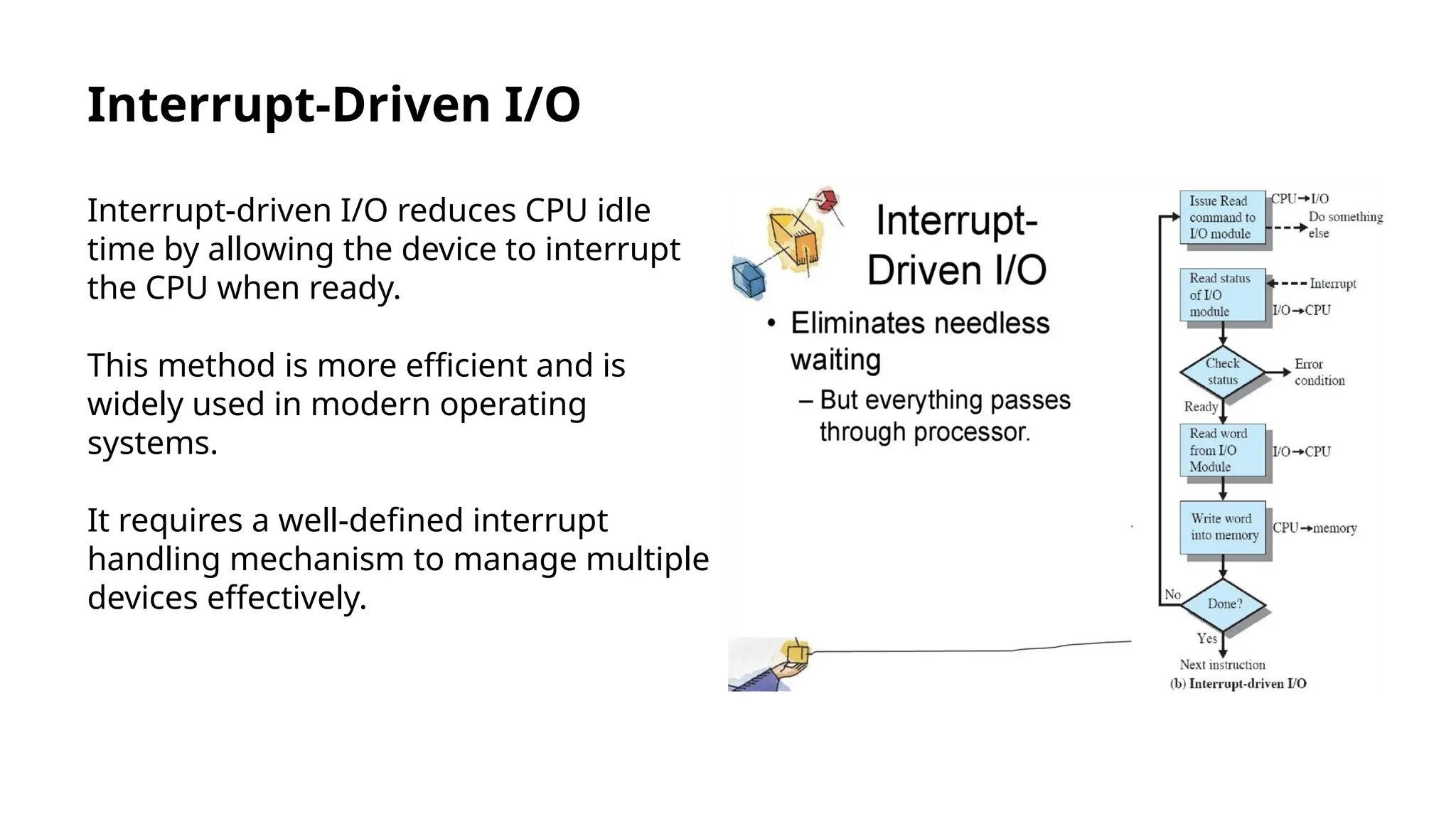
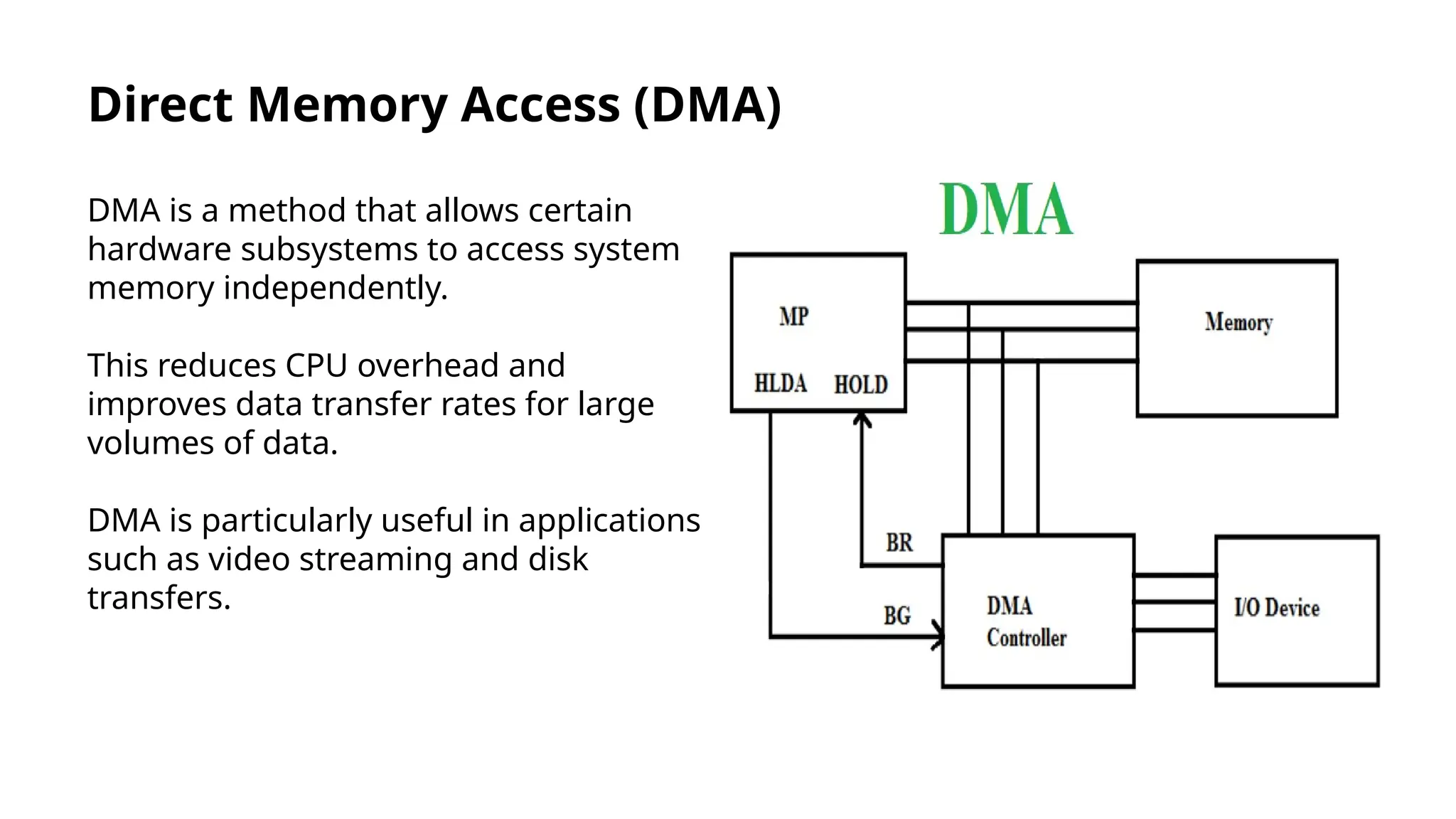
Input/output instructions are essential for communication between computers and peripheral devices, crucial for software development and hardware management. There are two main types: programmed I/O, which can be inefficient, and interrupt-driven I/O, which enhances efficiency by allowing devices to signal the CPU when ready. Direct Memory Access (DMA) further reduces CPU overhead by enabling hardware subsystems to access system memory independently, improving data transfer rates.