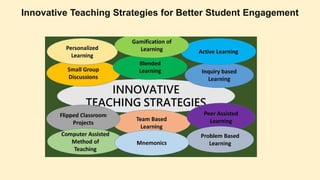
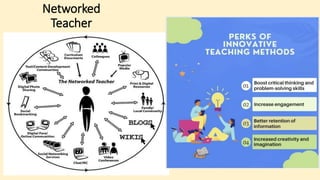
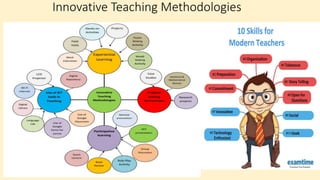
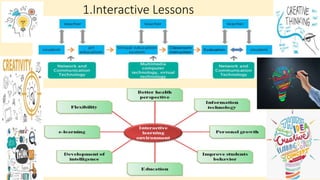
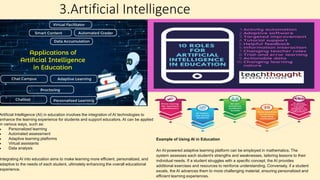
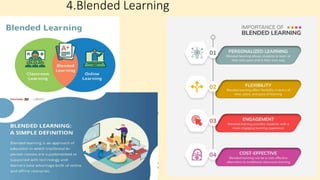
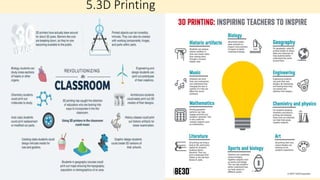
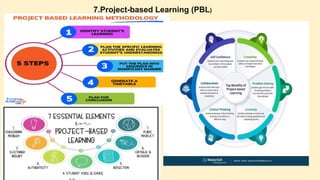
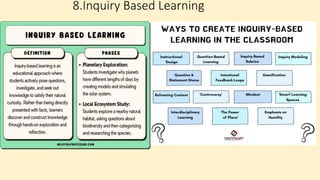
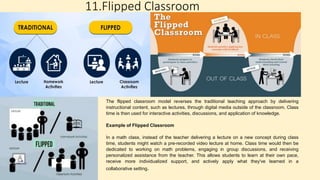
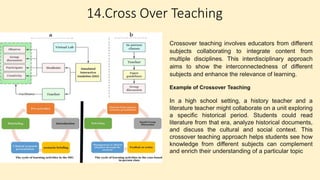
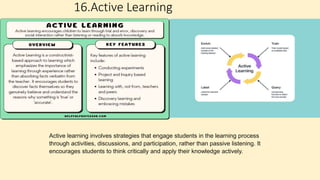
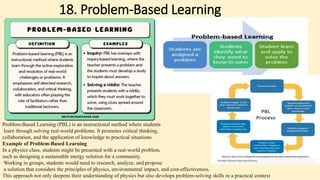
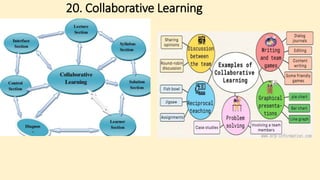
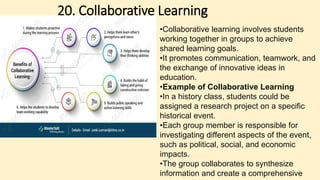
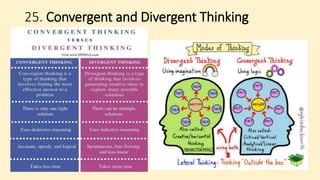
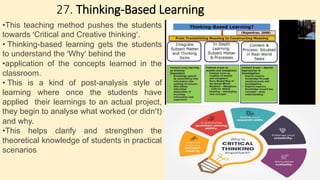
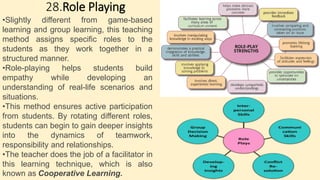
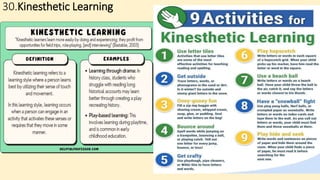
The document discusses innovative teaching methodologies that prioritize student engagement and collaboration beyond traditional classroom settings. It highlights various modern strategies such as blended learning, virtual reality, and project-based learning aimed at accommodating diverse learning styles and improving retention of knowledge. The article emphasizes the shift toward interactive and personalized approaches in response to evolving educational environments, ensuring that students actively participate in their learning process.