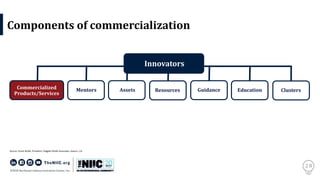
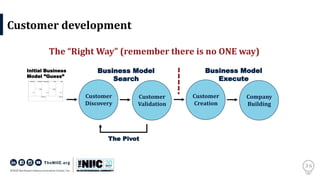
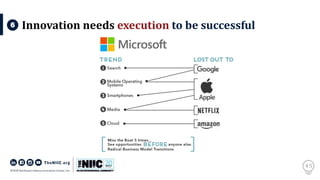
The document discusses the significance of innovation in the context of regional entrepreneurship and commercialization models, emphasizing the collaborative role of universities, industry, and students. It outlines the challenges of bringing innovative ideas to market, detailing the necessary steps and processes such as customer validation and product-market fit. It also highlights the importance of execution in transforming innovative concepts into successful ventures.