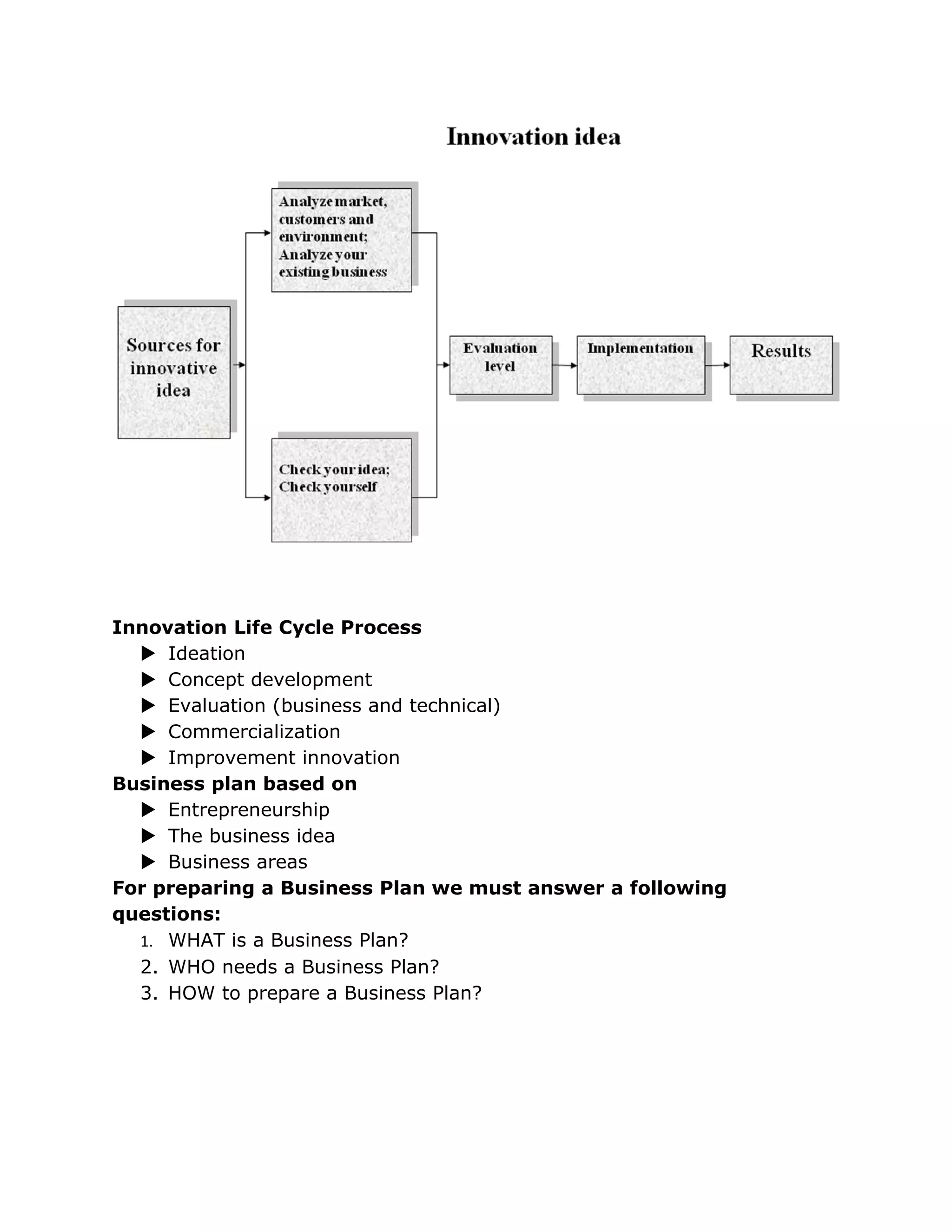
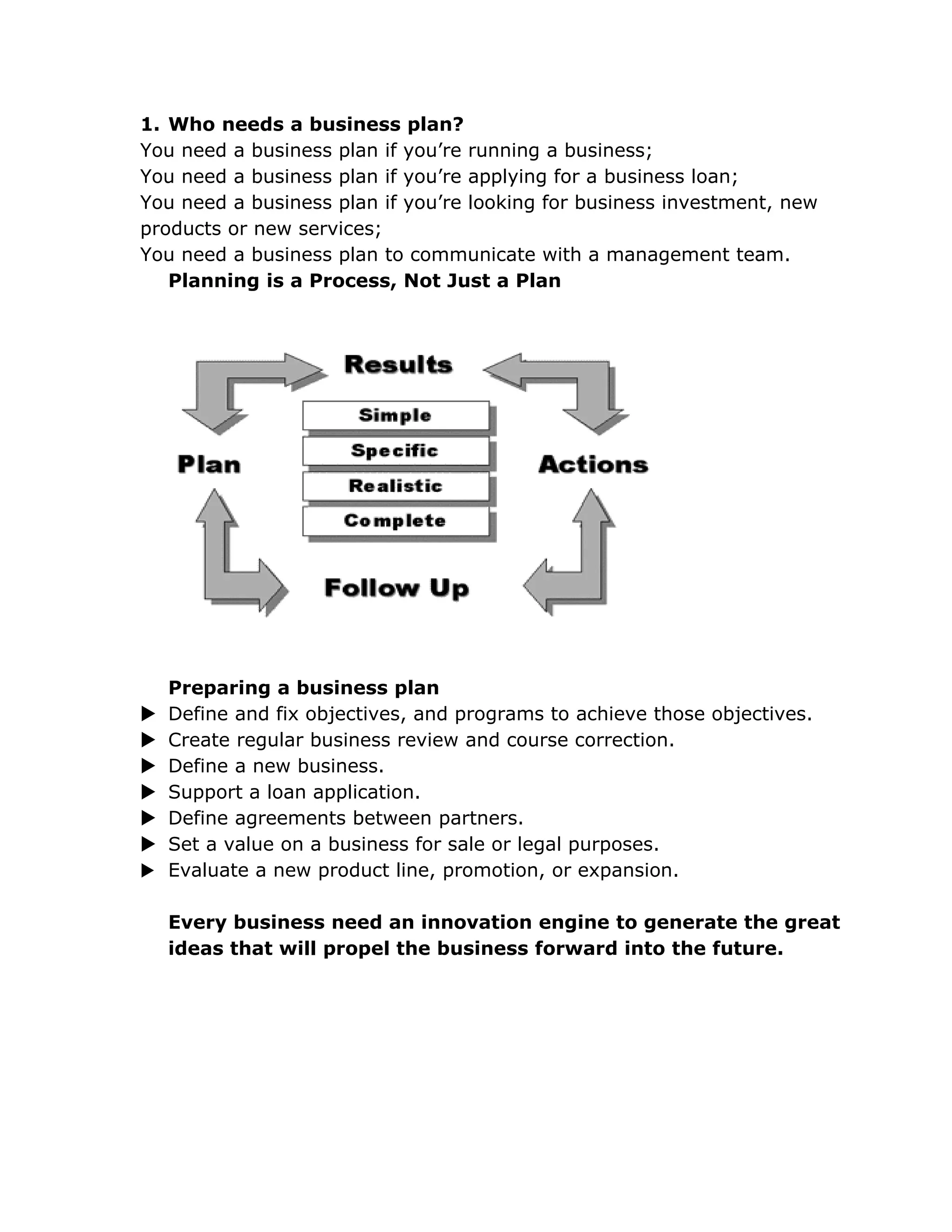
A business plan outlines key information about a business including goals, reasons for attainability, and plans for achieving goals. It typically includes sections on the business concept, market analysis, operations, management team, and financial projections. Developing a business plan helps evaluate the viability of a business idea, guide strategic decisions, and secure funding. The process of preparing a business plan involves defining objectives and programs, creating a regular review process, and answering questions about the business, its customers, and financials.