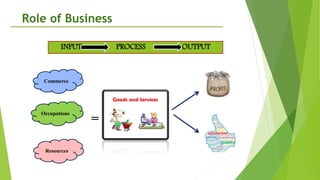
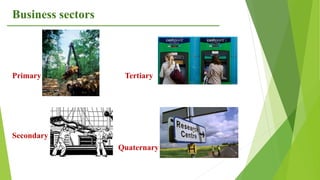
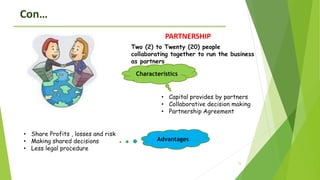
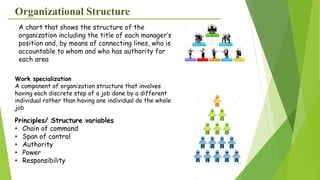
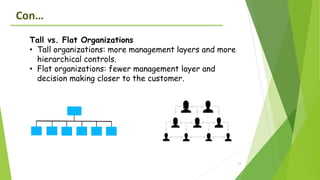
The document provides an overview of key concepts in business including definitions of business, the role and characteristics of business, different business sectors, types of business structures, and scope of commerce. It discusses concepts such as social responsibility, organizational structure, work specialization, and principles of organizational structure including chain of command, span of control, authority, and power.