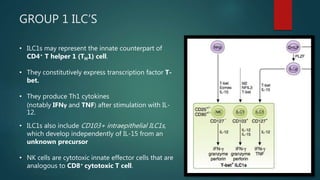
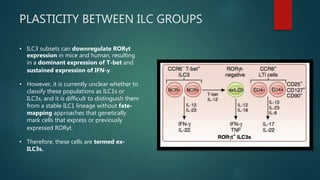
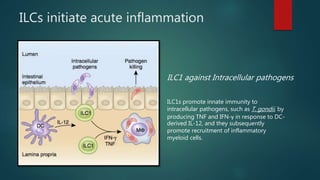
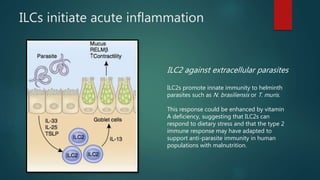
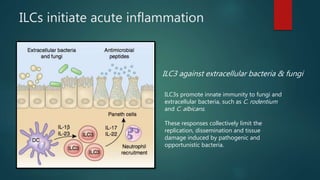
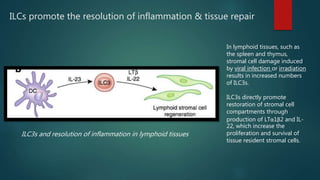
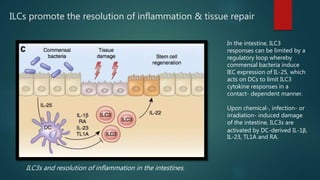
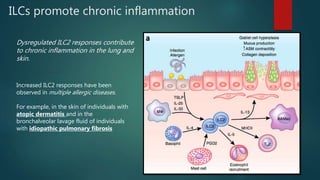
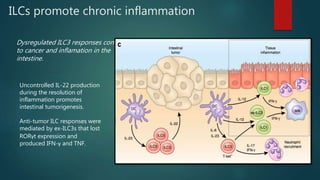
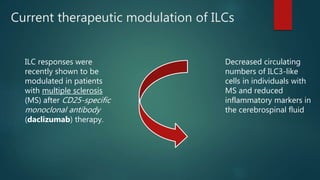
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a family of immune cells that act at the intersection of innate and adaptive immunity. ILCs are classified into three groups - ILC1s, ILC2s, and ILC3s - based on transcription factor expression and cytokine production profiles that mirror CD4+ T helper cell subsets. ILCs play roles in initiating inflammation through production of cytokines in response to pathogens or tissue damage, as well as promoting resolution of inflammation and tissue repair through production of cytokines that support epithelial cell repair and interactions with other immune cells. Dysregulation of ILC responses can also contribute to chronic inflammation in conditions like allergic diseases, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease.