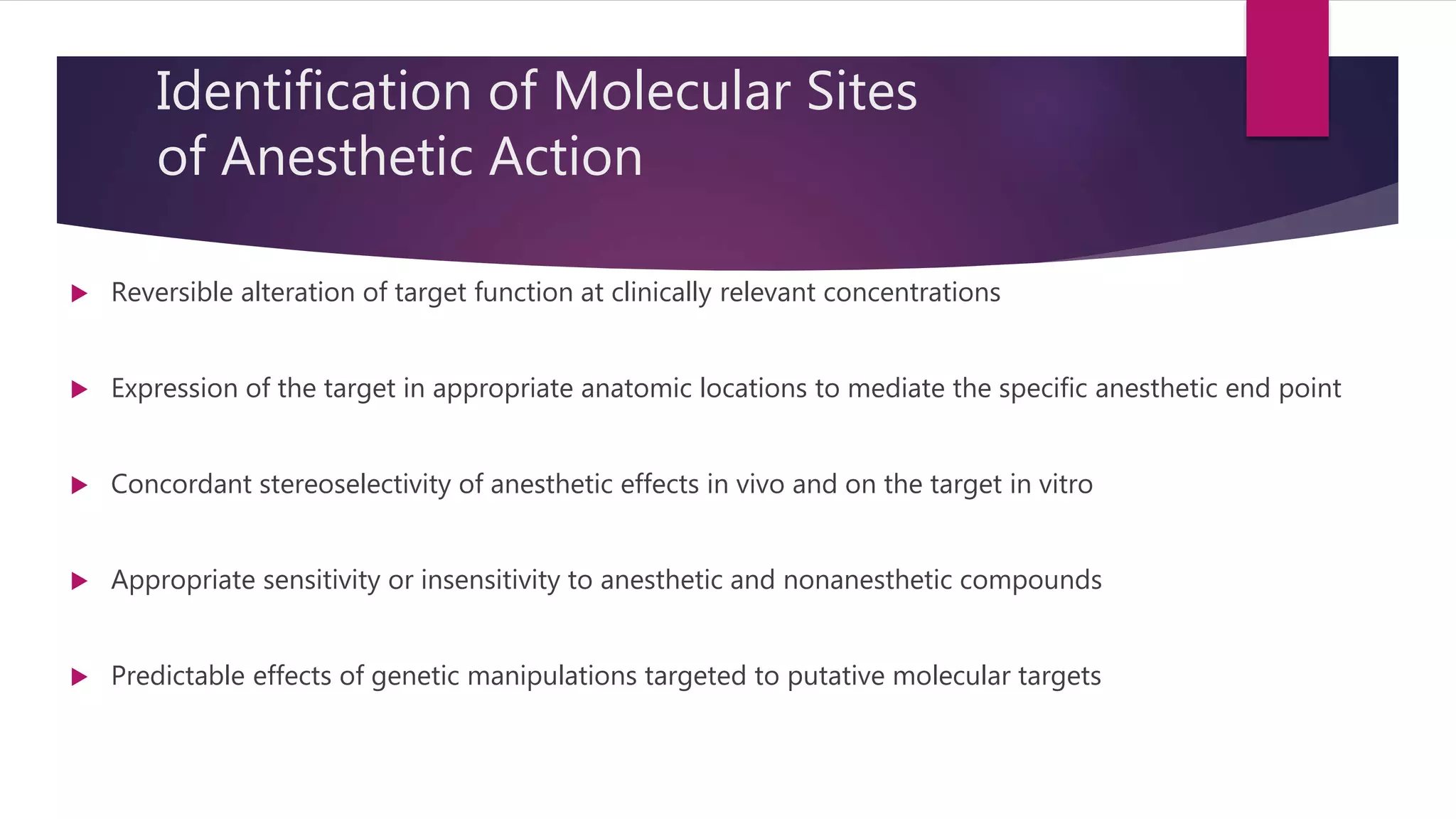
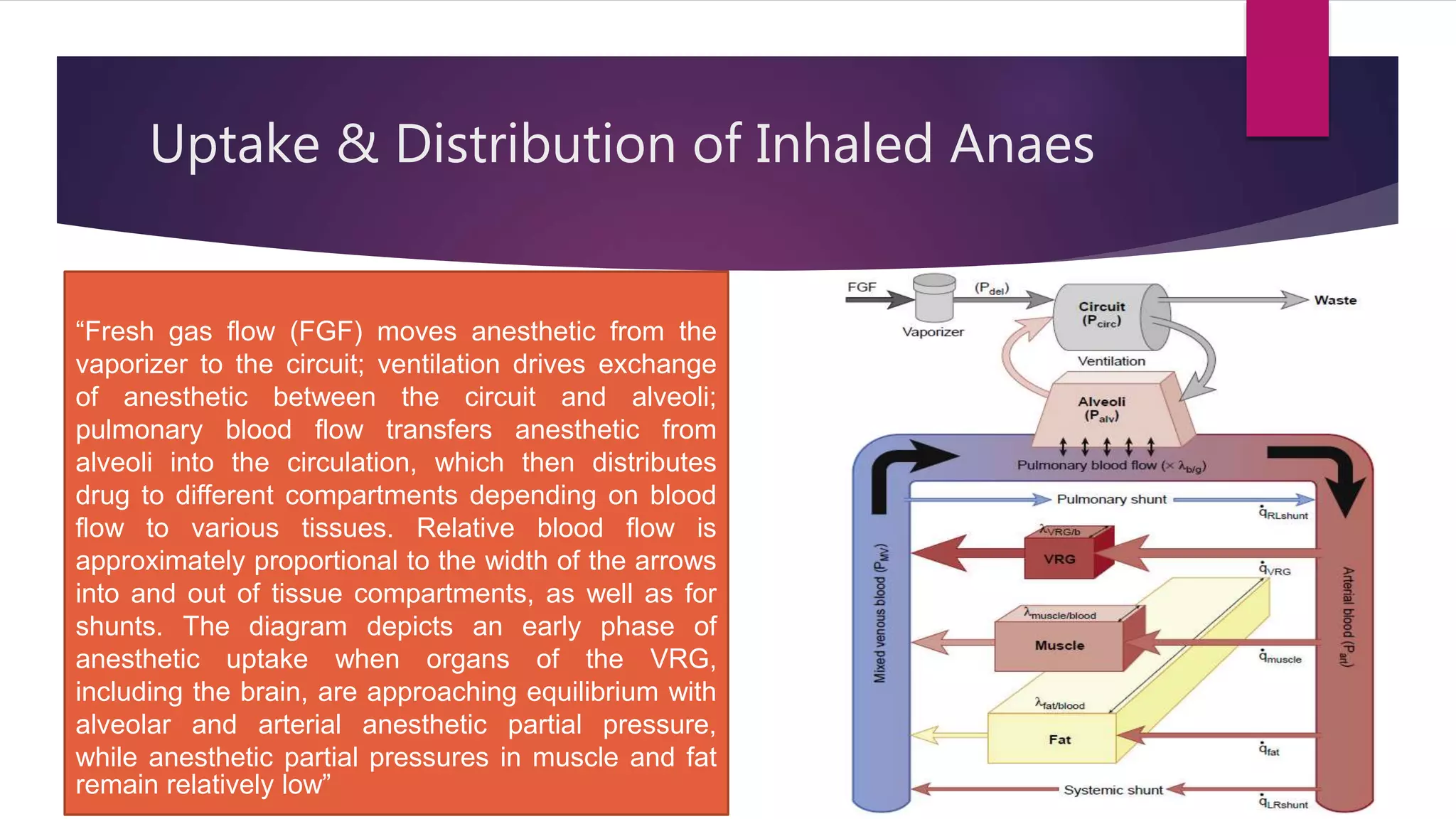
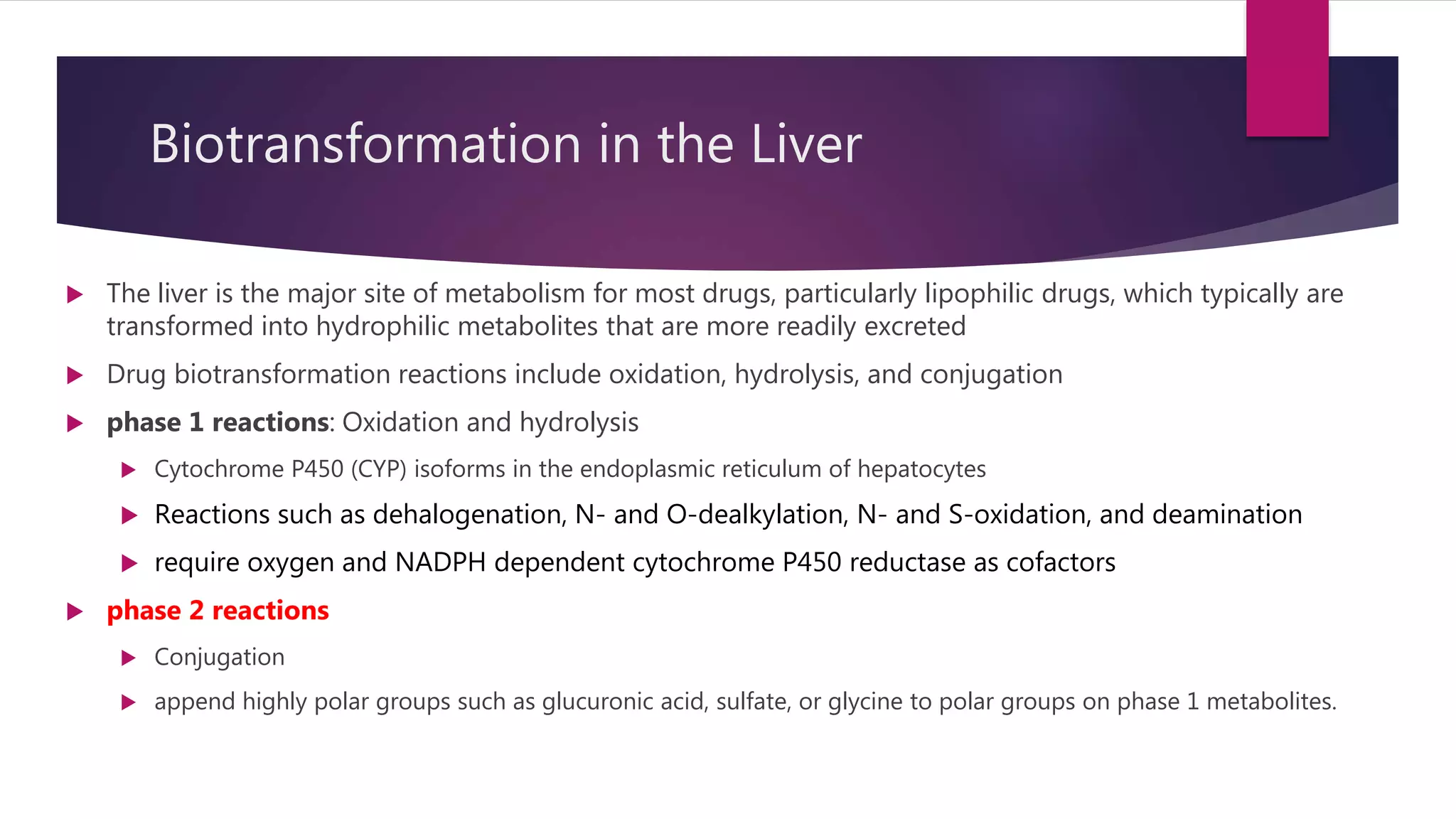
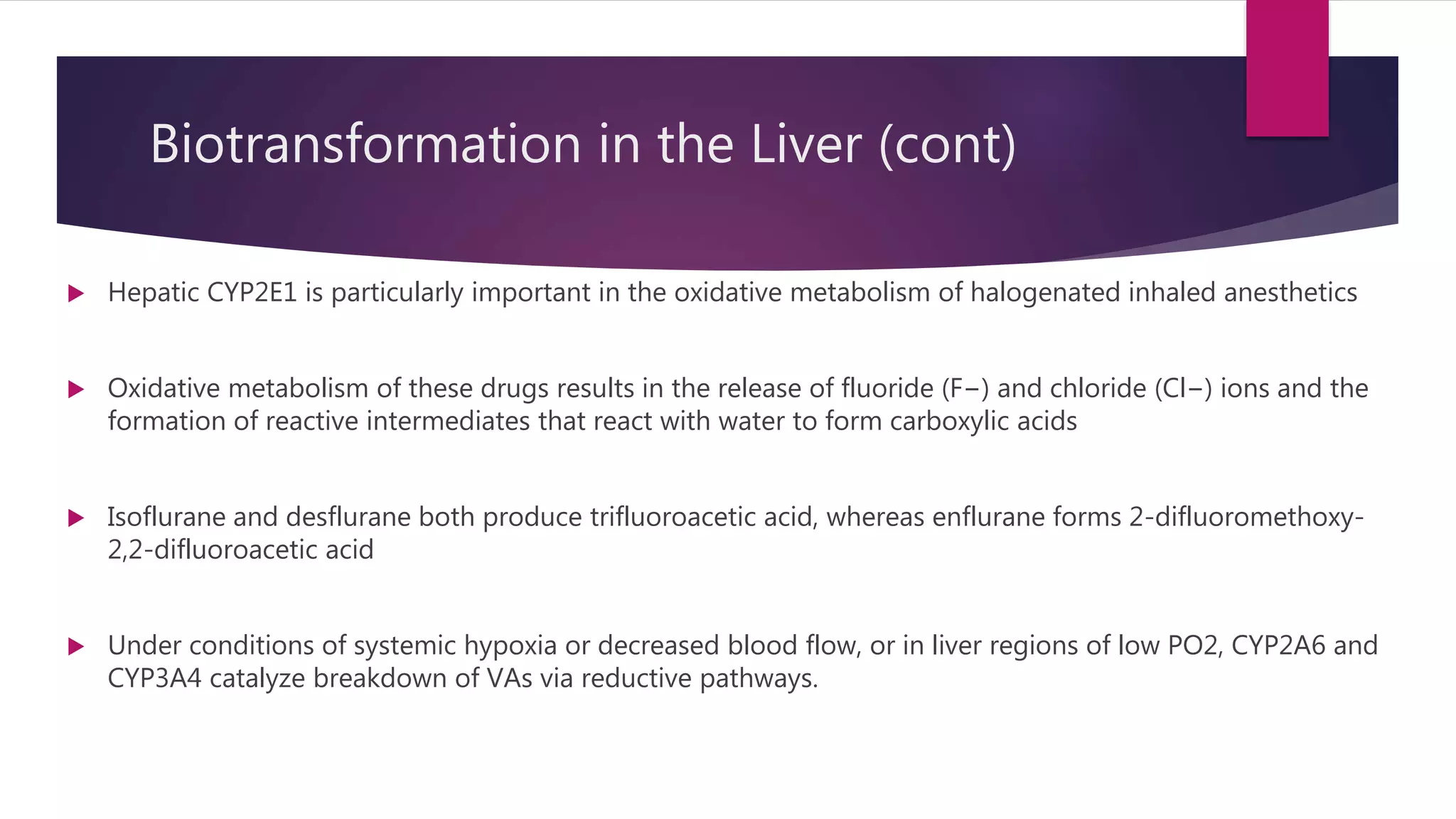
Inhalational agents act through various molecular targets in the brain to produce unconsciousness, immobility, sedation, and amnesia. They are absorbed through the lungs and distributed throughout the body via blood flow before being metabolized mainly in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. While generally safe, some agents like halothane can cause rare but serious liver toxicity and metabolites like fluoride require careful management to avoid kidney damage.

















![ Fluoride-Associated Nephrotoxicity
The first modern halogenated ether anesthetic, methoxyflurane was introduced in 1959.
Methoxyflurane causes polyuric renal insufficiency and is no longer used in clinical
practice
Serum inorganic F -levels < 50 μM had no evidence of renal injury
Typical peak fluoride concentrations after 2 to 3 MAC hours of sevoflurane anesthesia are
20 to 30 μM
ANESTHETIC DEGRADATION IN CARBON DIOXIDE ABSORBENTS
Halogenated anesthetics can undergo chemical breakdown while interacting with CO2
absorbents that contain strong bases such as NaOH and KOH, which are present in soda
lime and Baralyme
Strong bases extract a proton from the isopropyl group of sevoflurane, primarily forming
a haloalkene [fluoromethyl-2,2-difluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl) vinyl ether], known as
compound A
Biotransformation in Kidneys (cont)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inhalationalagents-210404181104/75/Inhalational-agents-24-2048.jpg)






