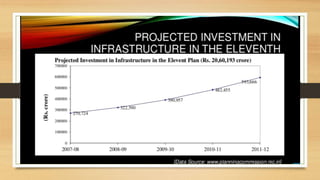
Infrastructure development in India plays an important countercyclical role in the economy. The Indian Prime Minister has directed that infrastructure projects and public-private partnerships be reviewed and expedited to ensure they are not hindered by funding issues. Infrastructure includes facilities, activities, and services that support and increase productivity across economic sectors. It involves basic needs like transportation, communication, energy, banking, and public services. Adequate infrastructure is important for faster economic growth, poverty alleviation, and integrating India's economy globally. However, India still needs to urgently address infrastructure gaps facing industries and citizens.