This document discusses the application of information technology to radiology. It defines radiology and information technology, and describes how various information technologies such as PACS, RIS, teleradiology, and computer-aided diagnosis have automated processes and improved access to radiological images and data. The document also provides examples of how computed radiography digitizes the film development process in radiography. Overall, the document outlines how information technology continues to add value to the field of radiology.


![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Radiology
Definition Medical specialty that uses imaging to diagnose
diseases [Wikipedia]
Fundamental Concerns Just two things:
1 Image acquisition
2 Interpretation of Images viz-a-viz Disease states
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-3-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Radiology
Definition Medical specialty that uses imaging to diagnose
diseases [Wikipedia]
Fundamental Concerns Just two things:
1 Image acquisition
2 Interpretation of Images viz-a-viz Disease states
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-4-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Information Technology
Definition Application of Computers and Telecommunications
equipment to store, retrieve, transmit and manipulate
data, often in the context of a business or other
enterprise [Wikipedia]
Fundamental Concern Automation
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-5-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Information Technology
Definition Application of Computers and Telecommunications
equipment to store, retrieve, transmit and manipulate
data, often in the context of a business or other
enterprise [Wikipedia]
Fundamental Concern Automation
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-6-320.jpg)





















![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
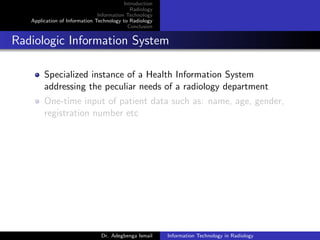
Radiologic Information System
Specialized instance of a Health Information System
addressing the peculiar needs of a radiology department
One-time input of patient data such as: name, age, gender,
registration number etc
Patient data can also be acquired from a hospital-wide HIS
Can Communicate via a Dicom Modality Work-list with
imaging equipments [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-32-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Radiologic Information System
Specialized instance of a Health Information System
addressing the peculiar needs of a radiology department
One-time input of patient data such as: name, age, gender,
registration number etc
Patient data can also be acquired from a hospital-wide HIS
Can Communicate via a Dicom Modality Work-list with
imaging equipments [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Same patient data can be linked with multiple images from
different imaging modalities
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-33-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Radiologic Information System
Specialized instance of a Health Information System
addressing the peculiar needs of a radiology department
One-time input of patient data such as: name, age, gender,
registration number etc
Patient data can also be acquired from a hospital-wide HIS
Can Communicate via a Dicom Modality Work-list with
imaging equipments [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Same patient data can be linked with multiple images from
different imaging modalities
Reduces clerical errors by eliminating multiple entry of same
patient information in different imaging equipment
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-34-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Radiologic Information System
Specialized instance of a Health Information System
addressing the peculiar needs of a radiology department
One-time input of patient data such as: name, age, gender,
registration number etc
Patient data can also be acquired from a hospital-wide HIS
Can Communicate via a Dicom Modality Work-list with
imaging equipments [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Same patient data can be linked with multiple images from
different imaging modalities
Reduces clerical errors by eliminating multiple entry of same
patient information in different imaging equipment
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-35-320.jpg)





![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Voice Recognition System
Seeks to automate stenography
Typical Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Secretary ⇒ Typed Report
Automated Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Voice Recognition Software ⇒
Computerized Report [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-41-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Voice Recognition System
Seeks to automate stenography
Typical Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Secretary ⇒ Typed Report
Automated Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Voice Recognition Software ⇒
Computerized Report [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Faster
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-42-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Voice Recognition System
Seeks to automate stenography
Typical Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Secretary ⇒ Typed Report
Automated Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Voice Recognition Software ⇒
Computerized Report [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Faster
Report is instantly verified and signed by radiologist author
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-43-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Voice Recognition System
Seeks to automate stenography
Typical Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Secretary ⇒ Typed Report
Automated Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Voice Recognition Software ⇒
Computerized Report [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Faster
Report is instantly verified and signed by radiologist author
Interfaces with the RIS and PACS
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-44-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Voice Recognition System
Seeks to automate stenography
Typical Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Secretary ⇒ Typed Report
Automated Reporting Work-flow:
Radiologist’s Dictation ⇒ Voice Recognition Software ⇒
Computerized Report [Grainger & Allison, 2008]
Faster
Report is instantly verified and signed by radiologist author
Interfaces with the RIS and PACS
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-45-320.jpg)


![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Computer-aided Diagnosis (CADx)
Uses pattern recognition to identify disease patterns in images
Machine learning technology is utilized to optimize algorithm
Images compared with anatomic databank of normal and
abnormal images
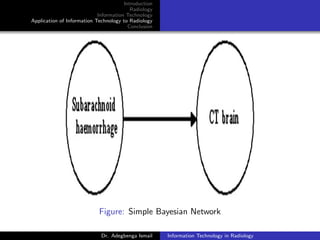
Uses Artificial Neural Network and Bayesian statistics in
analyzing images for probability of disease
[Stivaros et al, 2010]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-48-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Computer-aided Diagnosis (CADx)
Uses pattern recognition to identify disease patterns in images
Machine learning technology is utilized to optimize algorithm
Images compared with anatomic databank of normal and
abnormal images
Uses Artificial Neural Network and Bayesian statistics in
analyzing images for probability of disease
[Stivaros et al, 2010]
Technology also used in Computer-aided Simple Triage
(CAST)
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-49-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Computer-aided Diagnosis (CADx)
Uses pattern recognition to identify disease patterns in images
Machine learning technology is utilized to optimize algorithm
Images compared with anatomic databank of normal and
abnormal images
Uses Artificial Neural Network and Bayesian statistics in
analyzing images for probability of disease
[Stivaros et al, 2010]
Technology also used in Computer-aided Simple Triage
(CAST)
Supplements and assists, not replace, human evaluation
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-50-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Computer-aided Diagnosis (CADx)
Uses pattern recognition to identify disease patterns in images
Machine learning technology is utilized to optimize algorithm
Images compared with anatomic databank of normal and
abnormal images
Uses Artificial Neural Network and Bayesian statistics in
analyzing images for probability of disease
[Stivaros et al, 2010]
Technology also used in Computer-aided Simple Triage
(CAST)
Supplements and assists, not replace, human evaluation
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-51-320.jpg)





![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
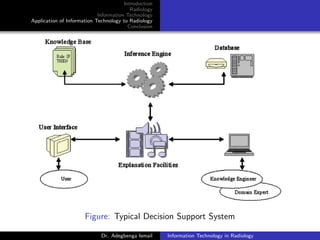
Decision Support Systems
Aimed at Automating the work of a Radiology Benefit
Manager
Assists clinicians in making appropriate Evidence-based Image
ordering
Increasingly being used by radiologists in making informed
imaging recommendations
More objective and transparent replacement of the job of a
Radiology Benefit Manager [ACR-RBMA, 2011]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-59-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
Decision Support Systems
Aimed at Automating the work of a Radiology Benefit
Manager
Assists clinicians in making appropriate Evidence-based Image
ordering
Increasingly being used by radiologists in making informed
imaging recommendations
More objective and transparent replacement of the job of a
Radiology Benefit Manager [ACR-RBMA, 2011]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-60-320.jpg)
![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
To What End?
Machinery . . . will facilitate and abridge labour [Smith, 1776]
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-61-320.jpg)




![Introduction
Radiology
Information Technology
Application of Information Technology to Radiology
Conclusion
References
Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiology
Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information technology
Stivaros SM, Gledson A, Nenadic G, Zeng XJ, Keane J, Jackson A.
Decision support systems for clinical radiological practice – towards the
next generation.
Br J Radiol. 2010 Nov;83(995):904-14. doi: 10.1259/bjr/33620087.
Review.
PMID:20965900 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Adam Smith (1776)
An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations
http://www2.hn.psu.edu/faculty/jmanis/adam-smith/wealth-nations.pdf
12(3), 45 – 678.
Dr. Adegbenga Ismail Information Technology in Radiology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talk-160619173519/85/Information-Technology-in-Radiology-66-320.jpg)


