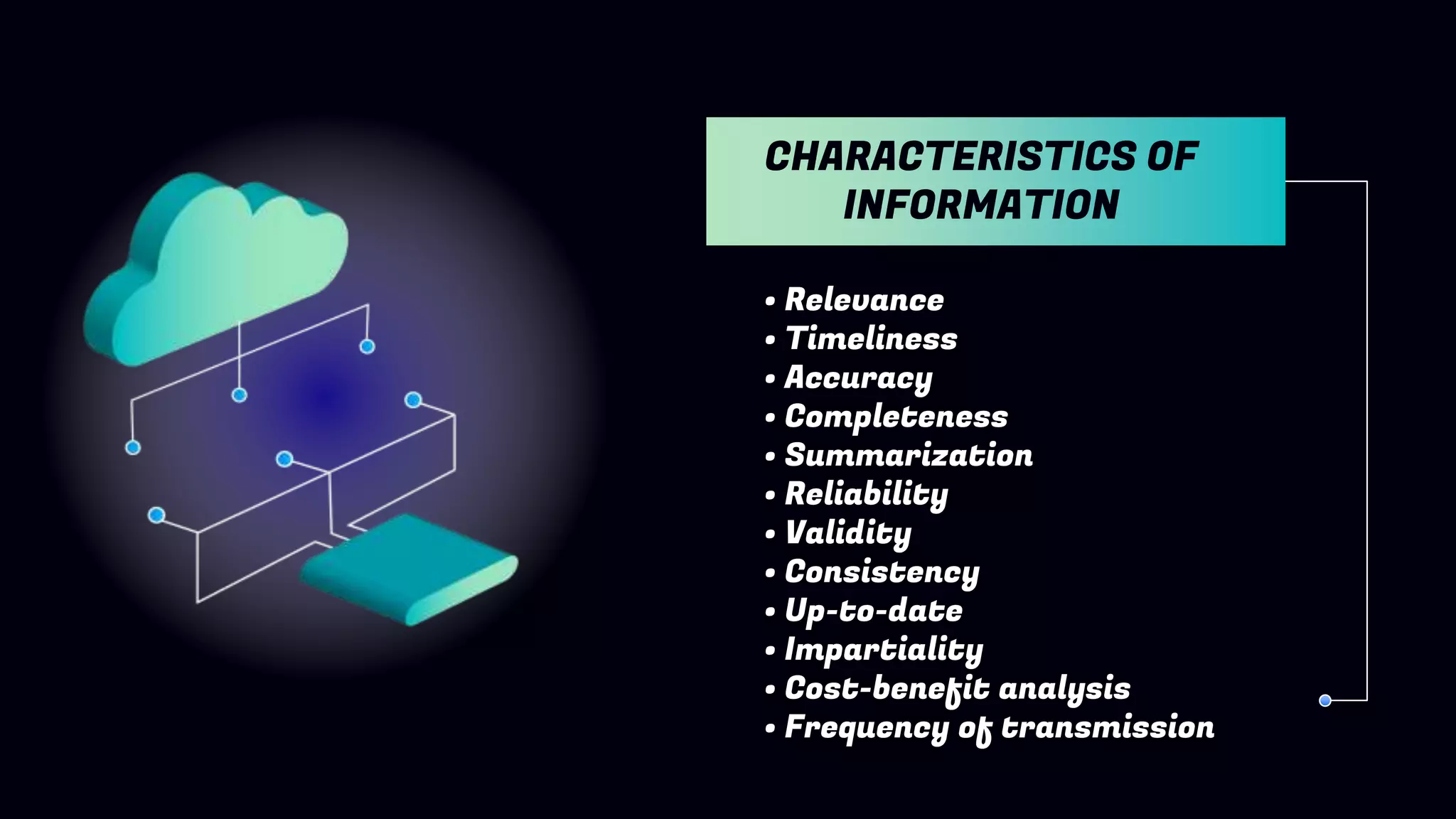
This document discusses different types of information systems. It begins by defining information and data, and the relationship between the two. An information system is then defined as a set of components that collect, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making. The main types of information systems discussed are:
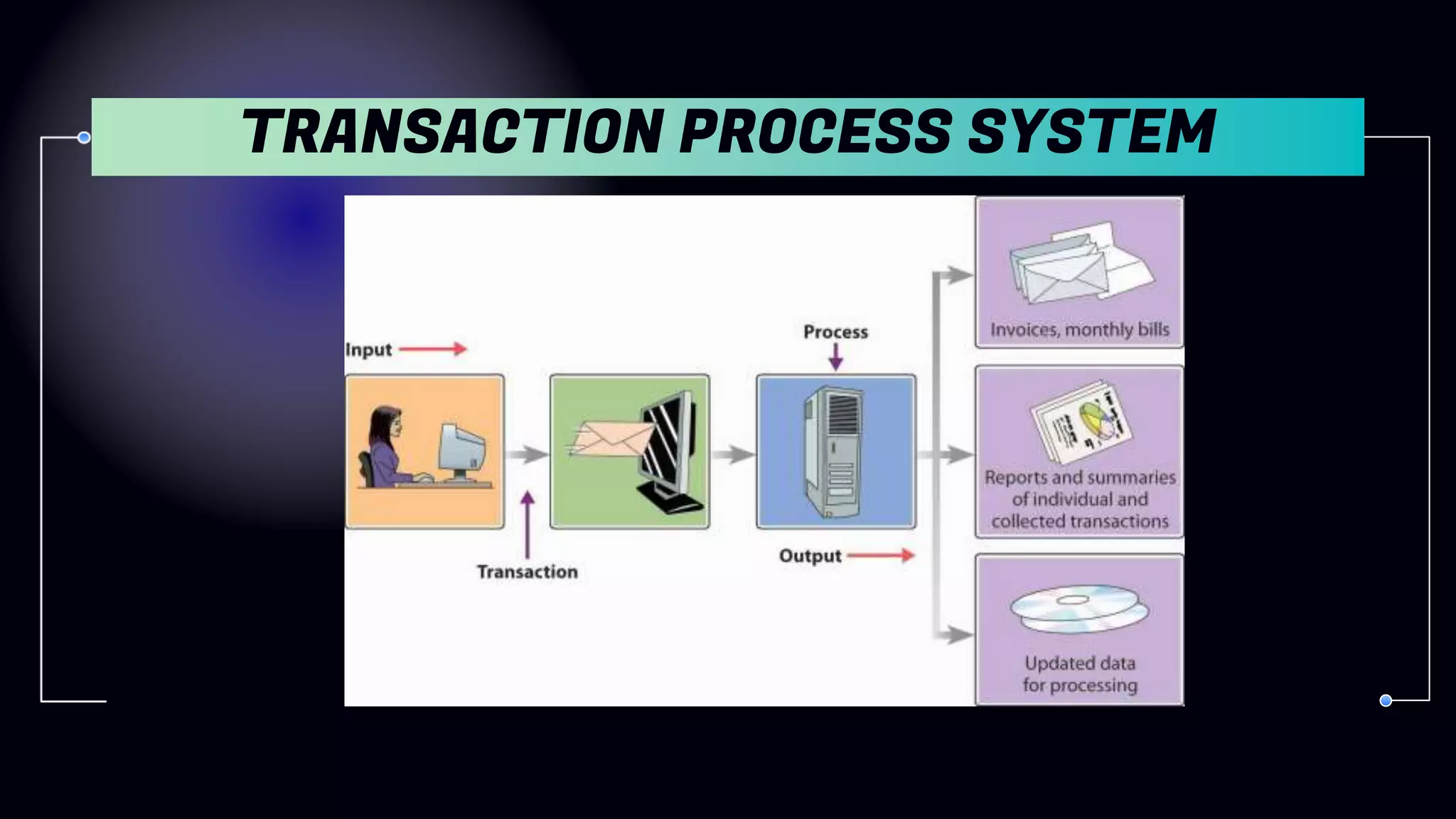
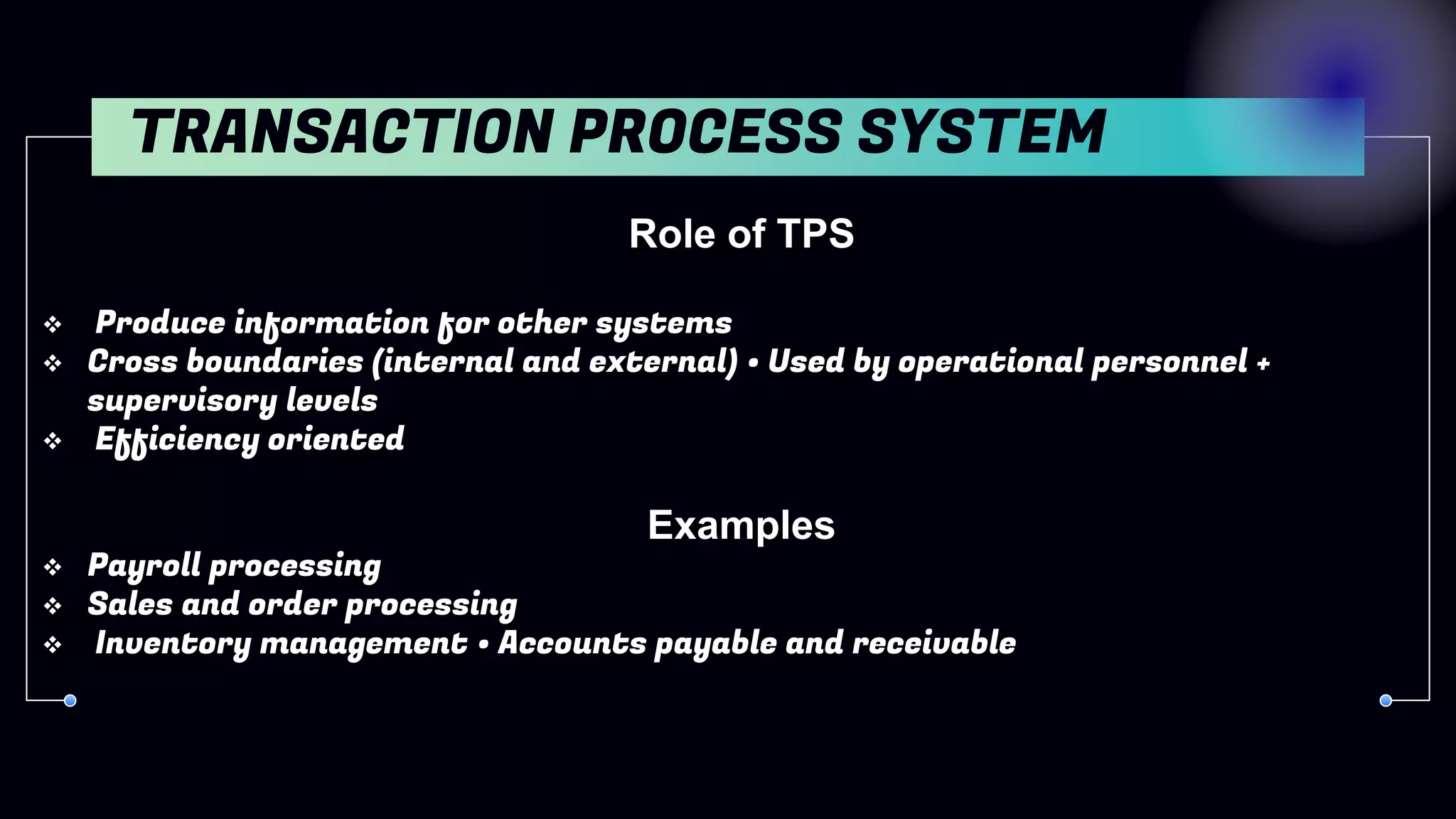
1. Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) - Automate routine business transactions and produce reports.
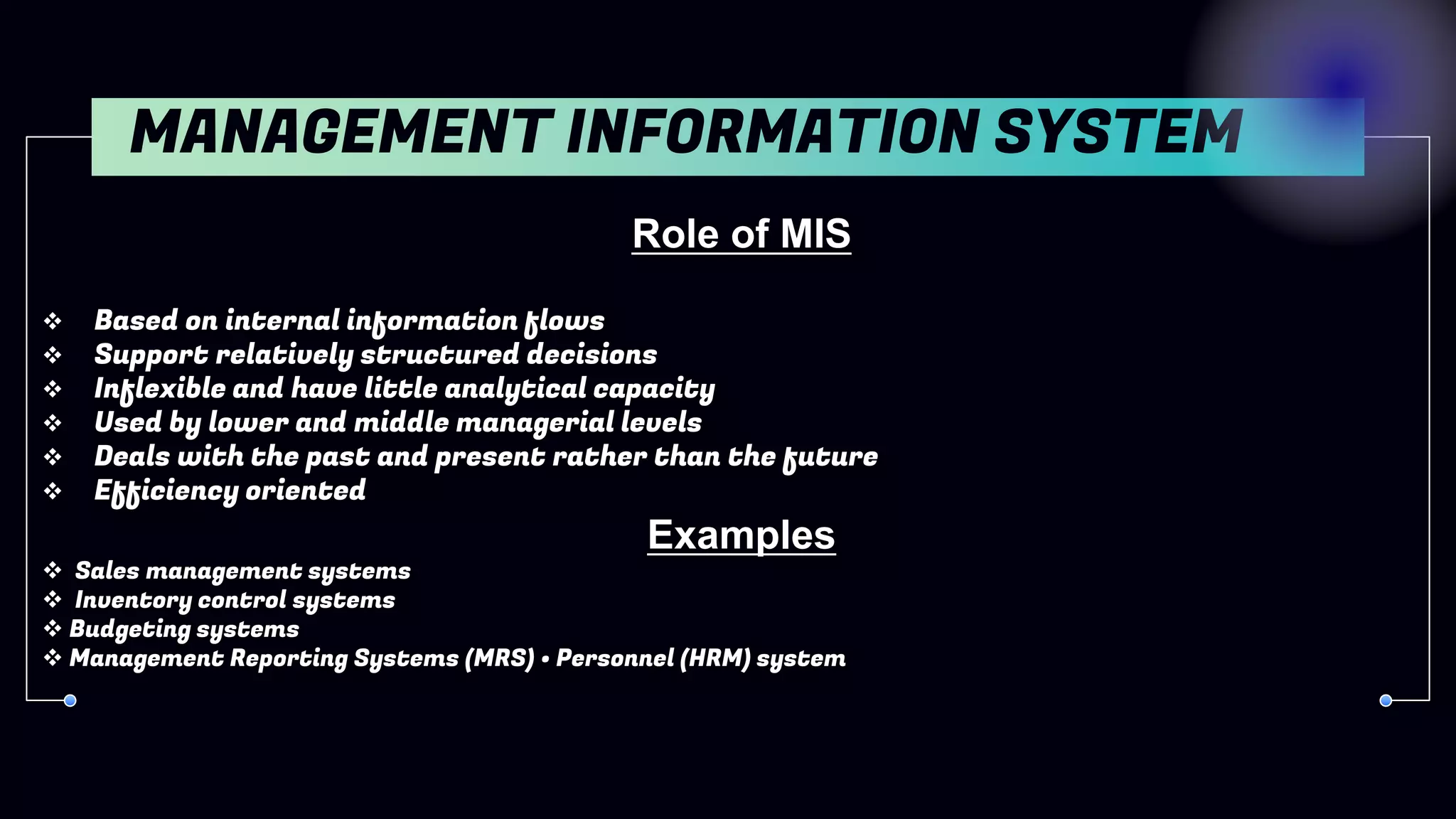
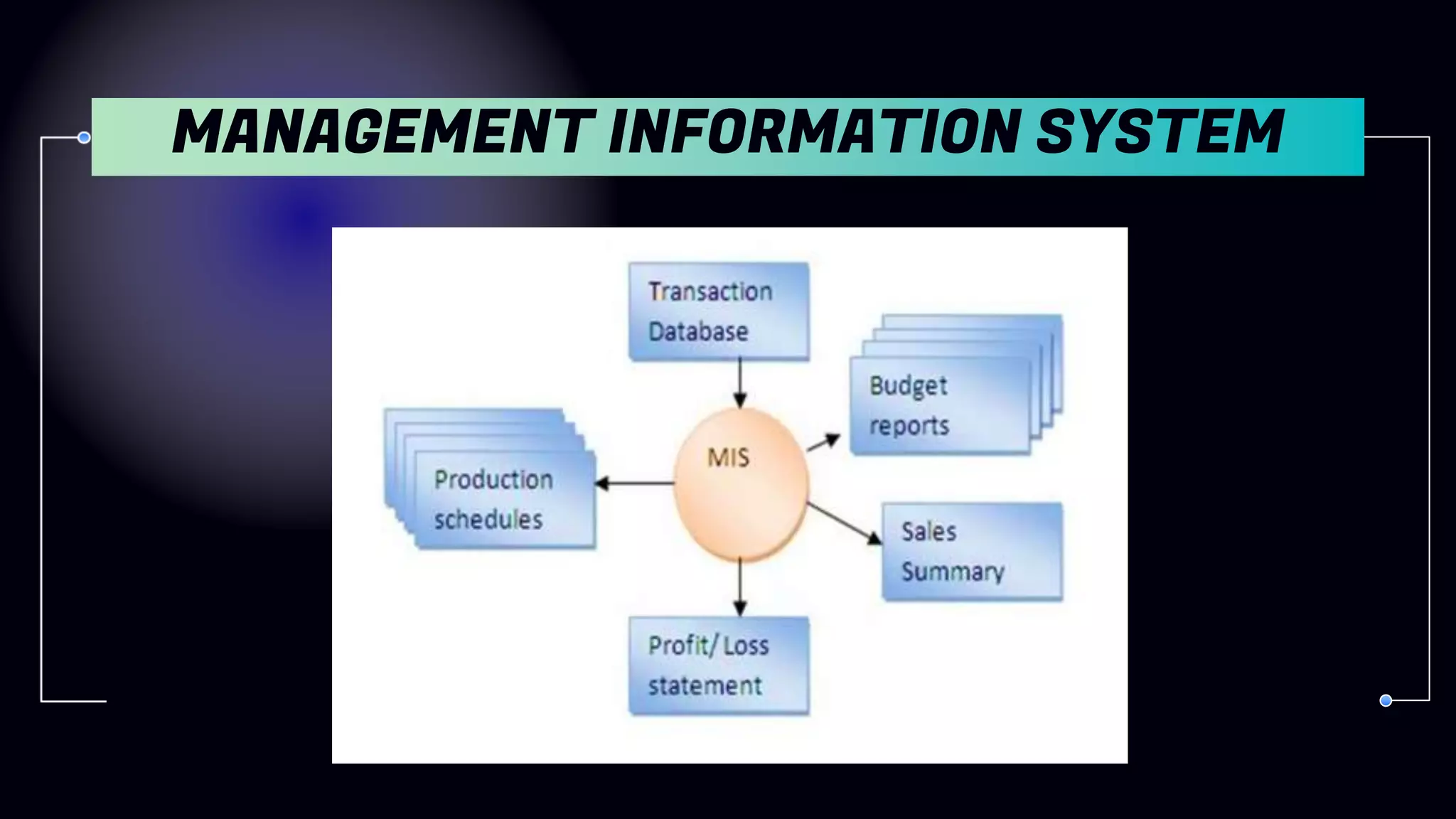
2. Management Information Systems (MIS) - Provide summary information to support lower/middle management.
3. Decision Support Systems (DSS) - Support non-routine decisions through analysis and modeling.
4. Executive Information Systems (EIS) - Provide flexible access to internal/external data to support top