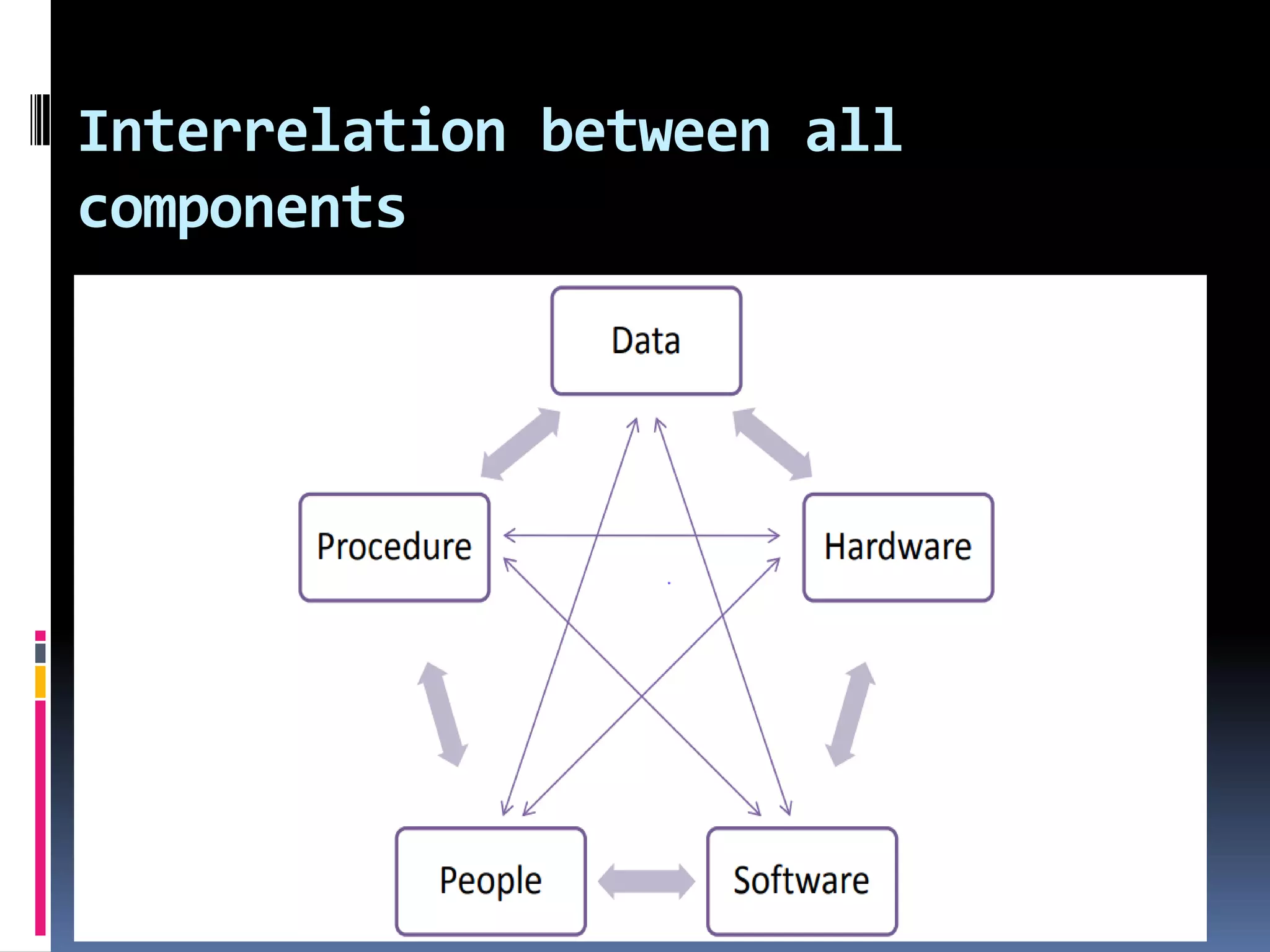
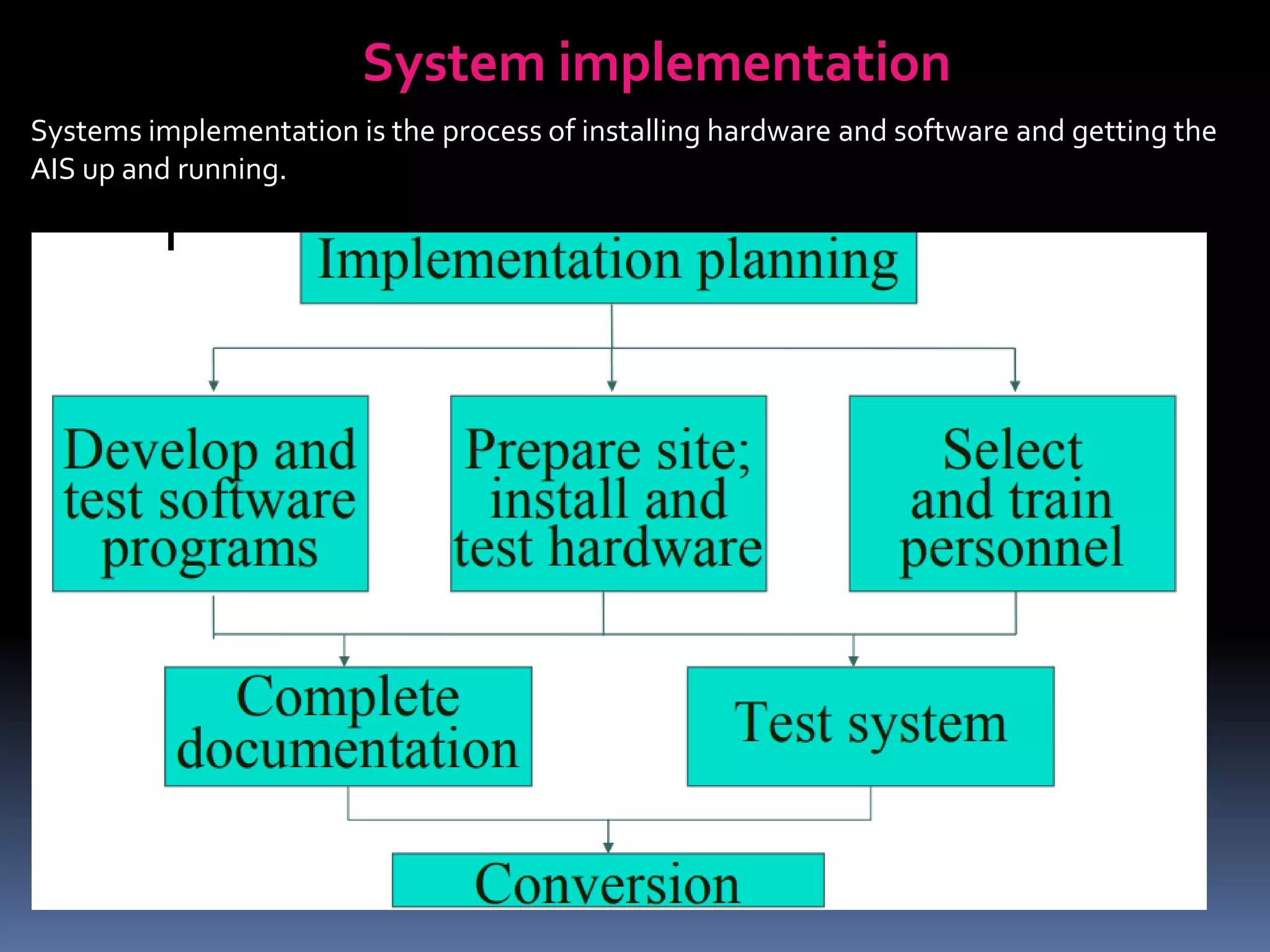
This document discusses information systems and their design. It defines information as organized data including text, numbers, audio, video and images. The key components of an information system are processes, data, hardware, software and people. There are several types of information systems including management information systems, transaction processing systems, decision support systems, executive information systems and expert/artificial intelligence systems. The design of information systems involves logical design, physical design, construction and testing. Logical design translates user requirements into functions and structures to organize information. Data flow diagrams and data dictionaries are important tools used in the design process.