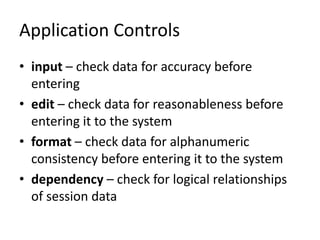
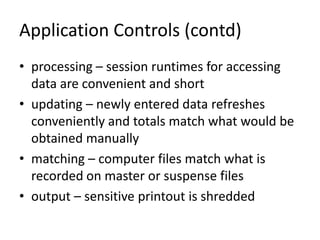
This document discusses various controls for computer systems, including general controls and application controls. General controls include systems development, system software, hardware, operations, data security, and administration. Application controls focus on input, edit, format, dependency, processing, updating, matching, and output of data. The document also defines key terms related to control models, such as implementation, prototype, request for permission, project management, deliverables, walkthrough, outsourcing, and metrics. Finally, it discusses the concept of survivability for mission-critical systems and defines attacks, failures, and accidents.