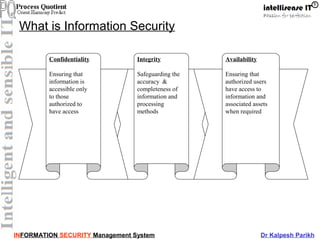
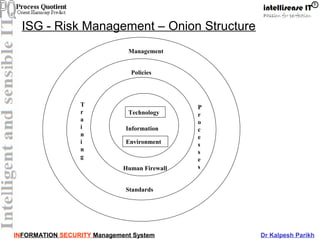
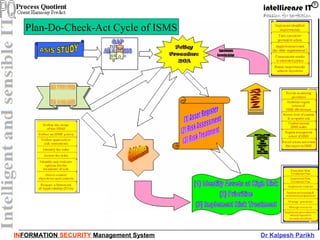
This document discusses information security management systems (ISMS). It defines information and its lifecycle, including how information can be created, stored, processed, transmitted, used, lost, corrupted, etc. It then defines the key aspects of information security - integrity, availability, and confidentiality. It emphasizes that information is a valuable asset for organizations that needs to be protected. The document outlines some of the main components of establishing an ISMS, including risk management, policies, training, and processes. It also discusses ISO 27001 as the international standard for ISMS and its various control areas.