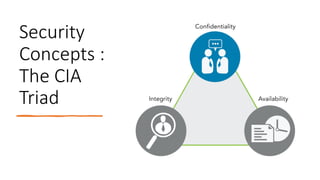
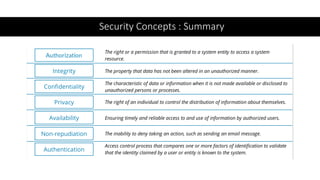
This document provides an overview of security principles including concepts like the CIA triad of confidentiality, integrity and availability. It discusses authentication methods, non-repudiation and privacy. It also covers risk management processes such as identification, assessment, treatment and priorities. Finally, it outlines security controls including physical, technical and administrative controls as well as governance elements and processes for standards development organizations.