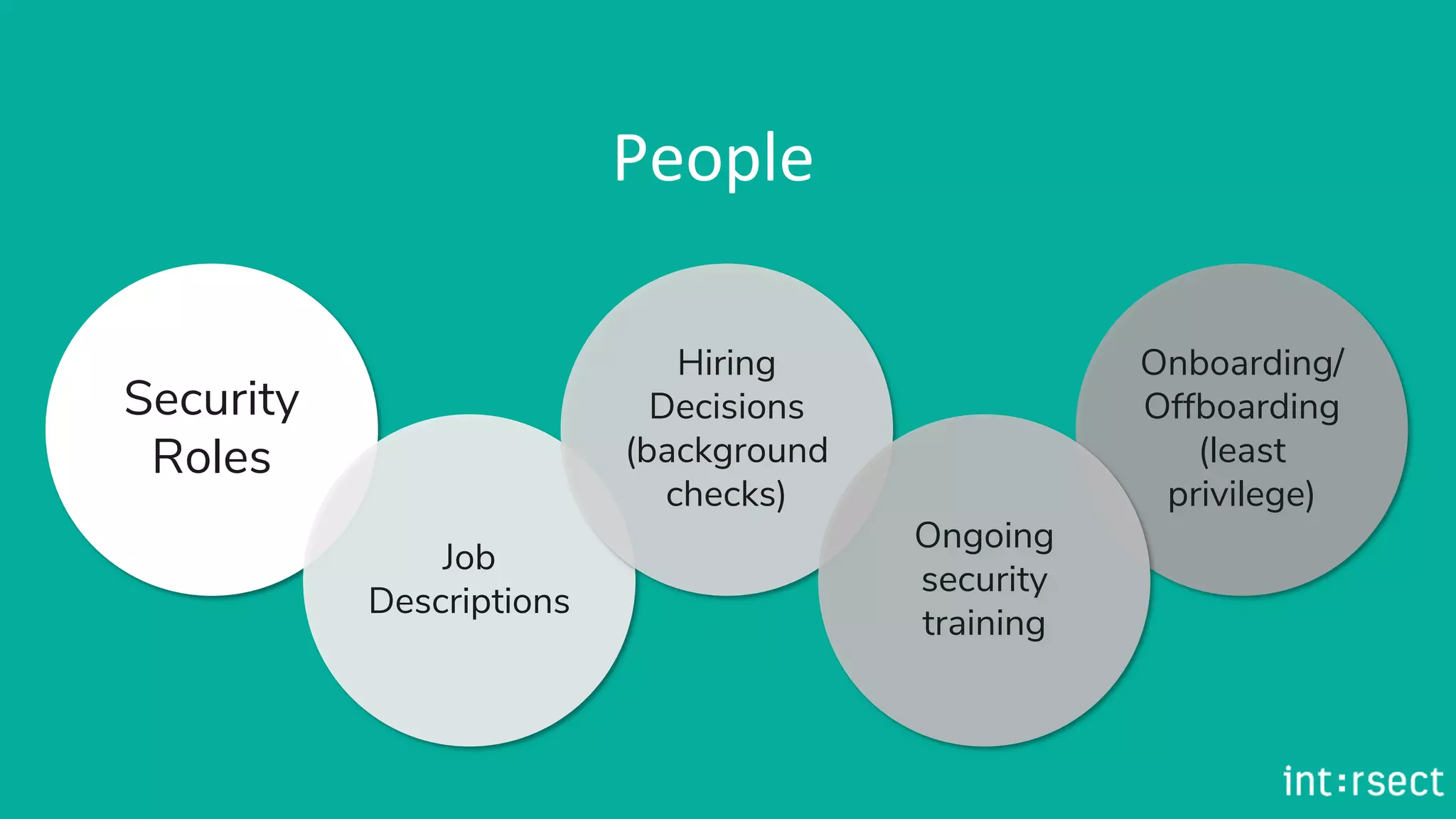
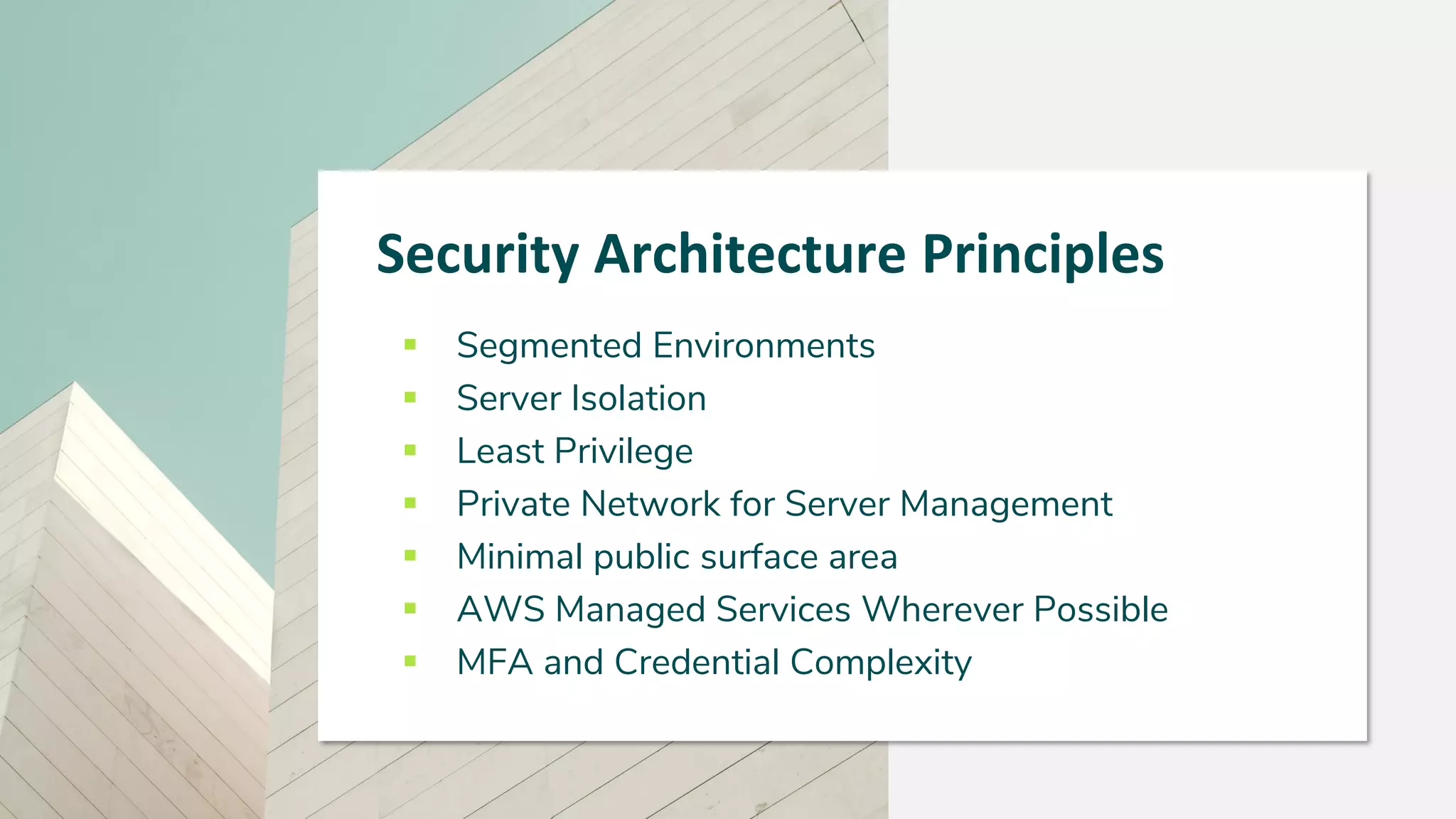
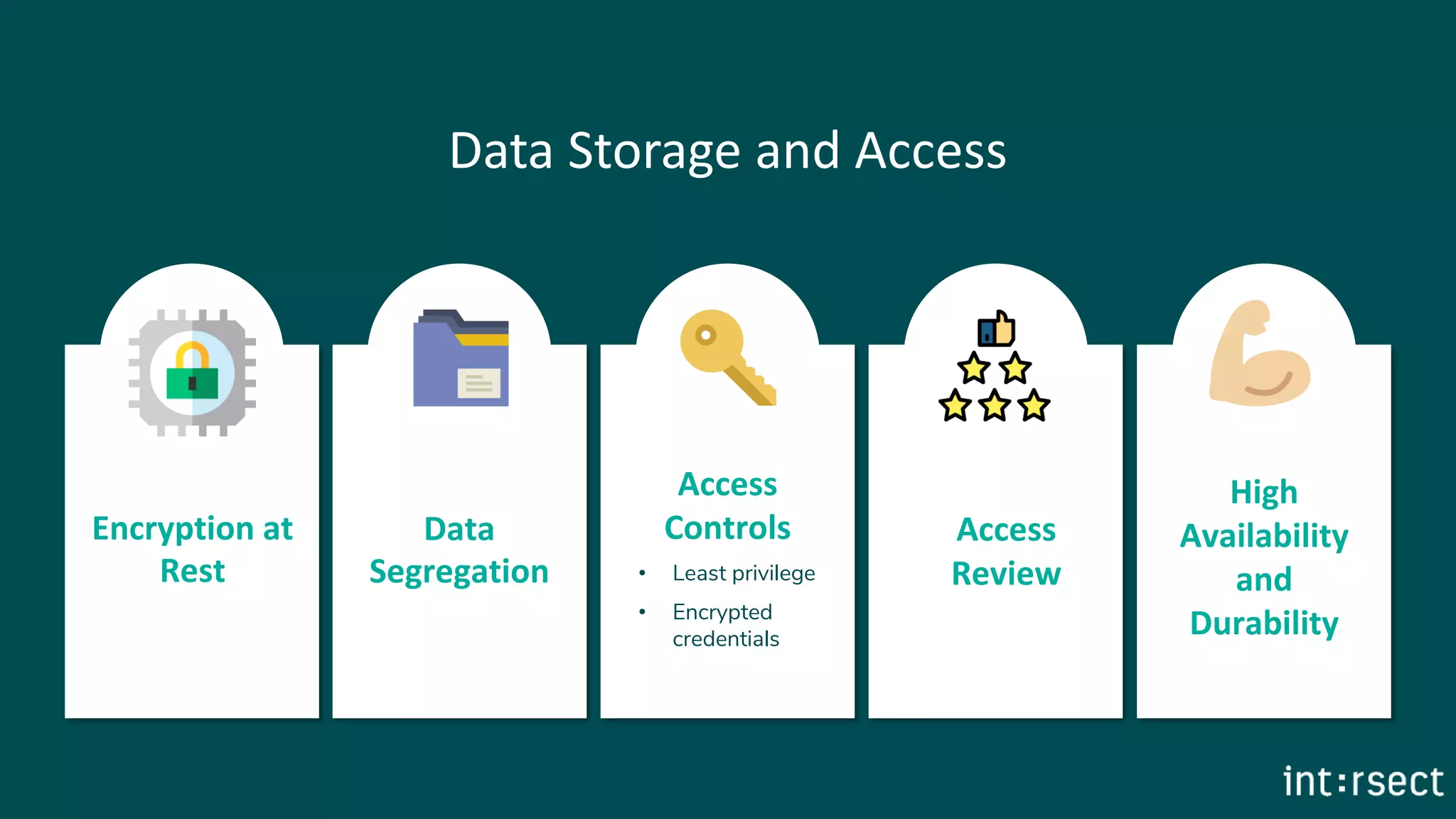
The document outlines best practices for information security, emphasizing principles such as least privilege and defense in depth. It details technical controls for network, operating systems, and applications, alongside policies for business continuity, disaster recovery, and ongoing security training. The importance of a strong security culture and third-party validation is also highlighted to ensure data protection and risk management.