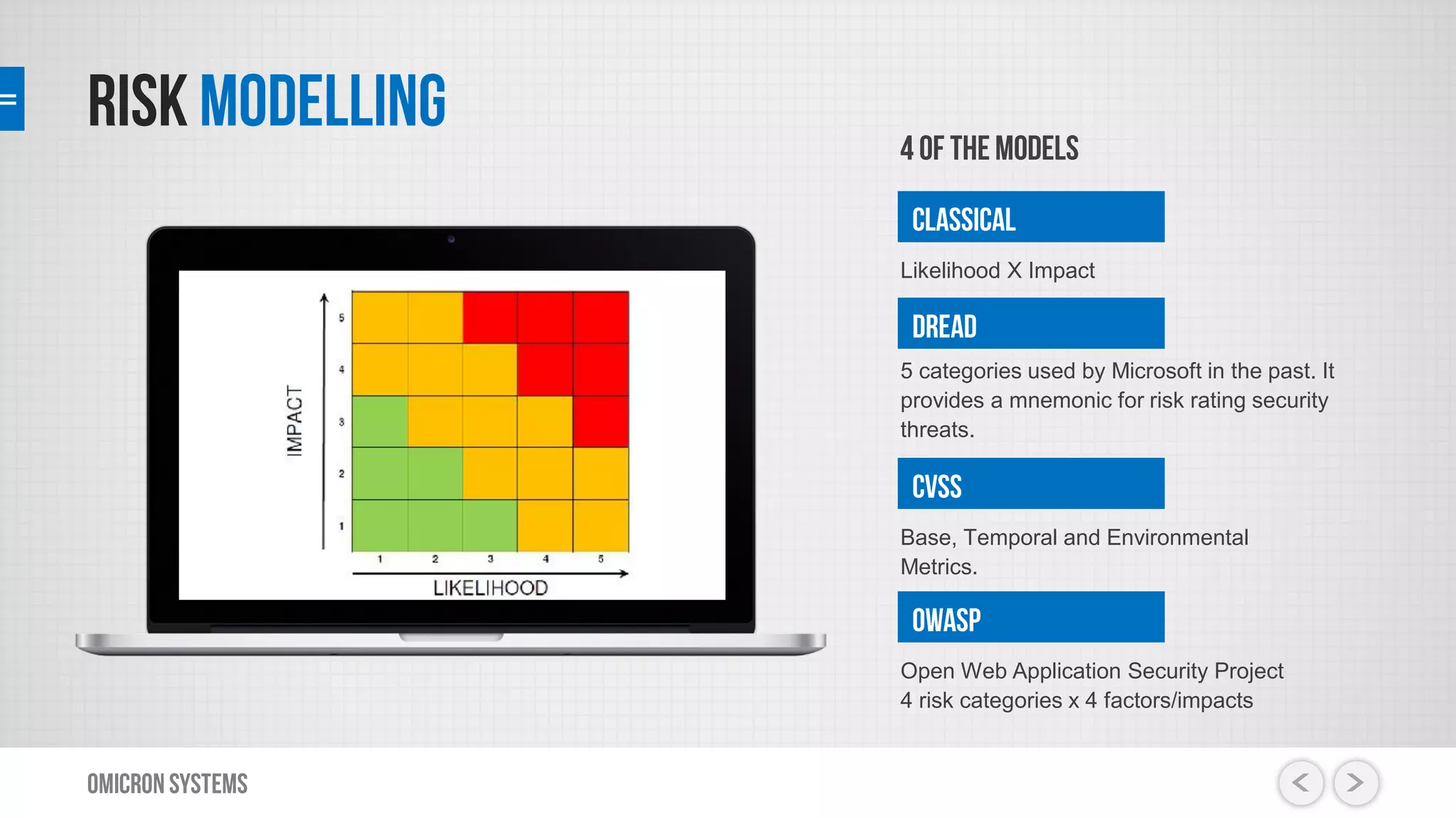
This document outlines a risk management process using an IT tool. It describes how users can log risks and priorities, which triggers automated workflows to notify engineers. Engineers then create risk records in the system. Managers periodically review risks and key metrics to prioritize activities and ensure targets are met. The tool allows for efficient collaboration and compliance across the risk management life cycle from identification to treatment and review.