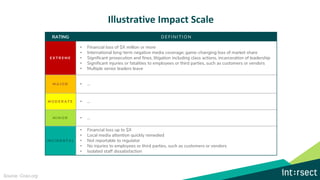
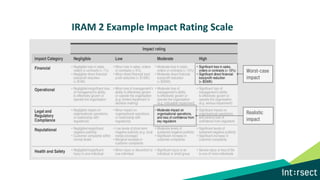
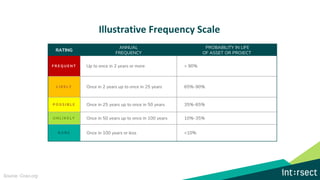
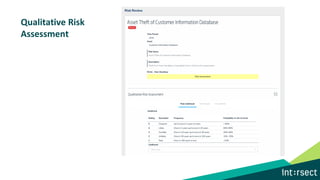
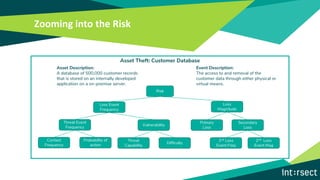
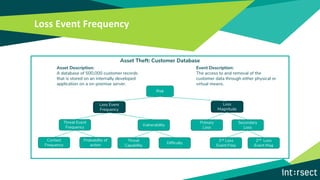
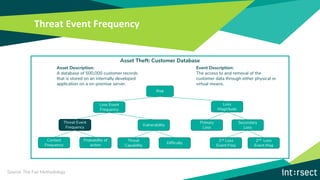
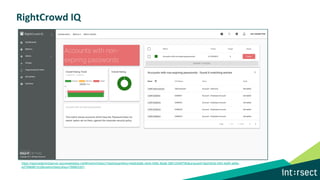
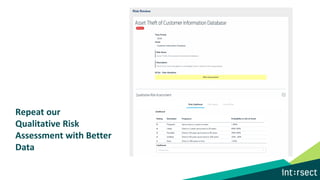
The document discusses how data can be used to improve risk assessment accuracy by mapping data to risk events. It provides examples of qualitative risk assessment terminology and scales used to rate likelihood, impact, vulnerability, and risk. It then walks through an example risk scenario of customer database theft and shows how collecting additional data on past incidents, threat actors, vulnerabilities can provide a more factual basis to estimate likelihood and improve the risk assessment. The benefits of a data-driven approach include more accurate assessments, automatic tuning of the risk register, improved resource allocation, and better executive reporting.