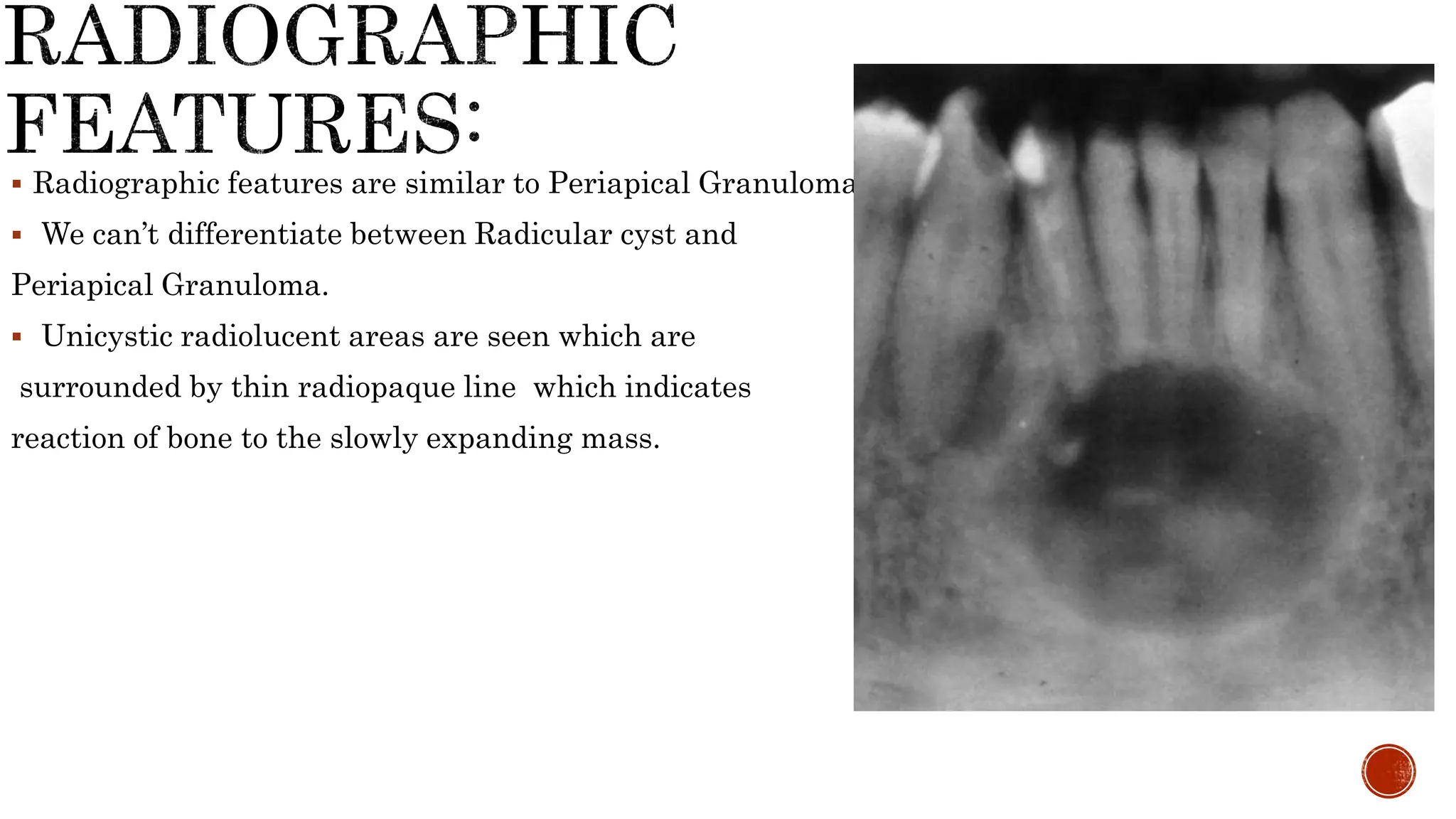
Radicular cysts are the most prevalent odontogenic cysts, making up around 60% of jaw cysts and 15% of periapical lesions, typically resulting from dental infections or pulp necrosis. Generally asymptomatic and slow-growing, radicular cysts may lead to complications like abscess formation; they exhibit specific radiographic features that resemble periapical granulomas and contain straw-colored fluid with cholesterol crystals. Treatment often involves root canal therapy or tooth extraction to prevent recurrence or the development of residual cysts.