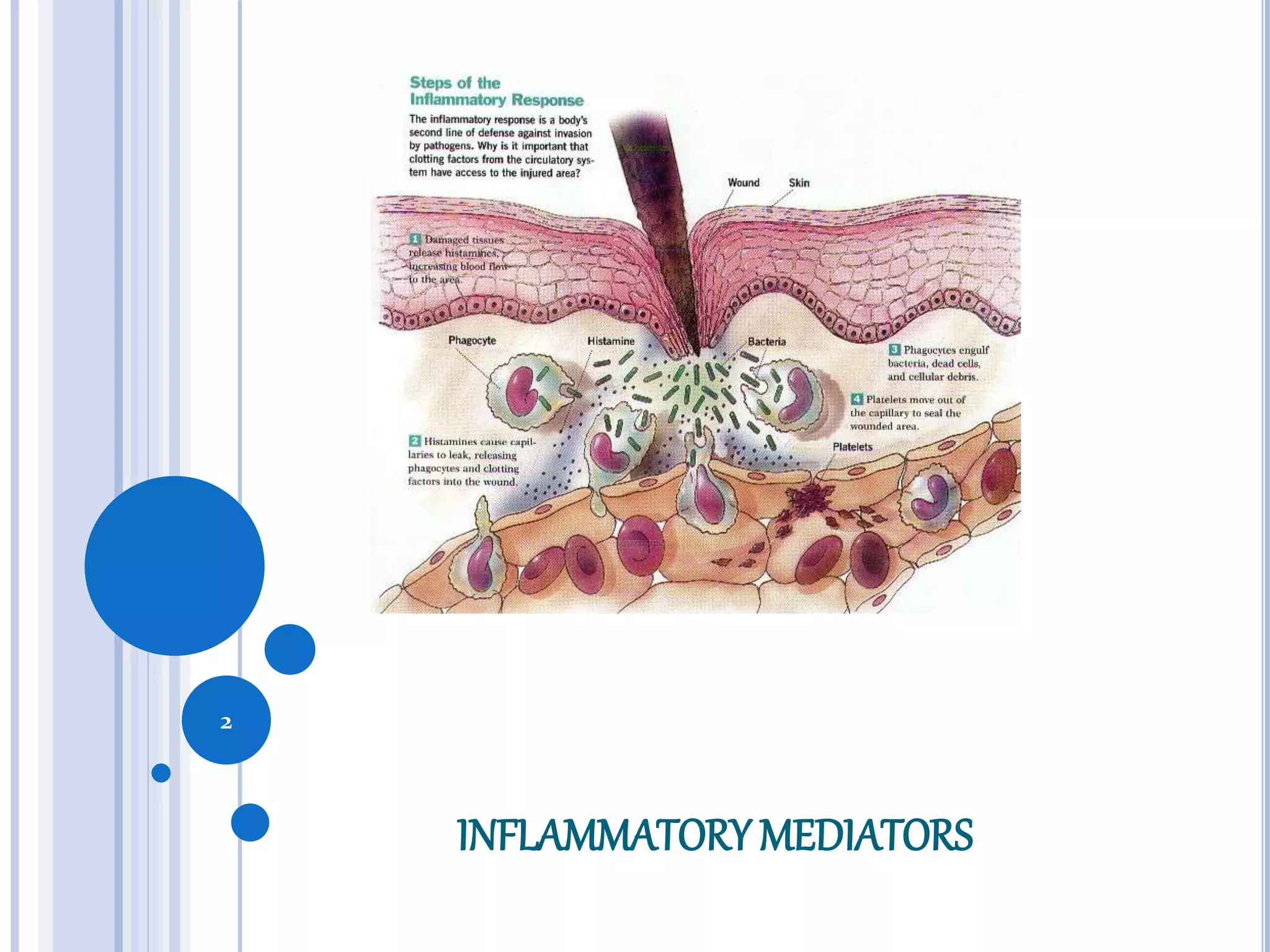
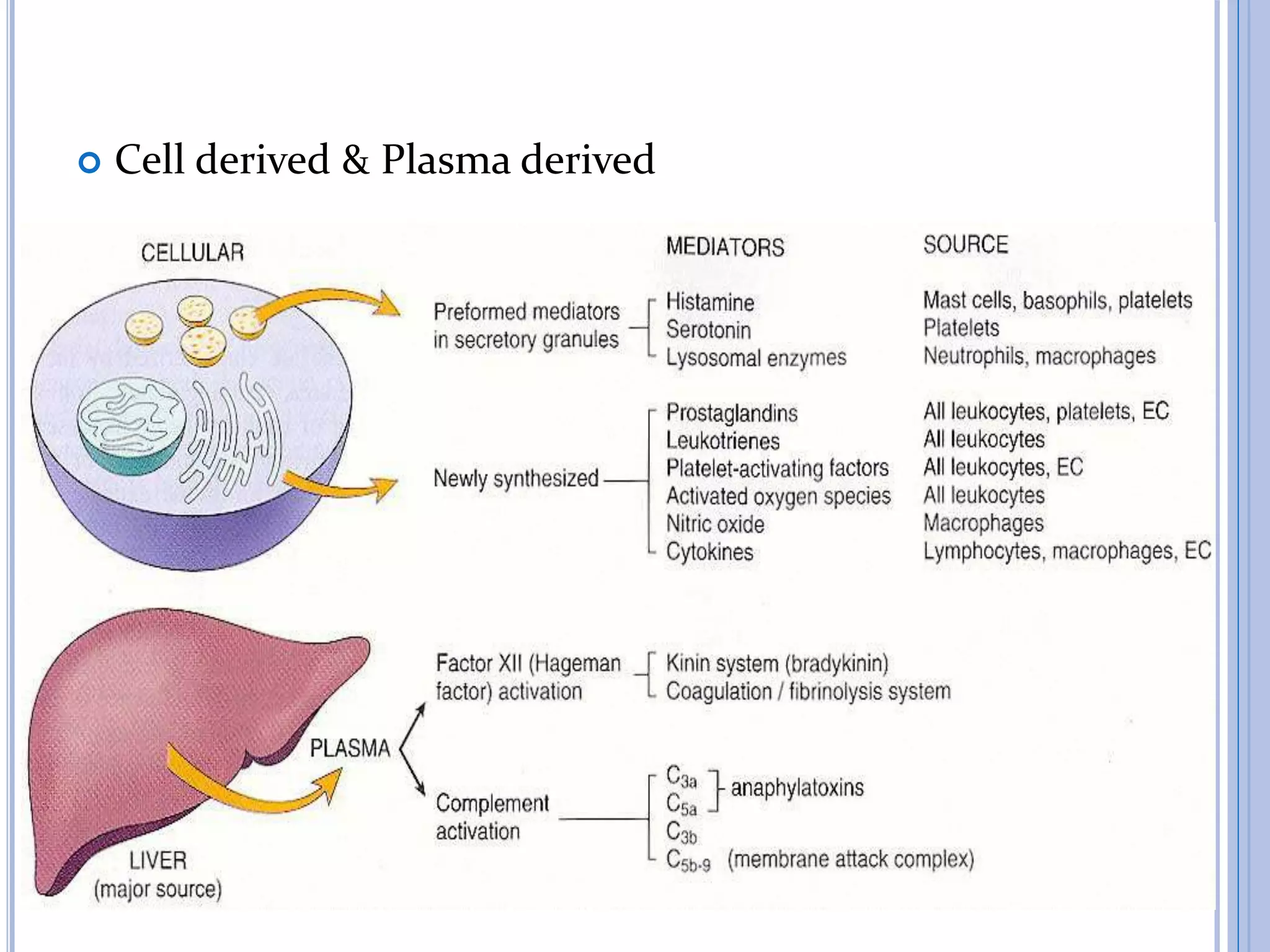
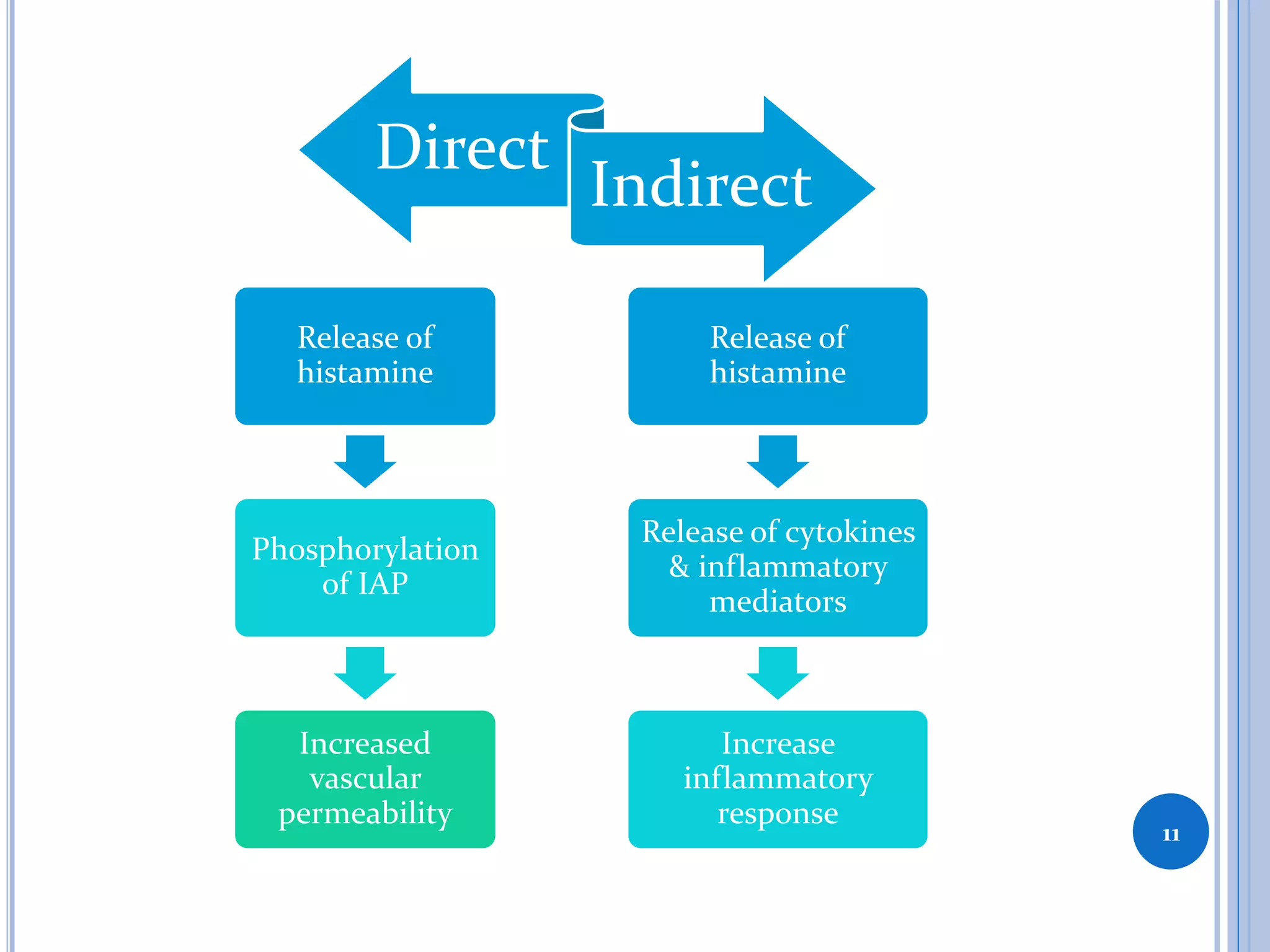
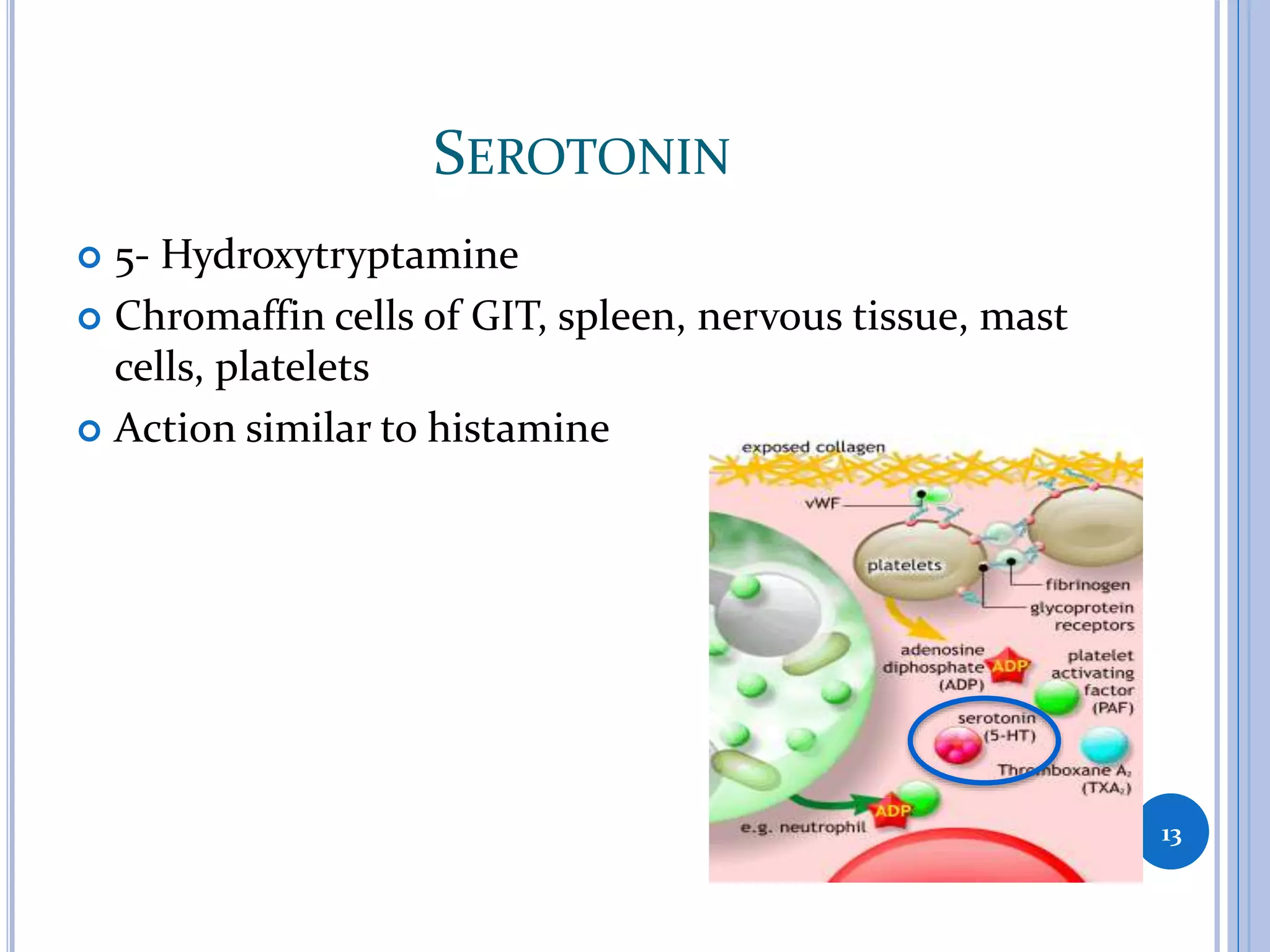
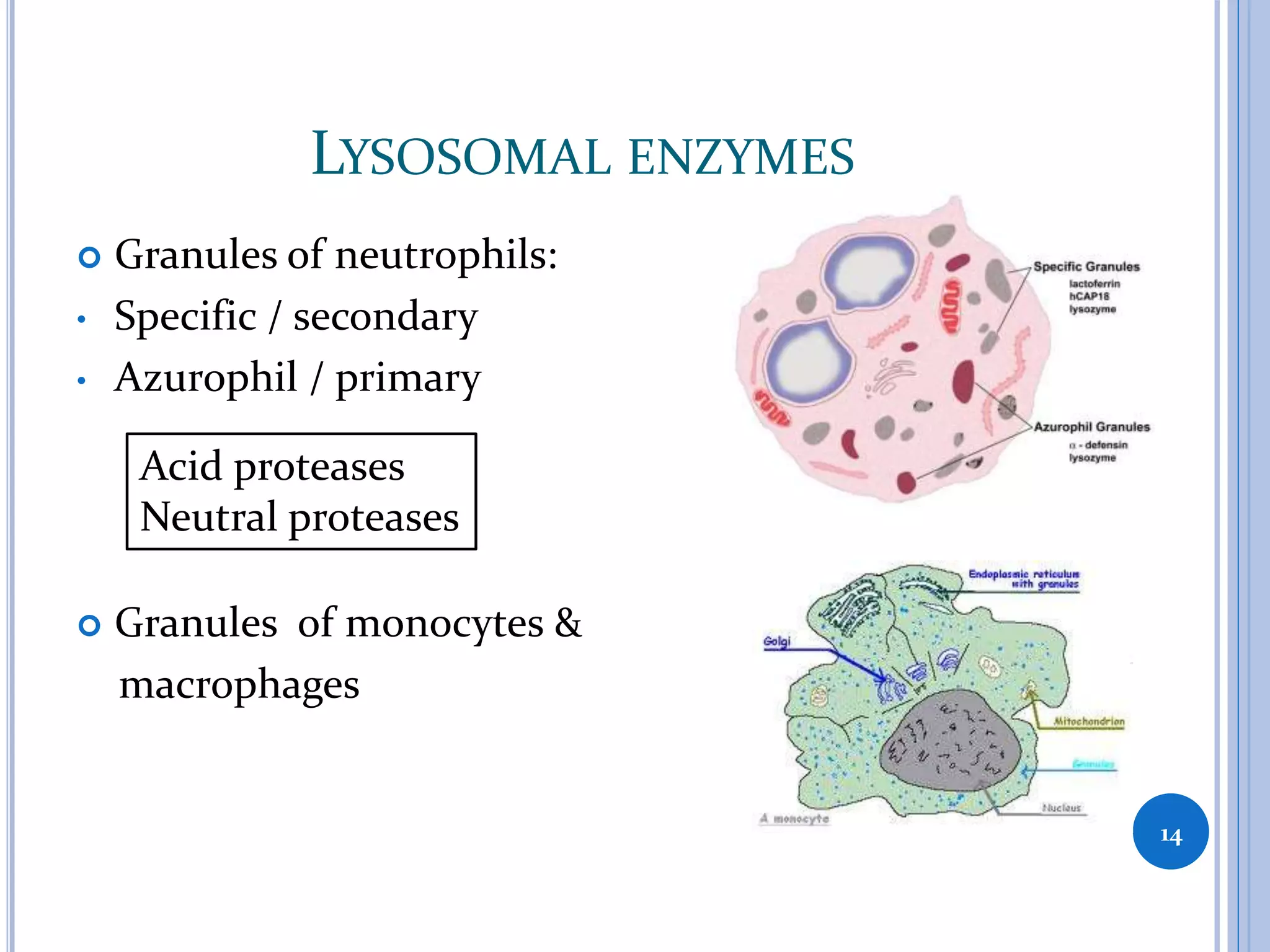
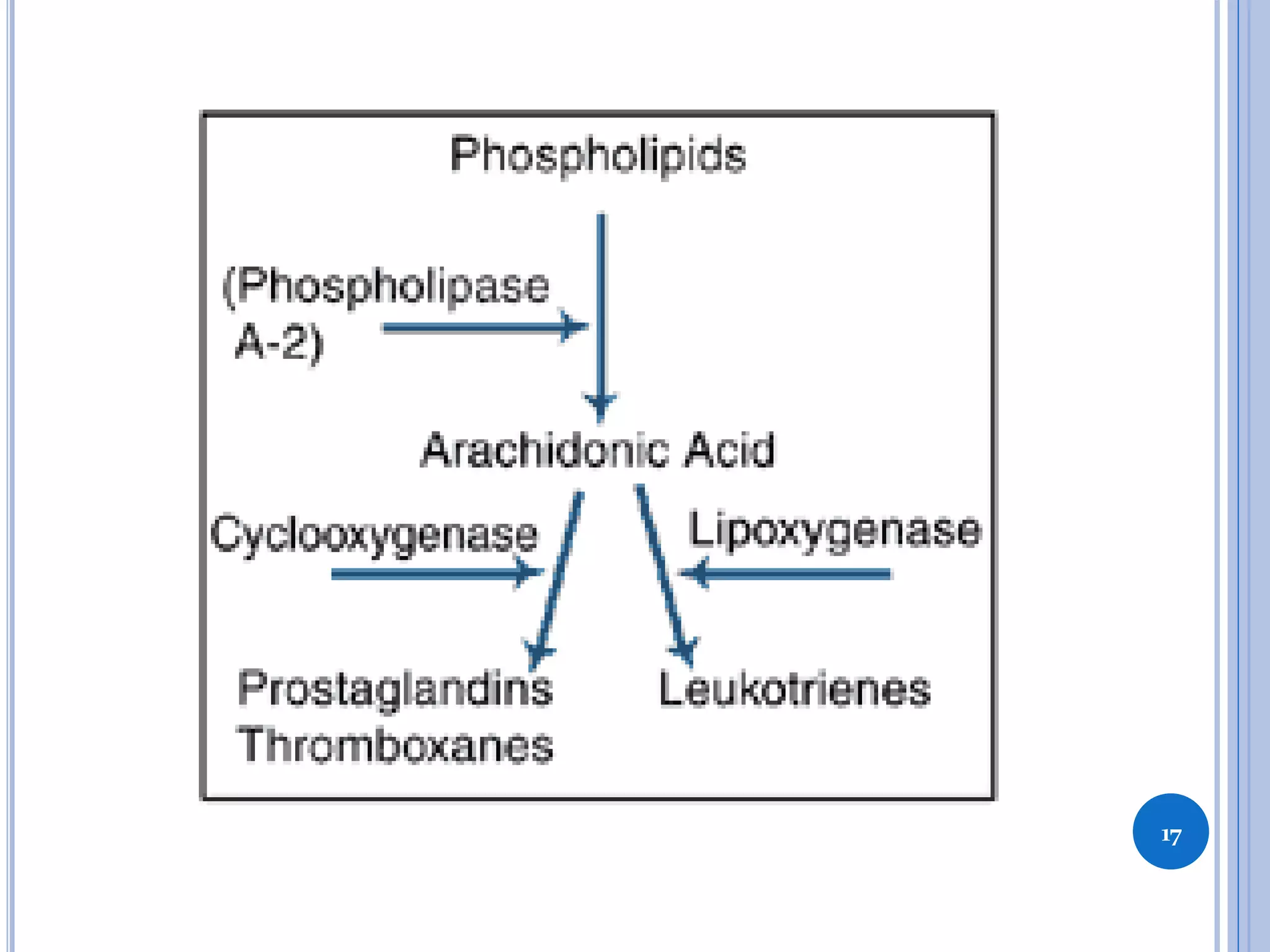
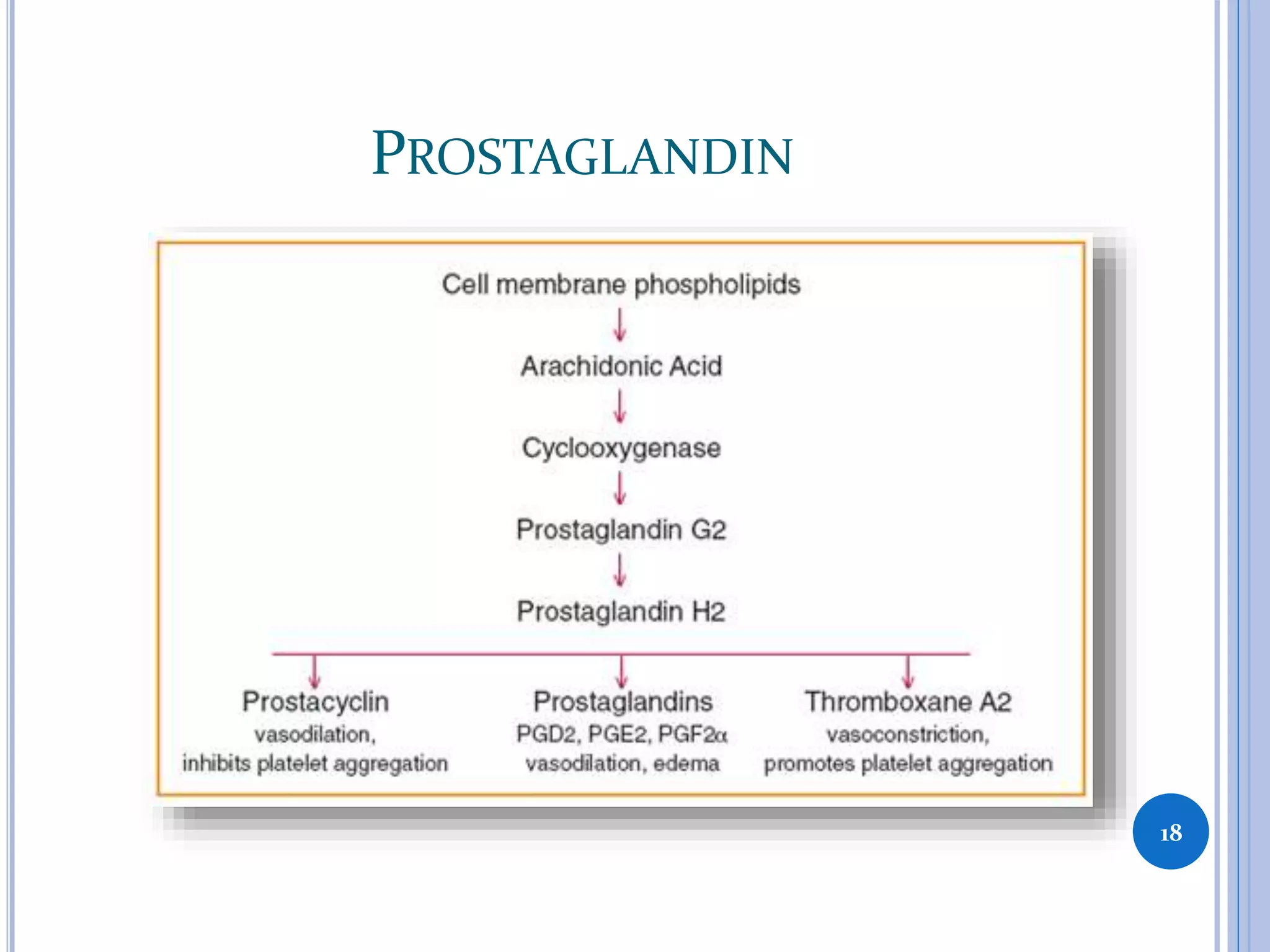
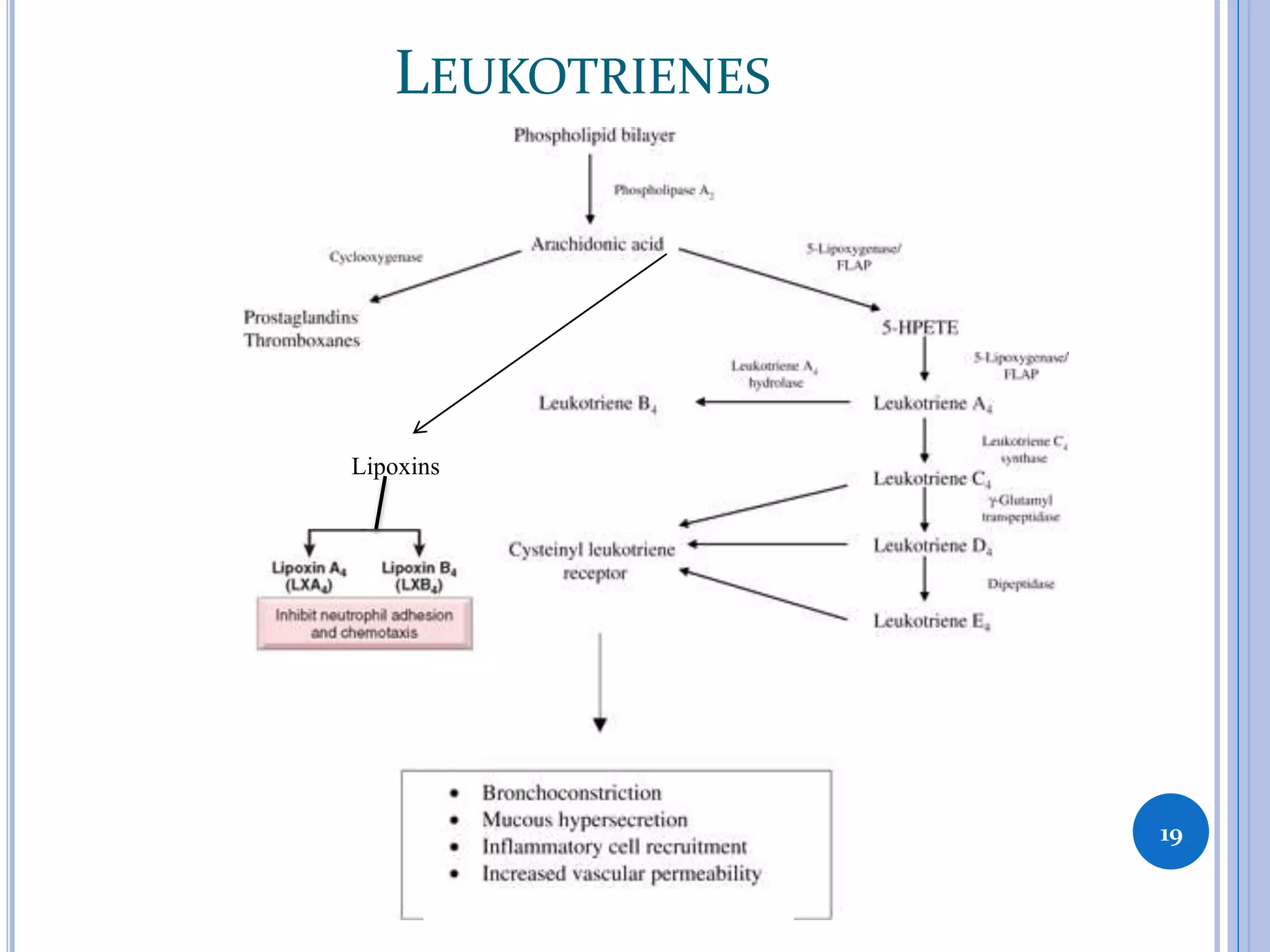
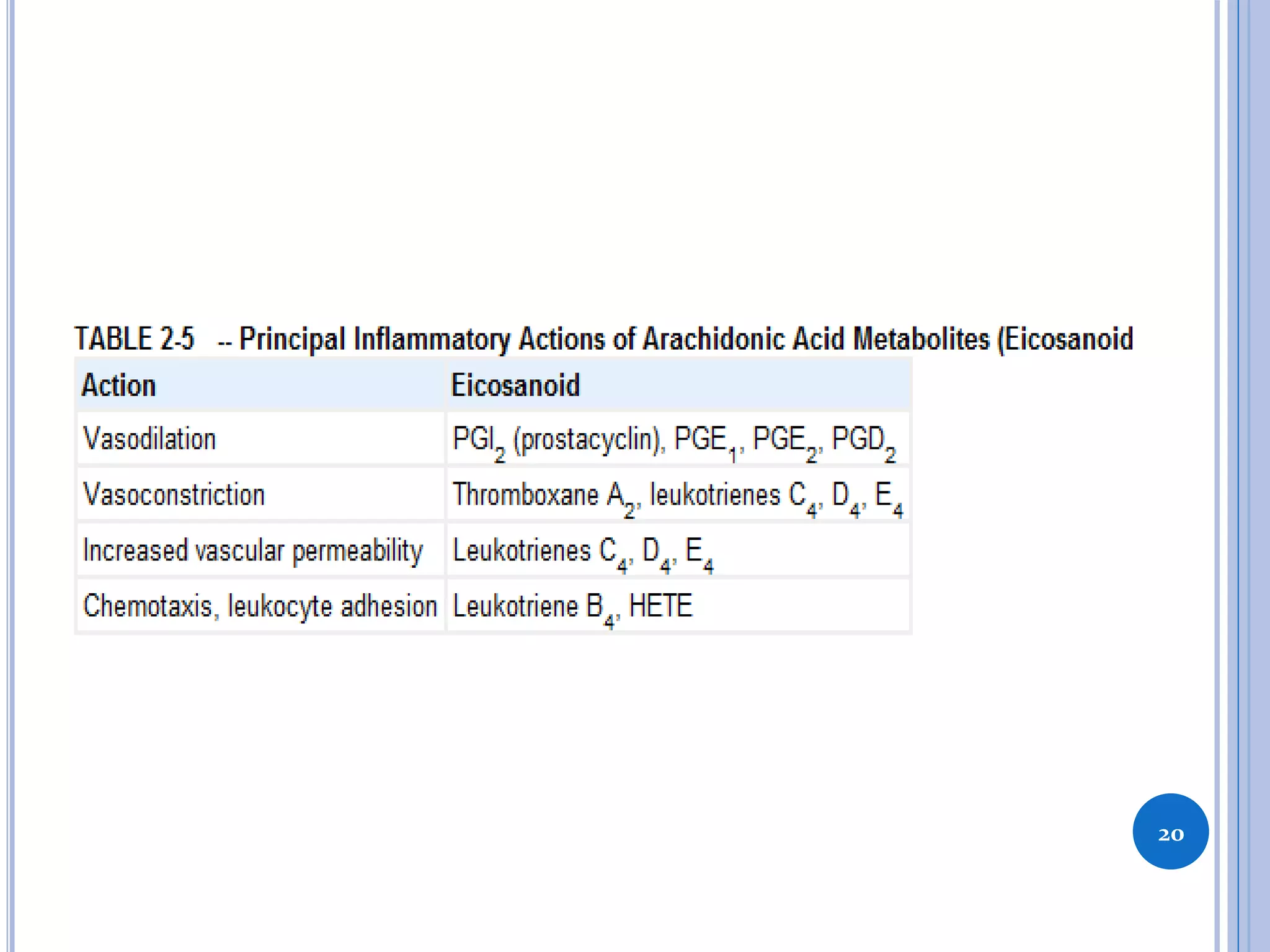
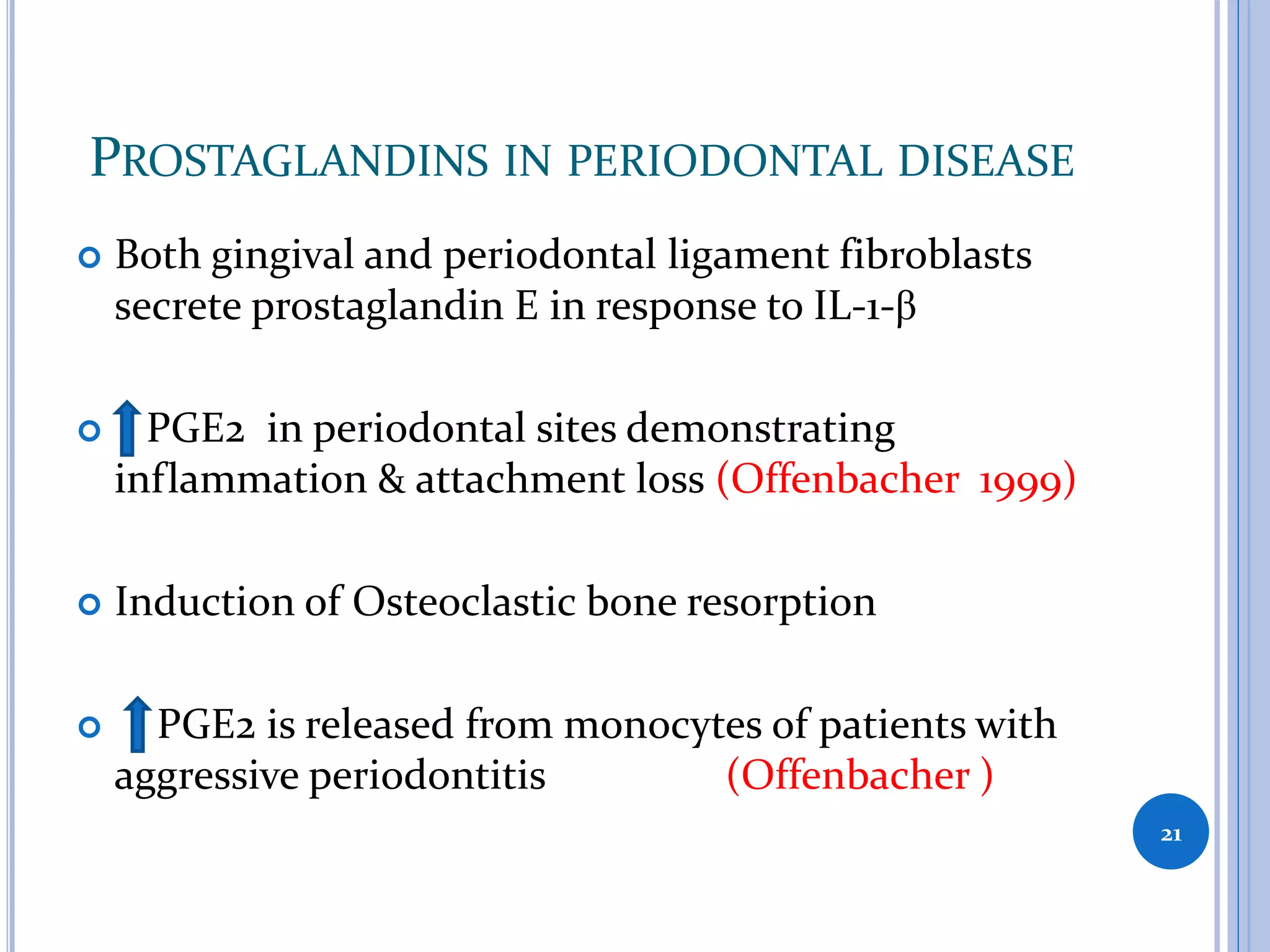
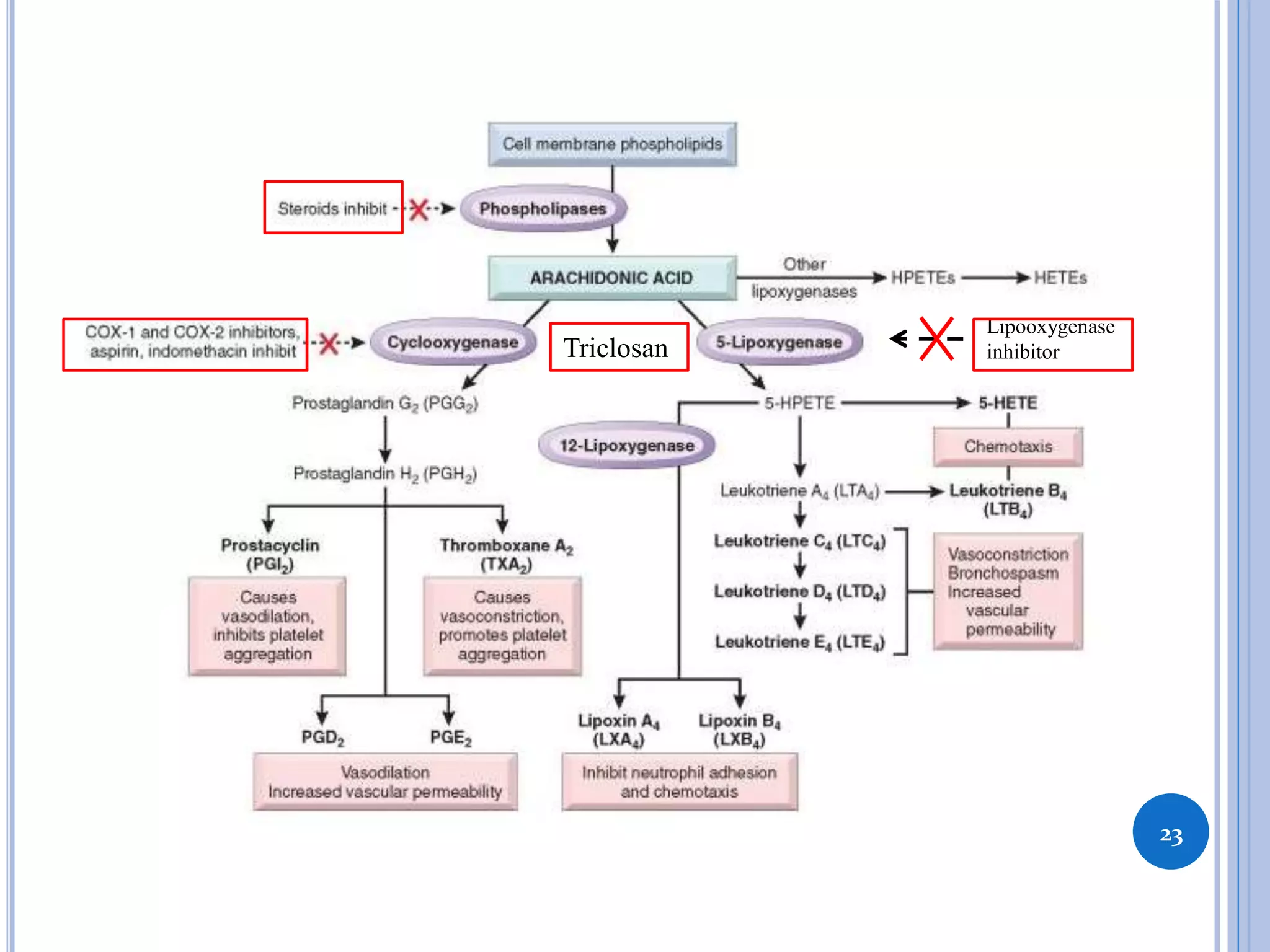
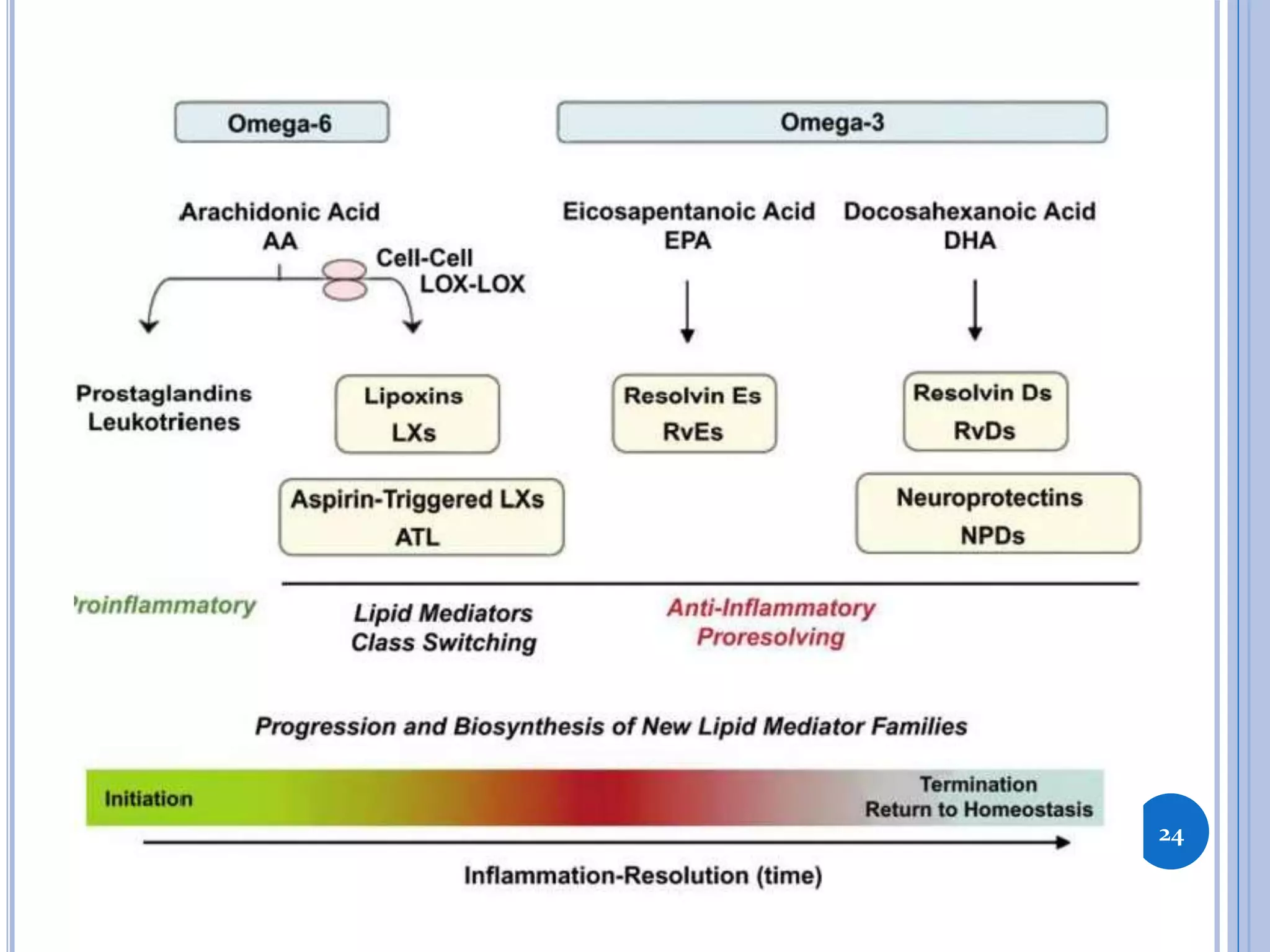
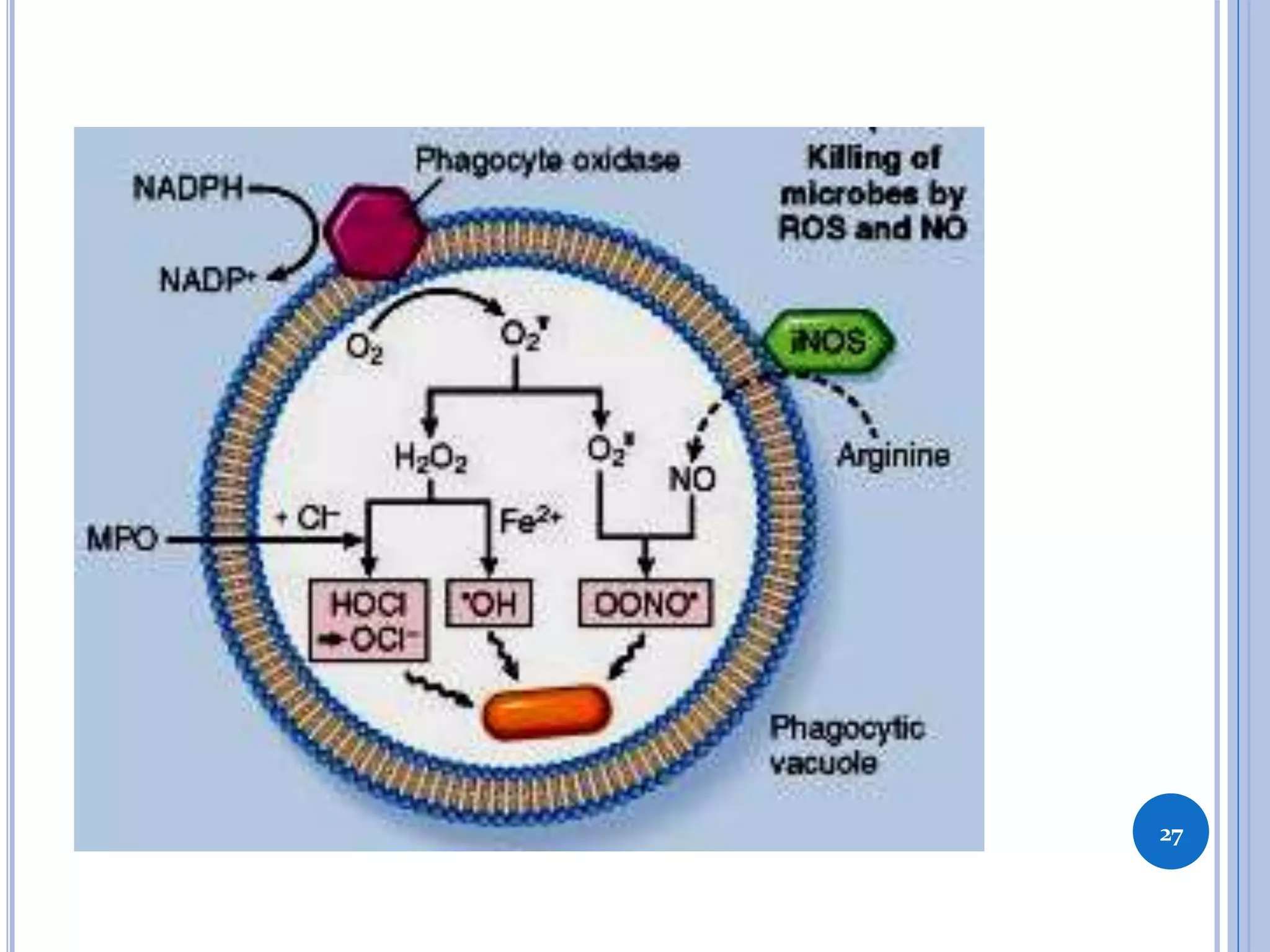
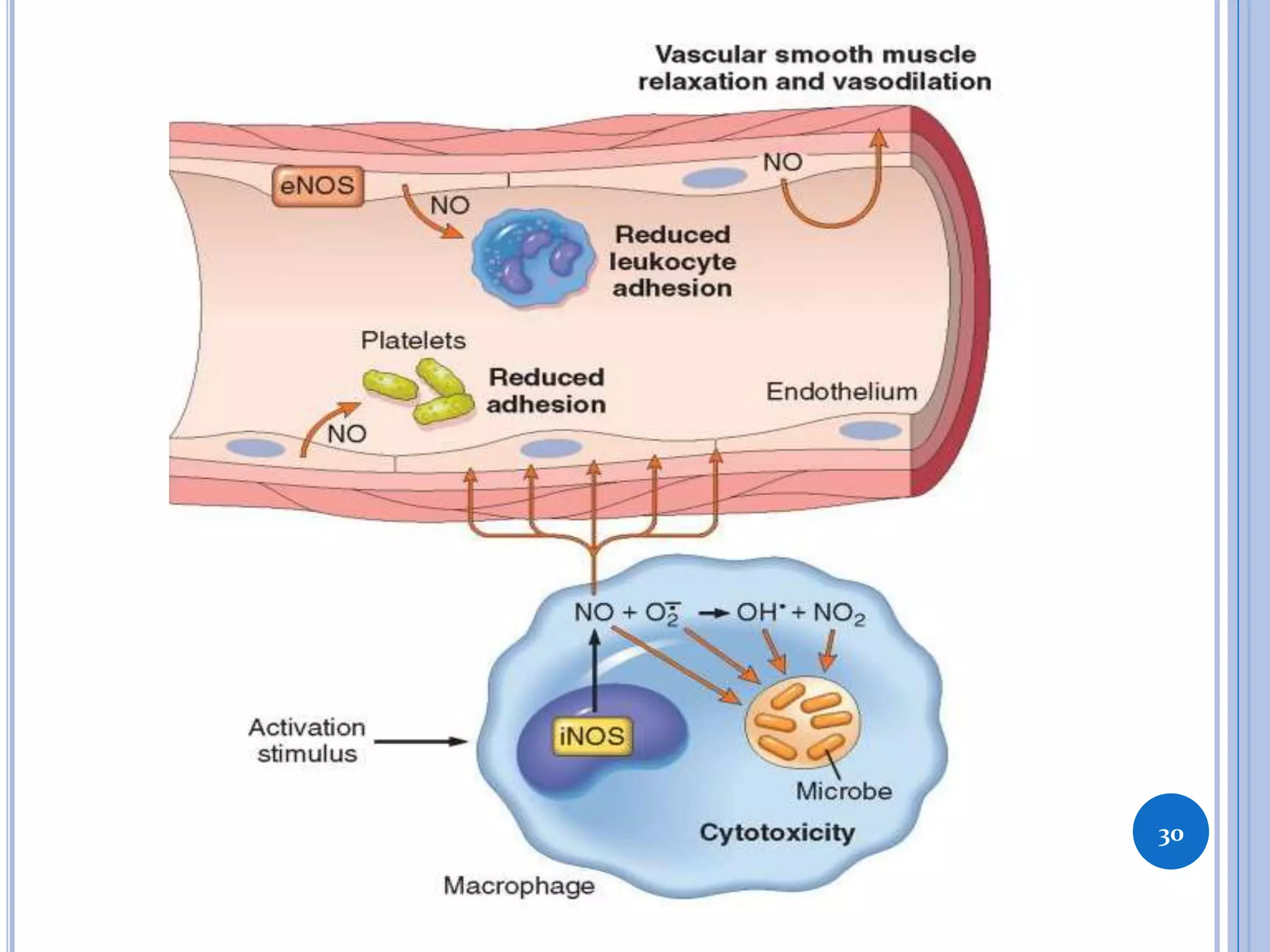
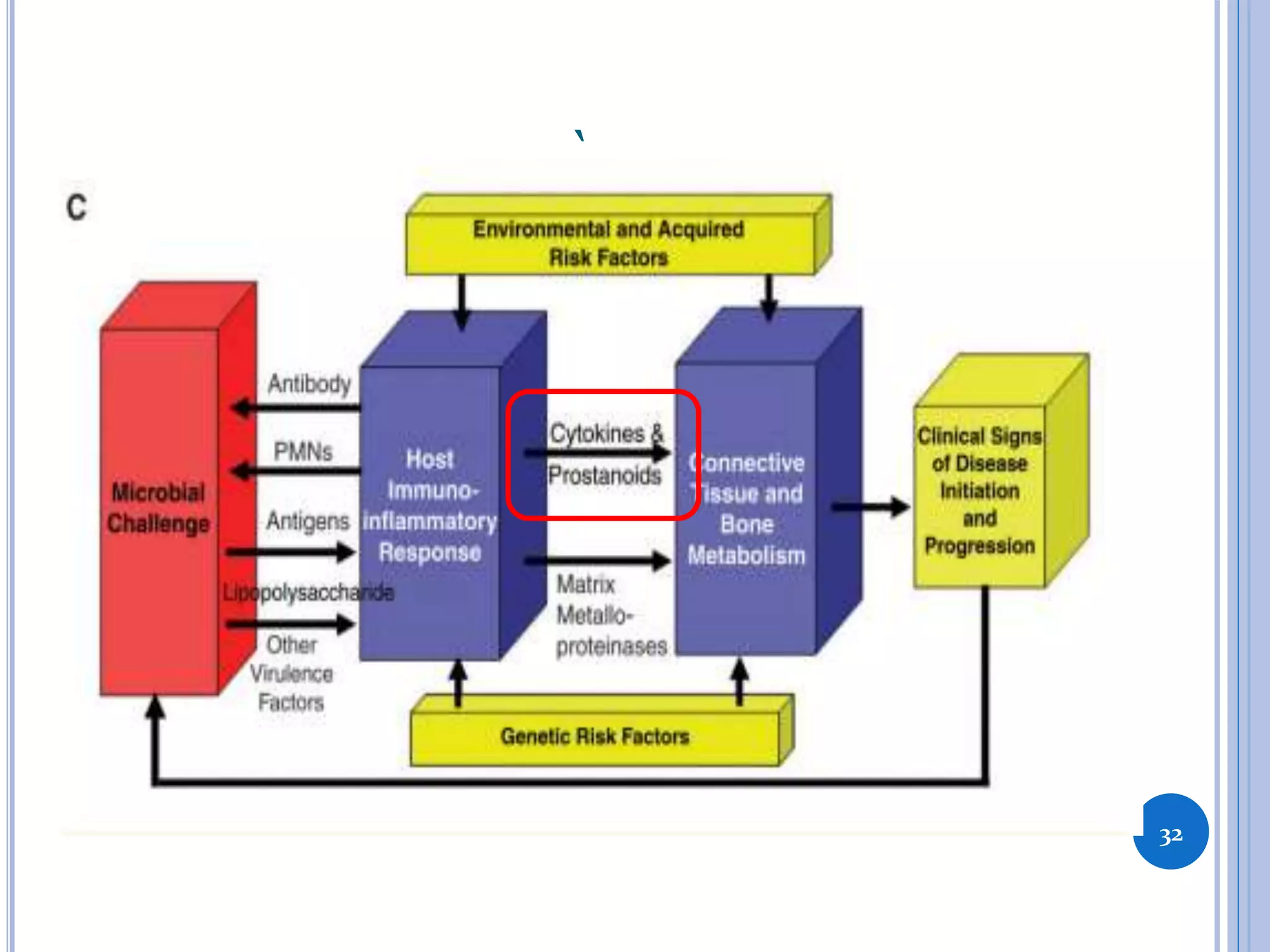
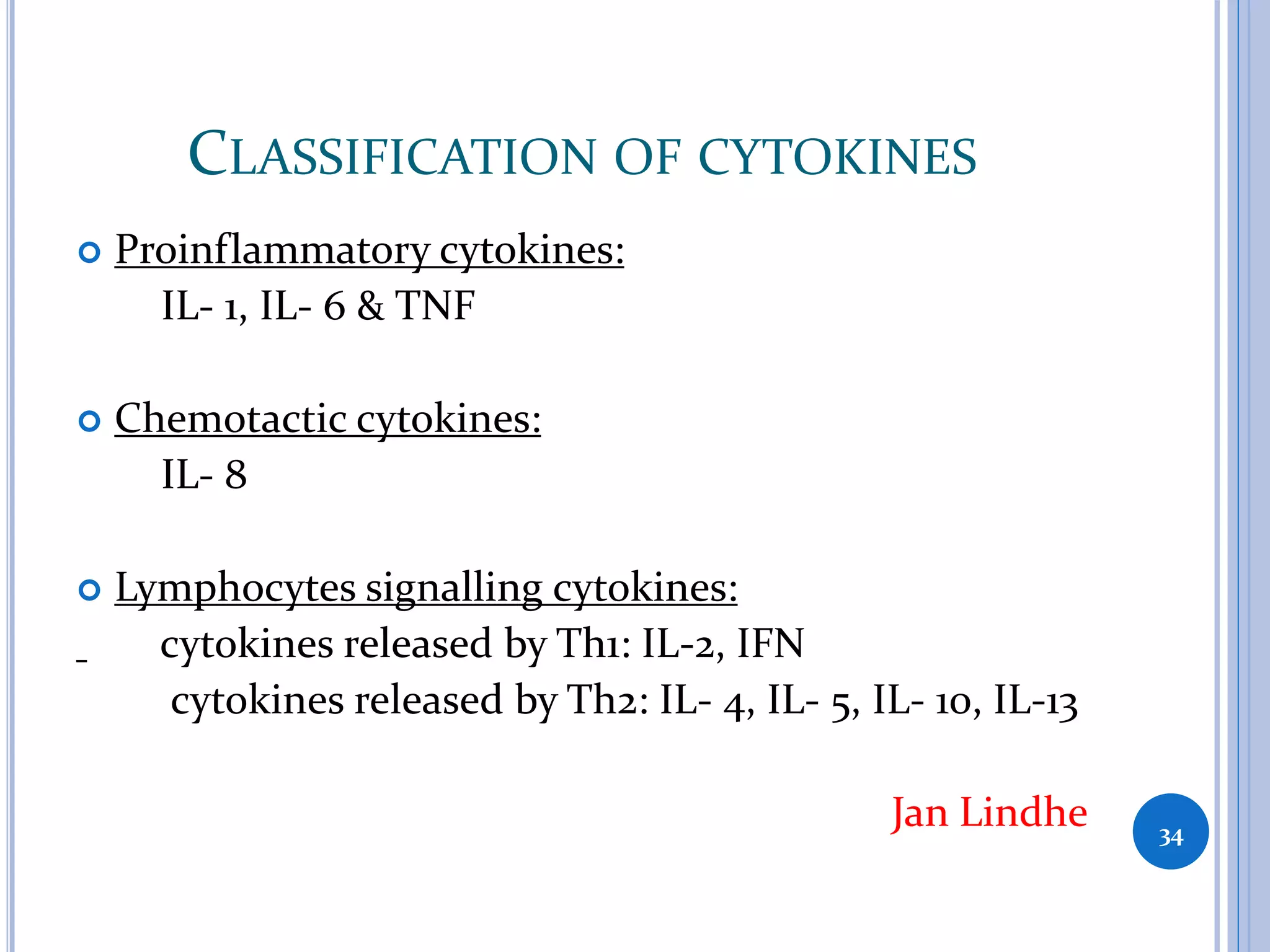
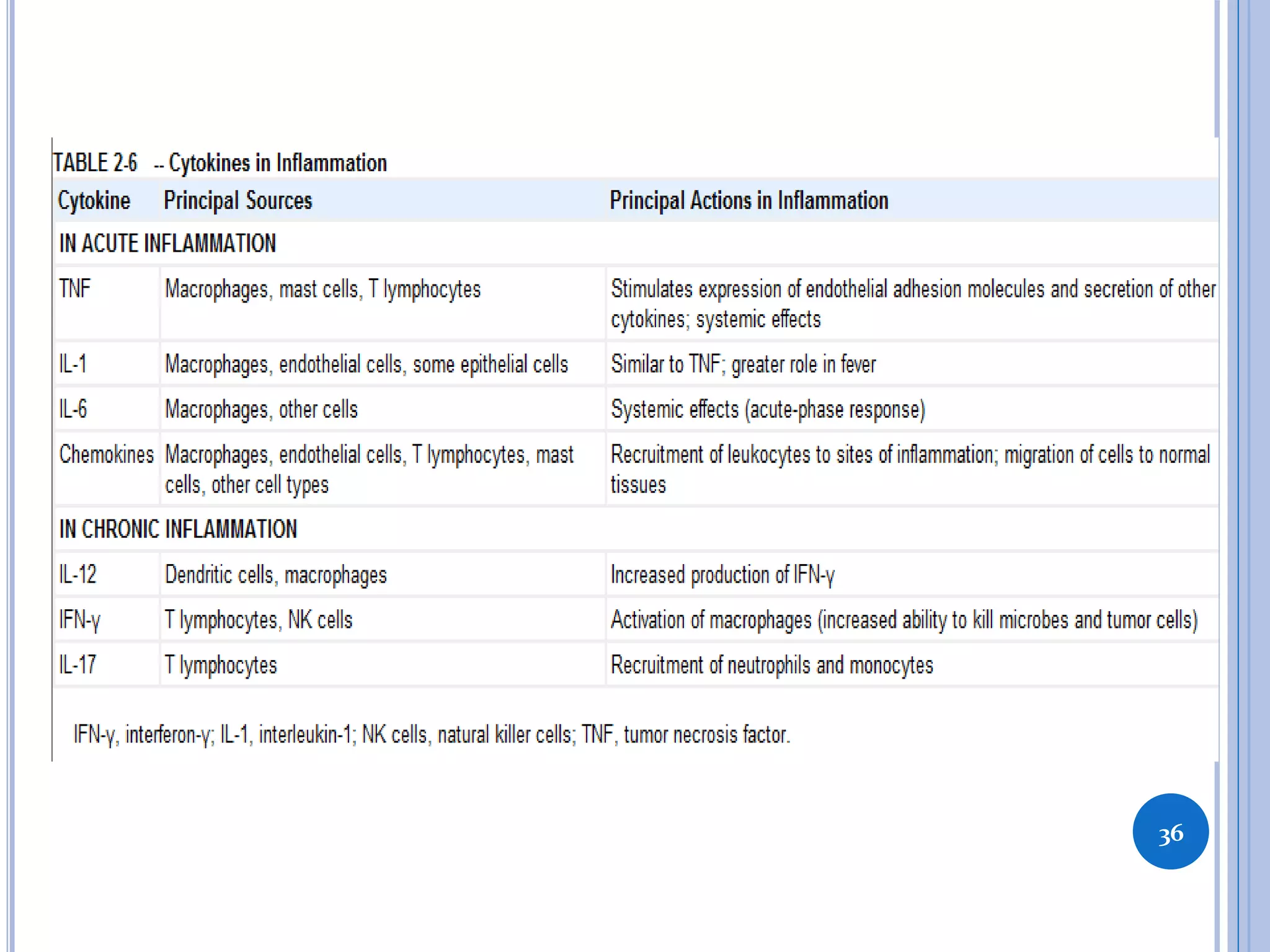
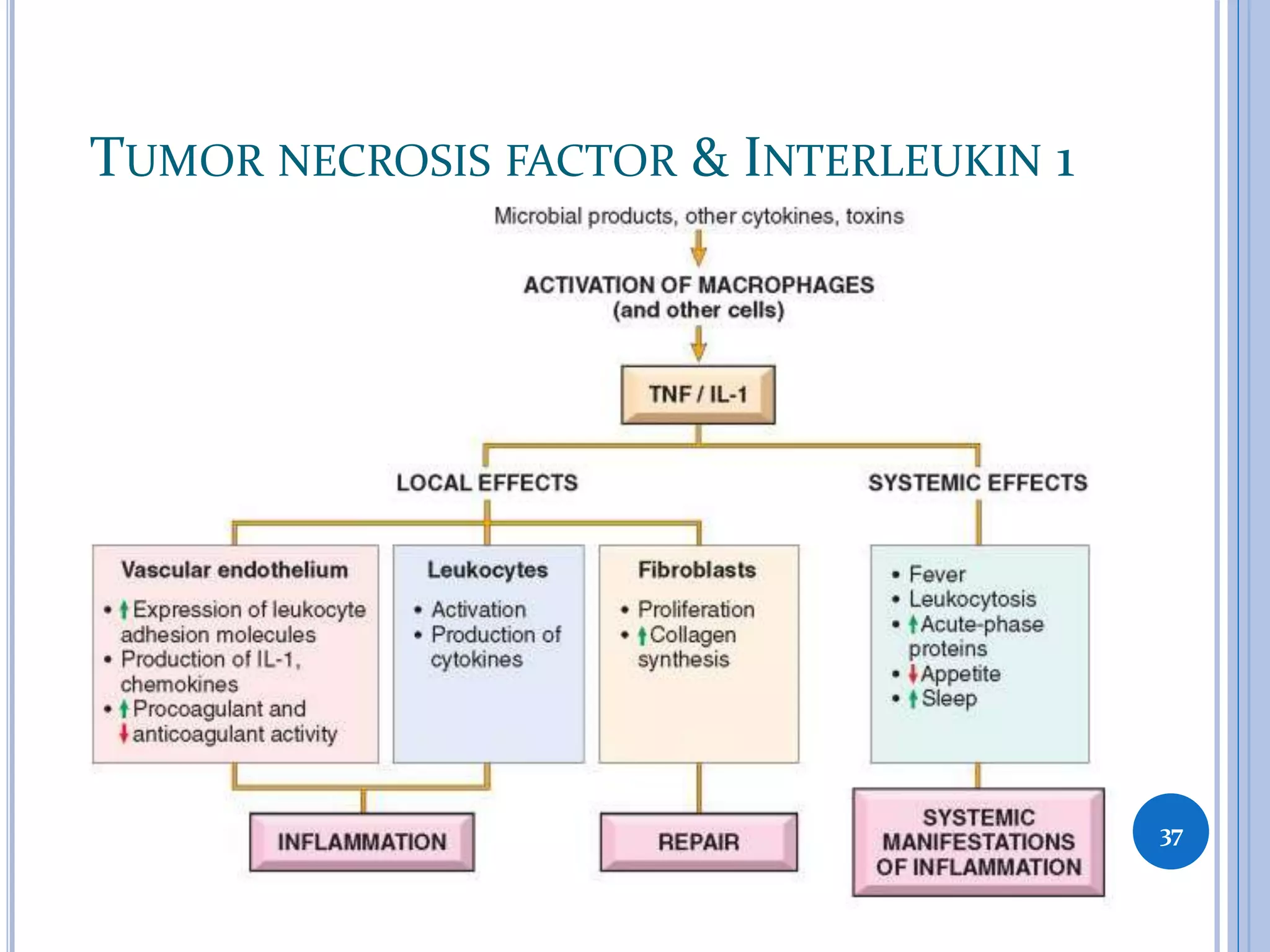
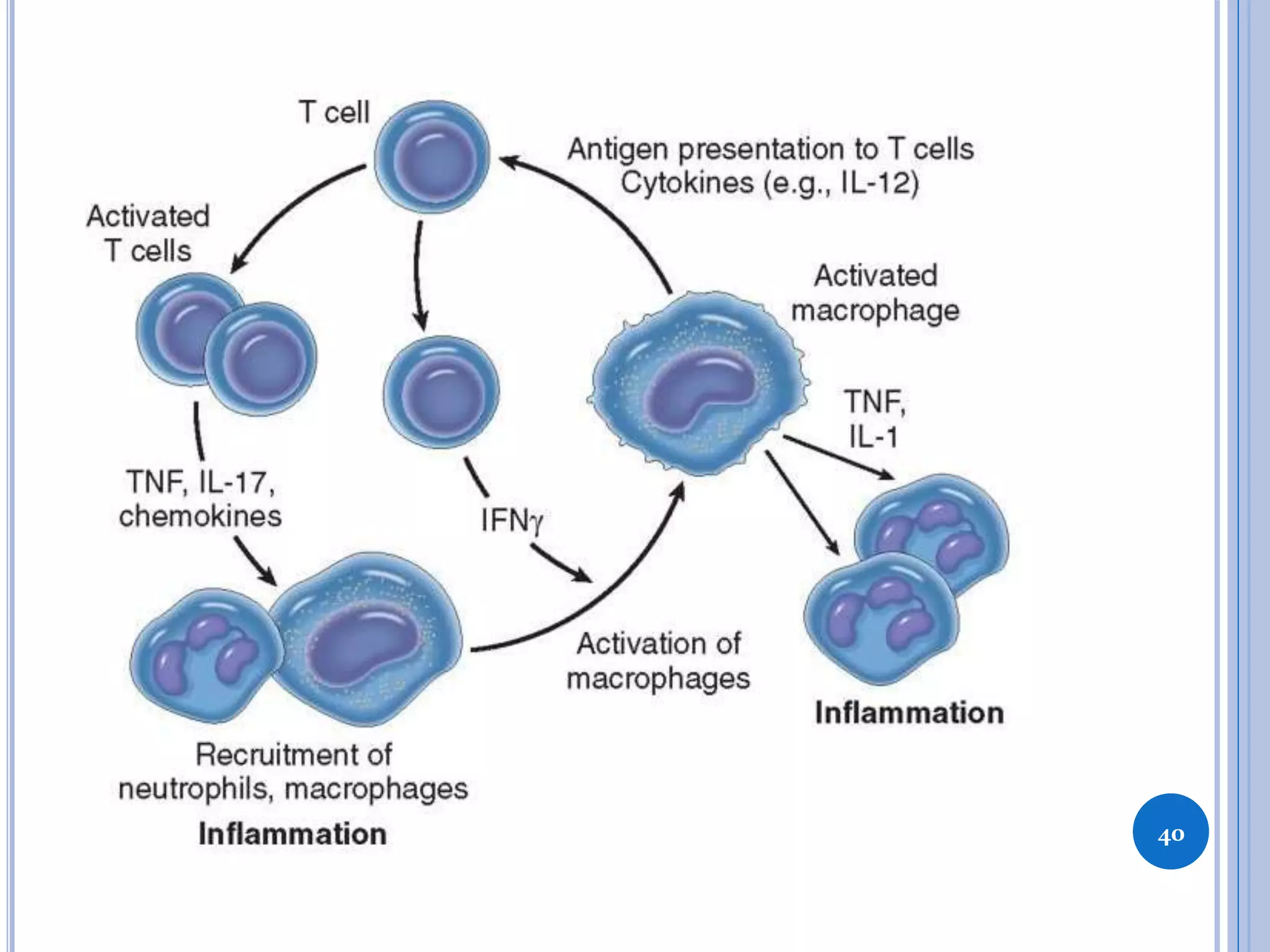
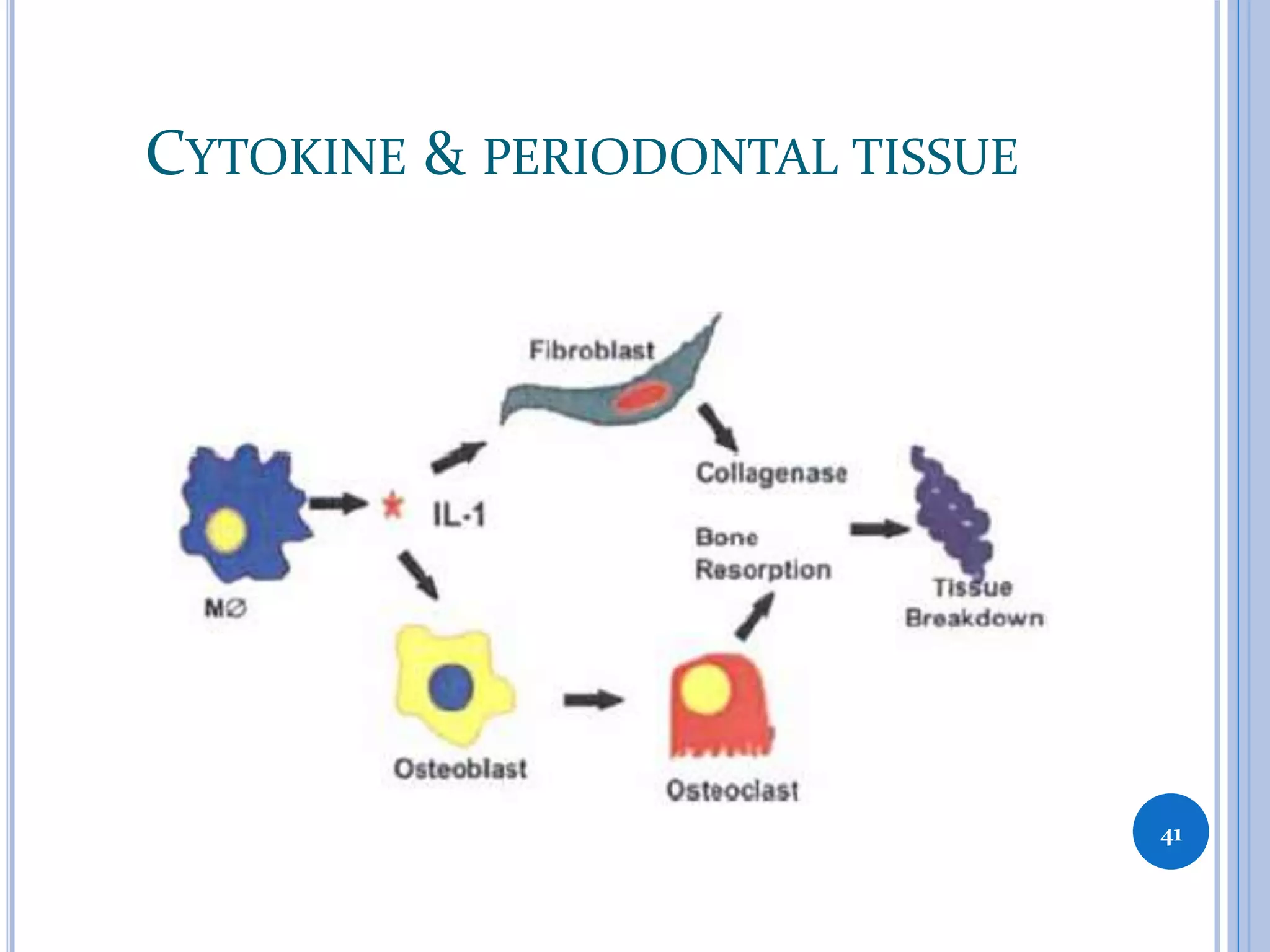
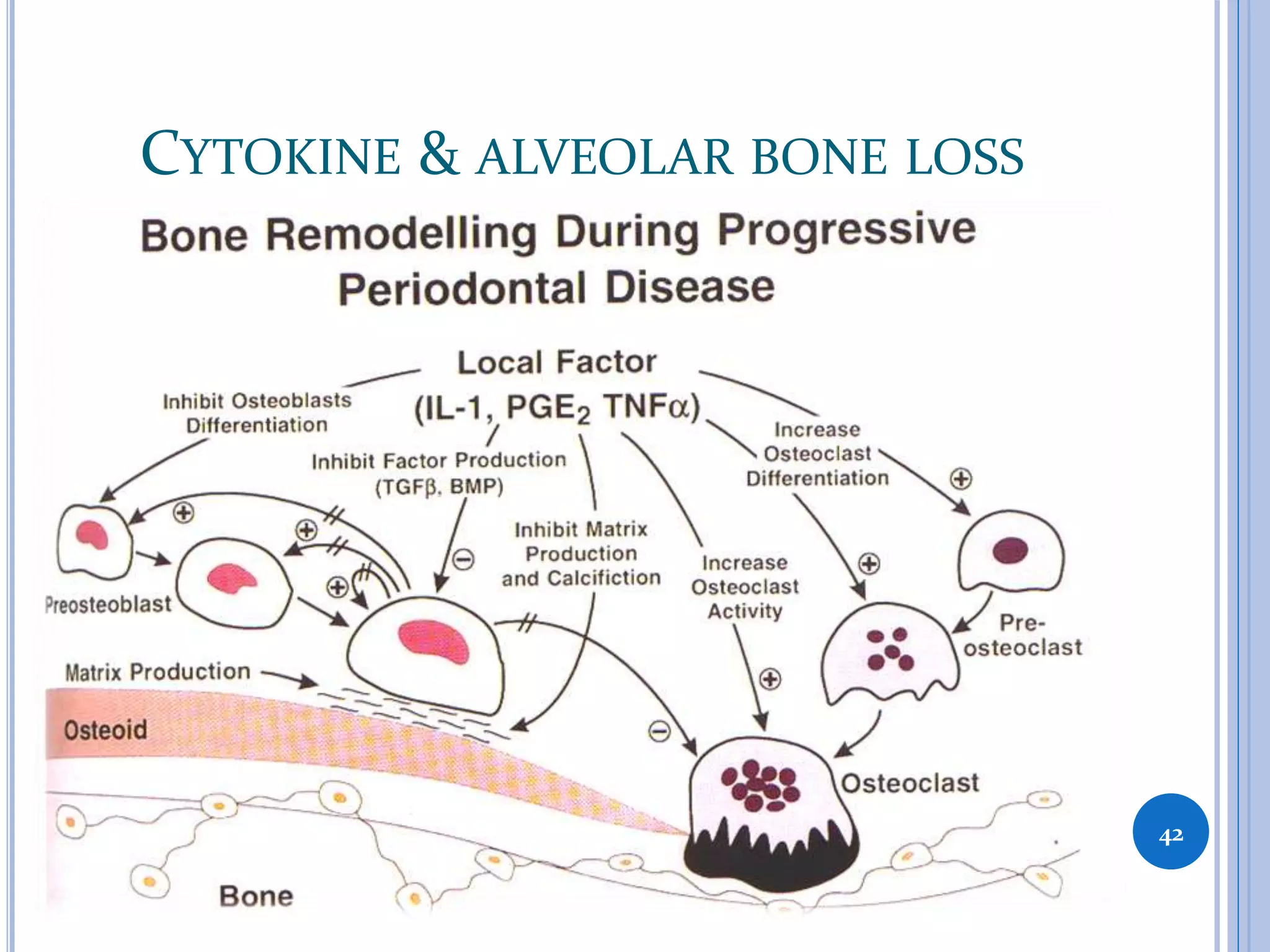
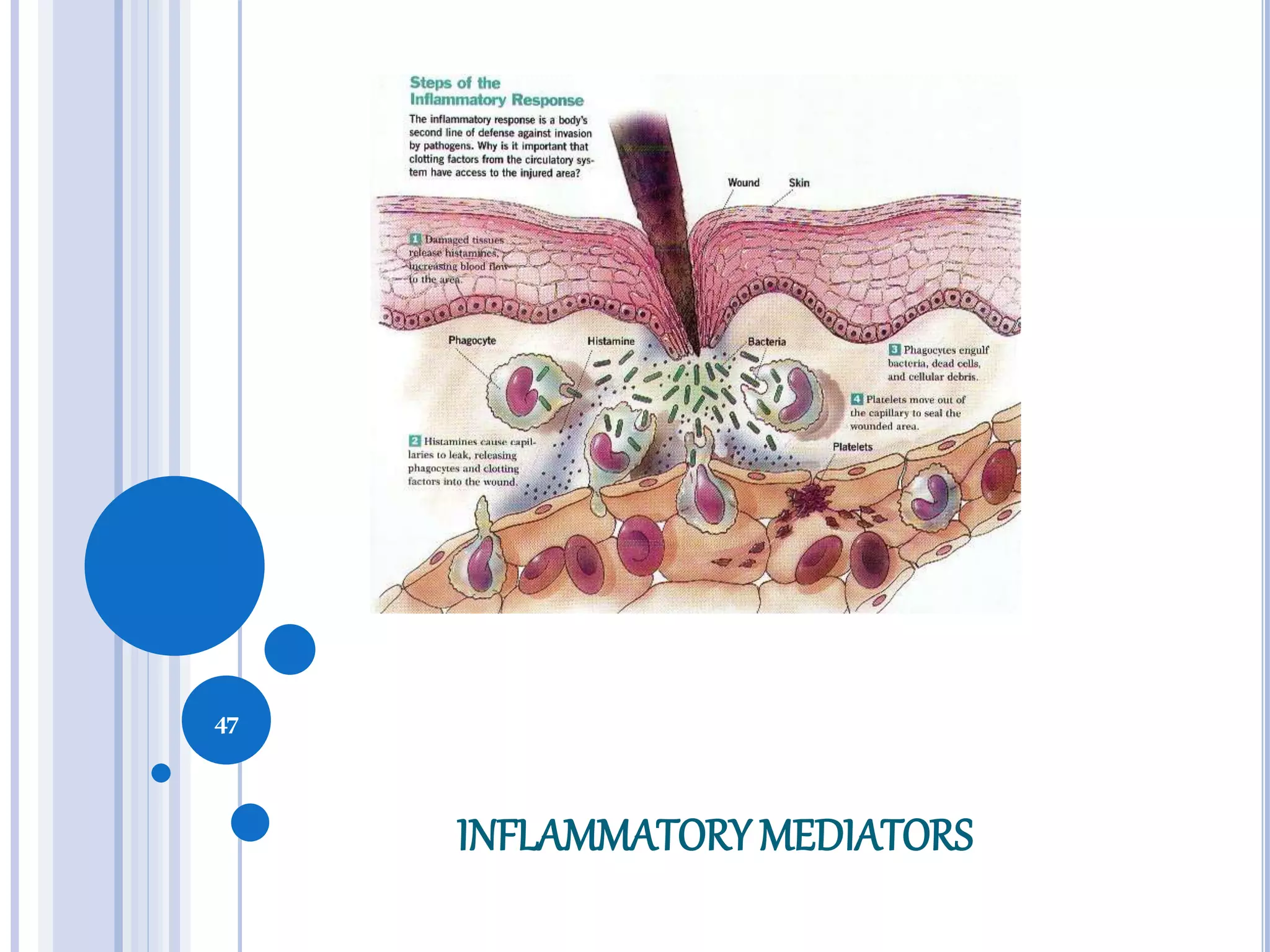
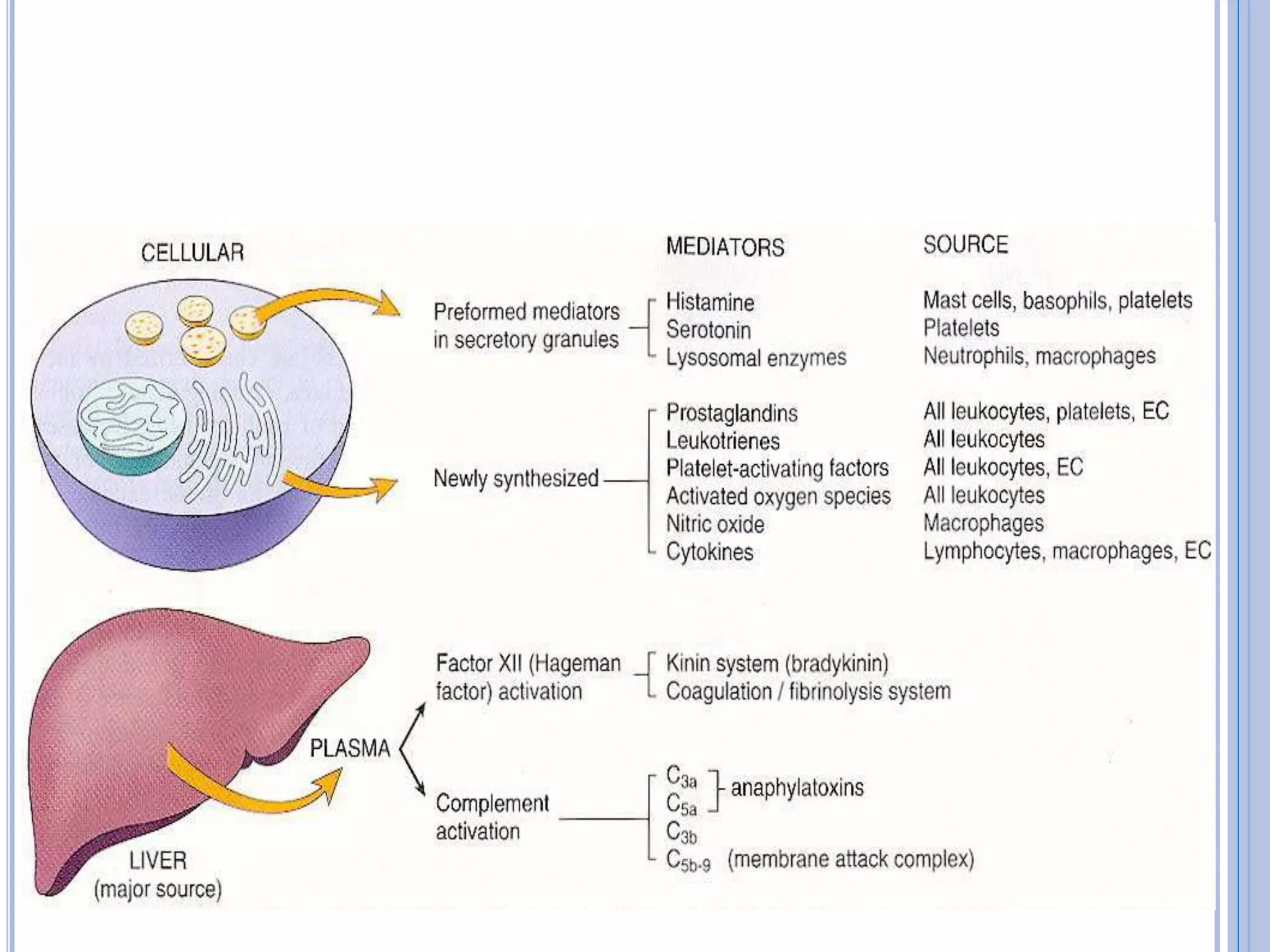
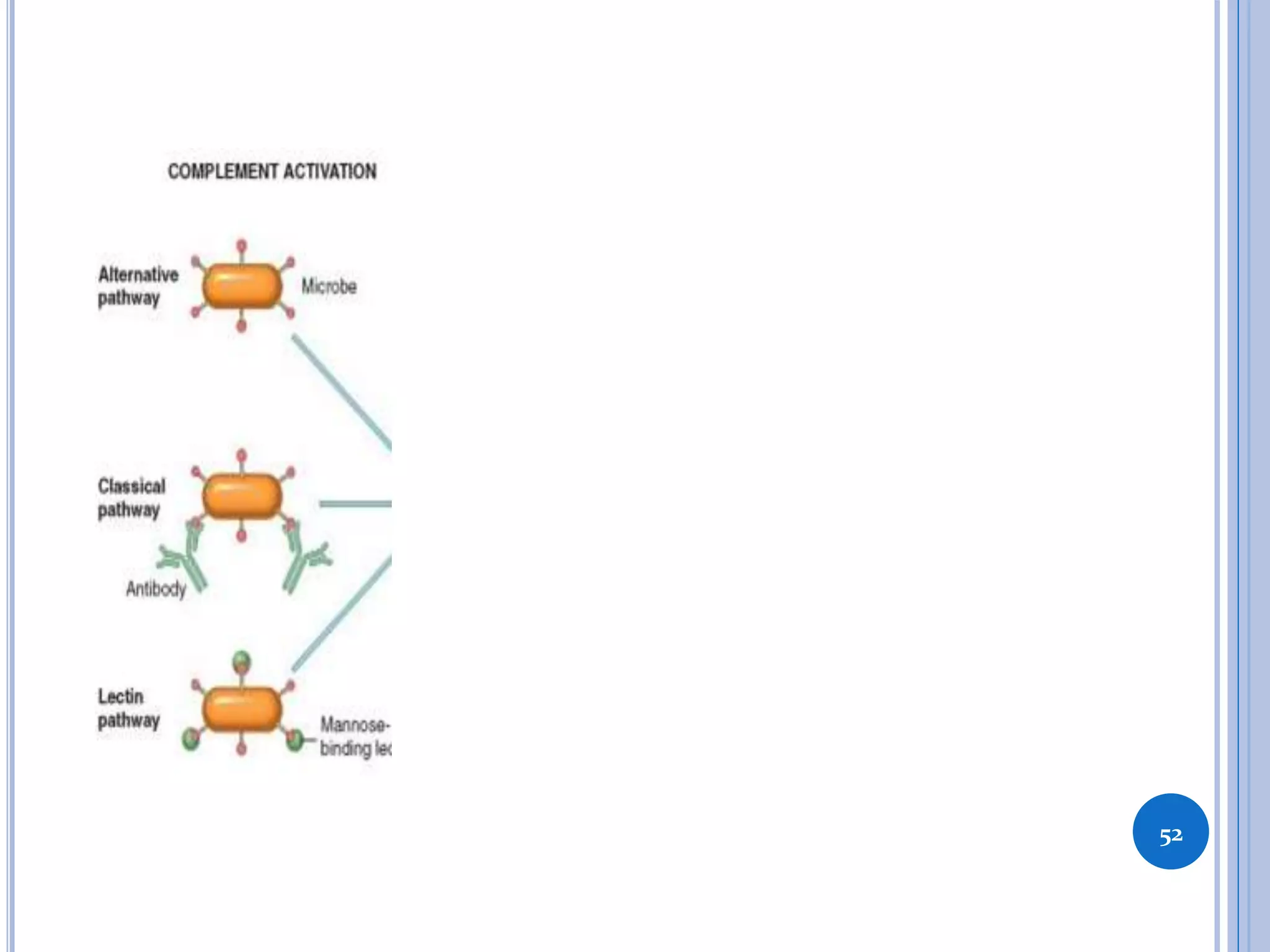
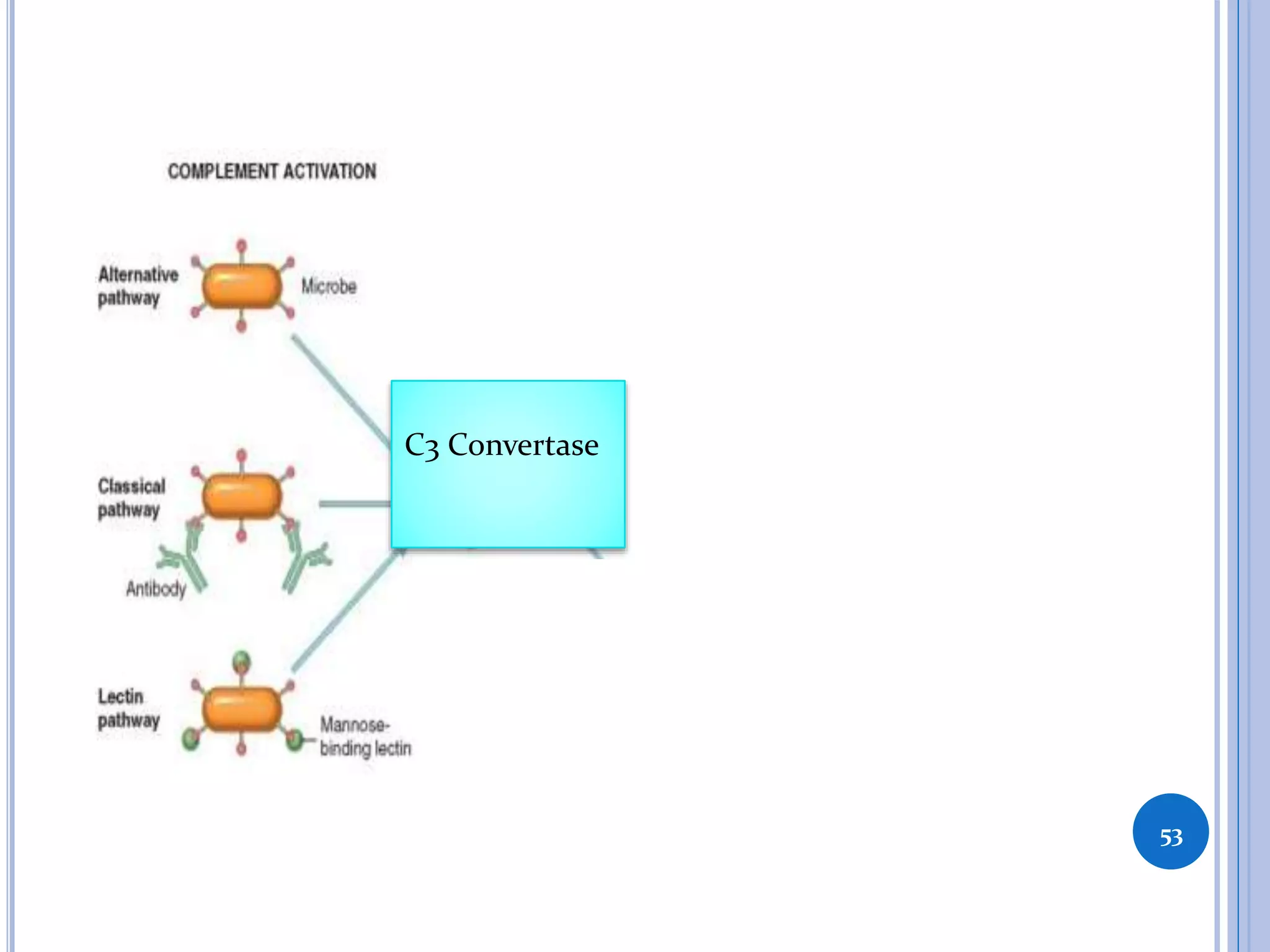
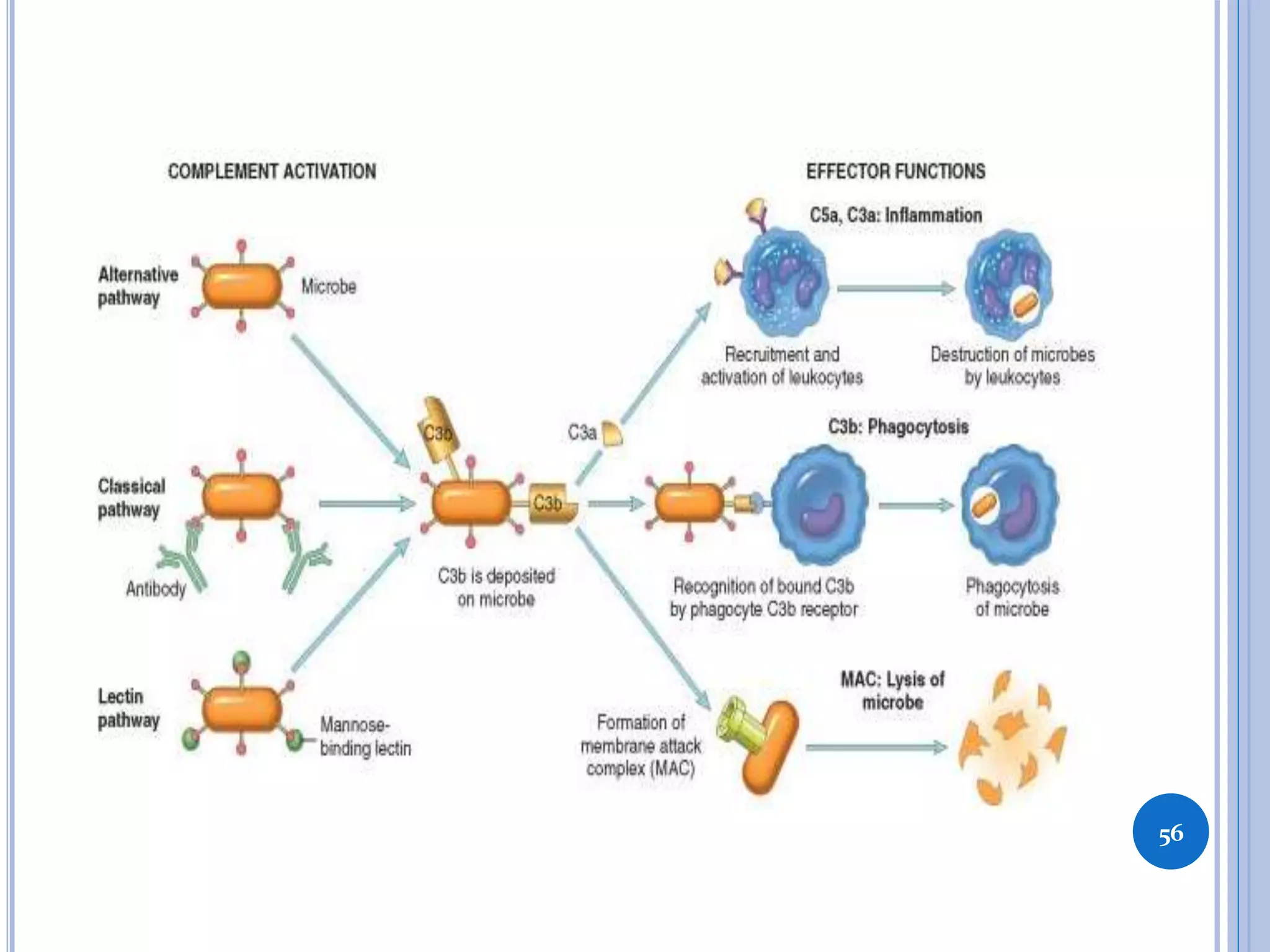
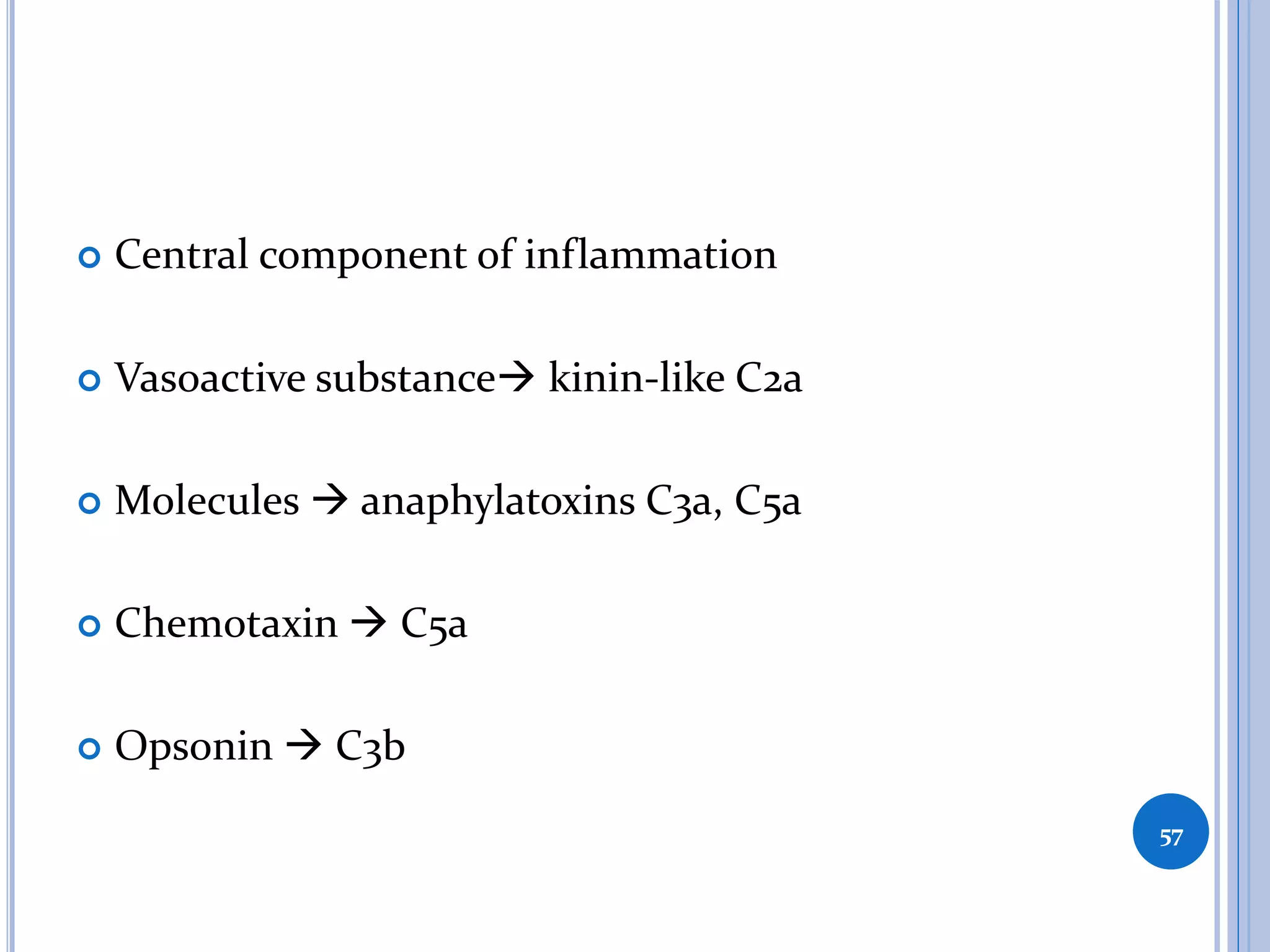
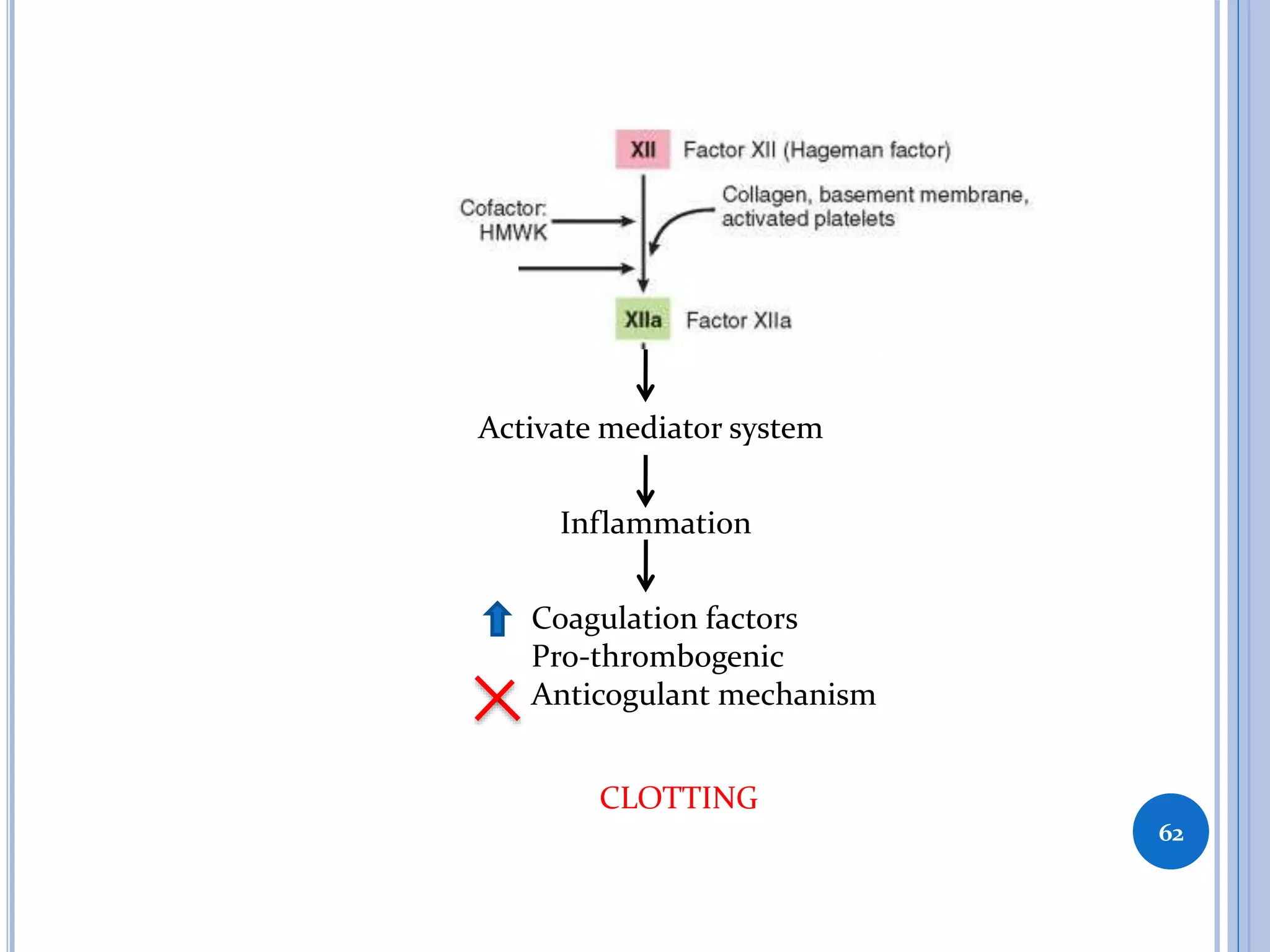
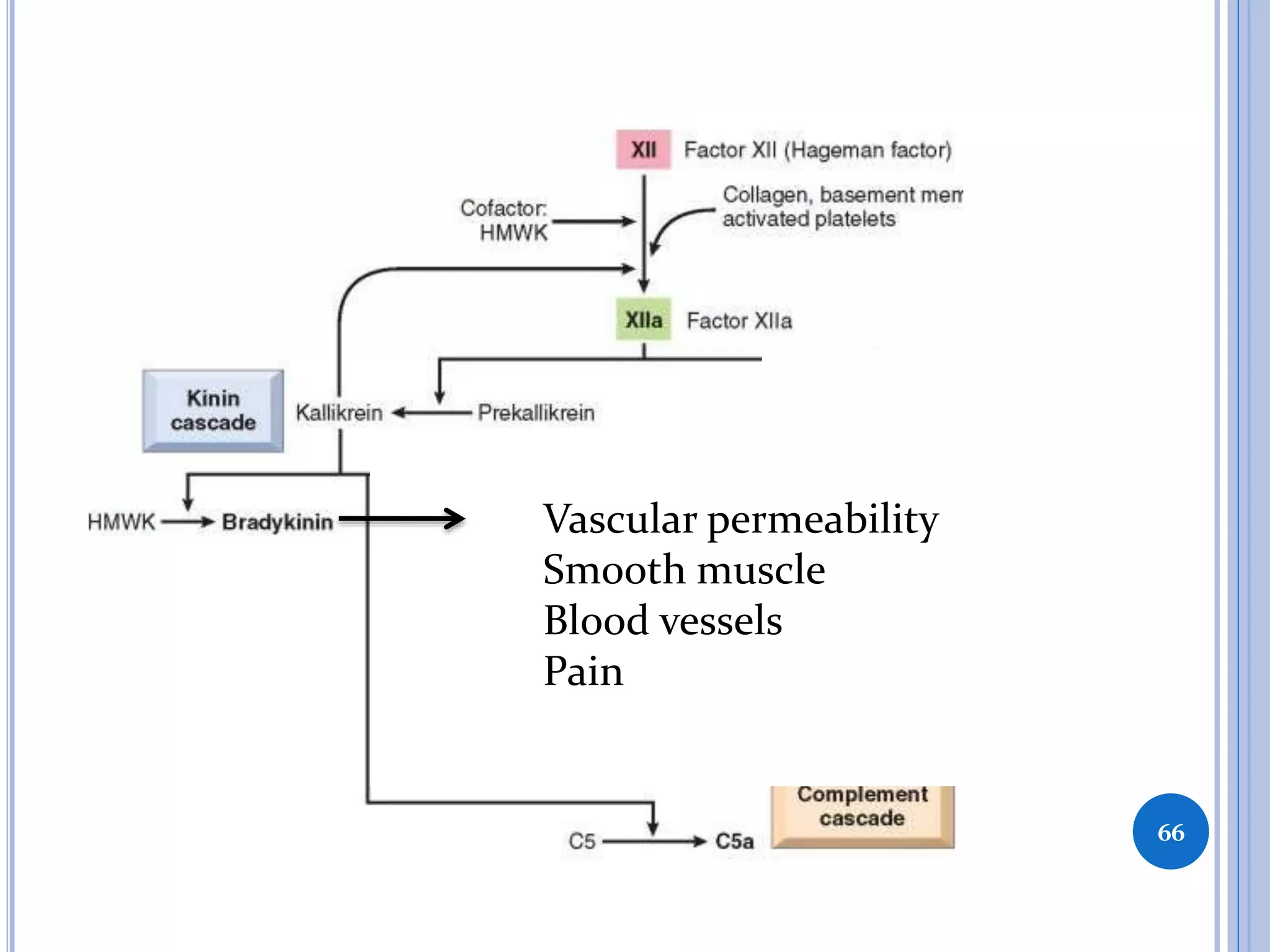
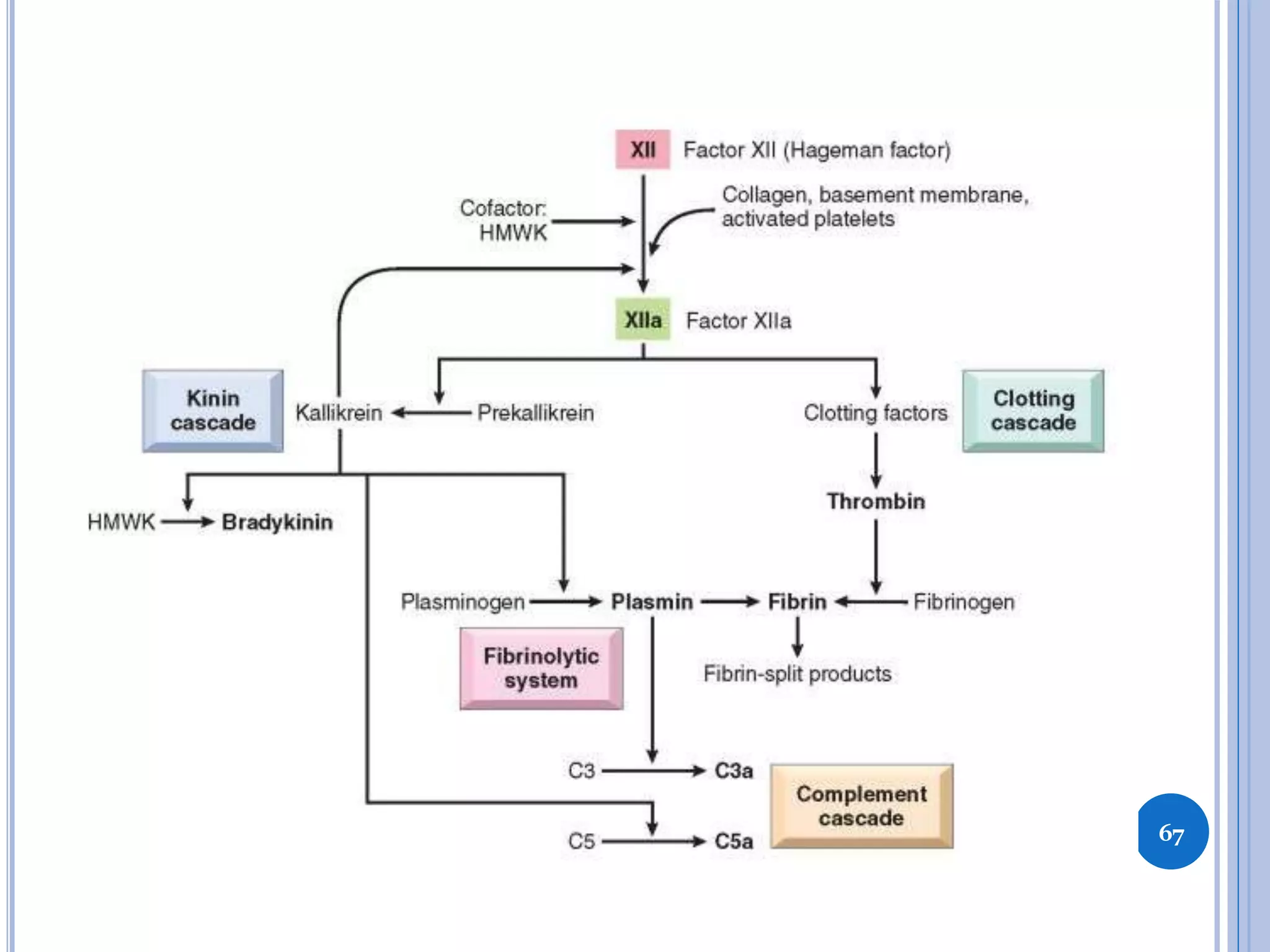
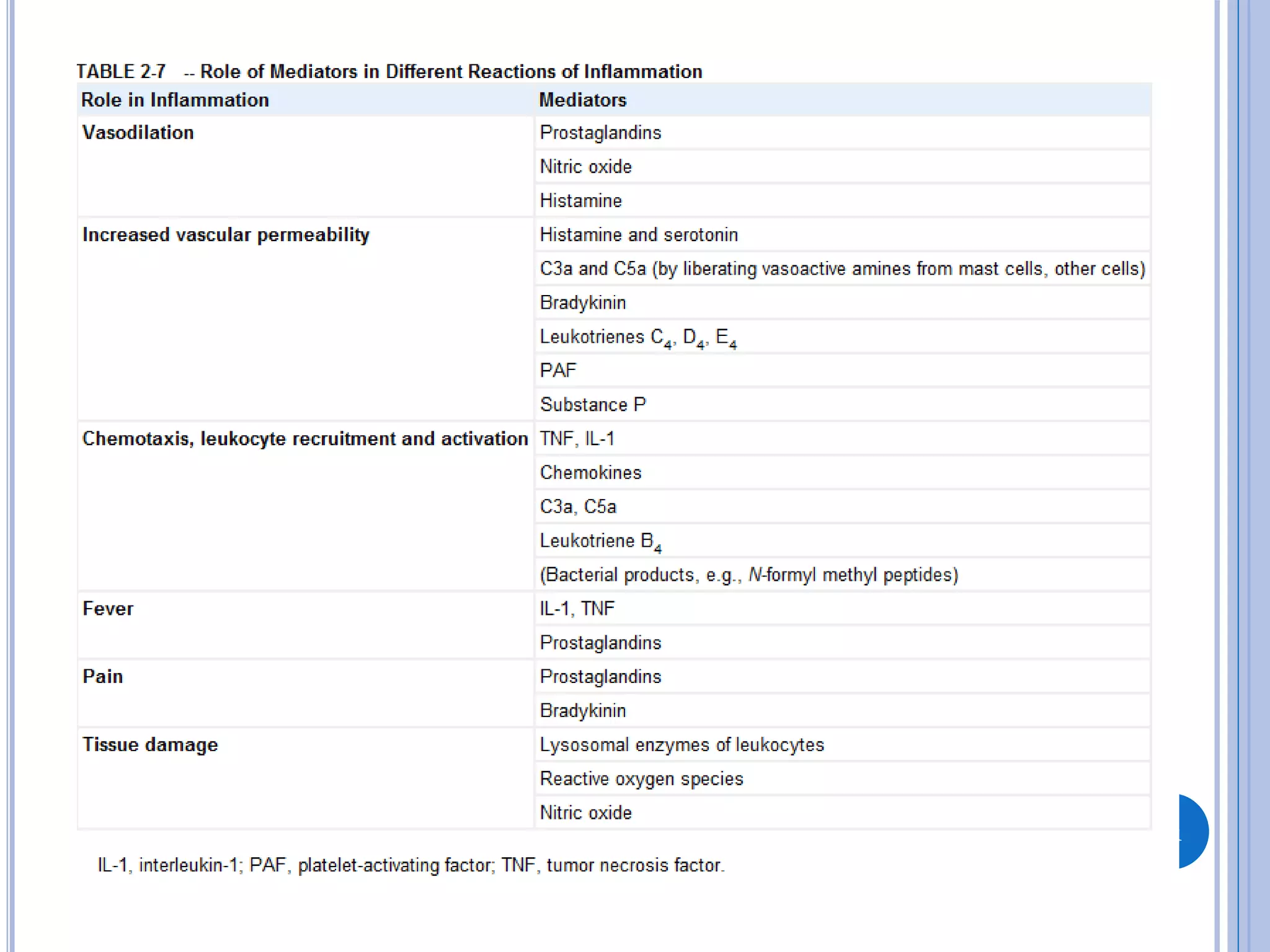
This document discusses inflammatory mediators, which are messengers that contribute to the inflammatory response by acting on blood vessels, immune cells, or other cells. Inflammatory mediators can be classified as either cell-derived or plasma-derived. Cell-derived mediators include histamine, serotonin, lysosomal enzymes, eicosanoids such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, platelet-activating factor, reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and cytokines. Plasma-derived mediators include components of the complement, coagulation, kinin, and fibrinolytic systems. Many of these mediators stimulate the release of other mediators and have effects like increasing vascular permeability and chemotaxis. Cytokines and