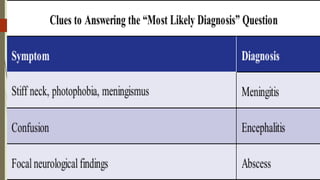
This document discusses infectious diseases and treatment of various bacterial infections. It begins with an introduction to antibiotics and how the bacteria that cause disease remain the same but the antibiotics used to treat them can change. It then discusses treatment of methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. The remainder of the document covers various classes of antibiotics including penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides and others; the bacteria and infections they treat; and treatments for central nervous system infections like meningitis and encephalitis.