1) Infected nonunions occur when a fracture healing process halts due to mechanical or biological failure, with a gap filled with fibrous tissue, and infection is present.
2) Common causes include open fractures that become infected, or infections developing after surgery to repair closed fractures. The infection can lead to bone and tissue loss.
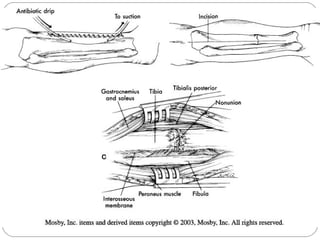
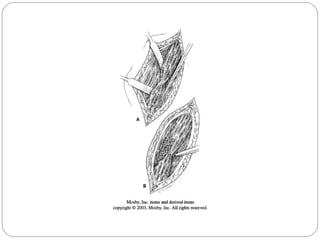
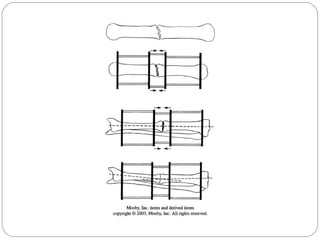
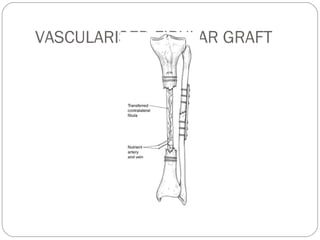
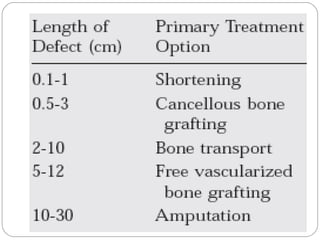
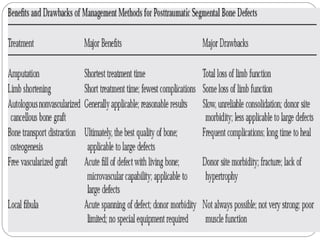
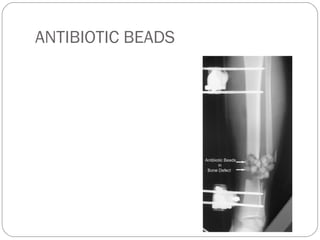
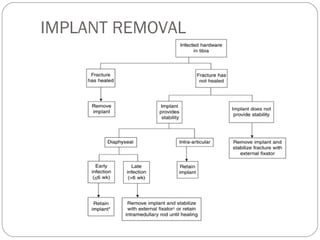
3) Treatment requires aggressive debridement of all infected and dead tissue, stabilization of the fracture, soft tissue coverage to prevent reinfection, and bone grafting to fill defects and promote healing.


![INFECTED NONUNION
That state existing after considerable time [6-8 months] has
elapsed, when there is no evidence that fracture will unite
and infection still persists. Therefore other method of
treatment to be done to achieve union and eradicate
infection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectednonunion2-130423121623-phpapp01/85/Infected-nonunion2-3-320.jpg)



![BIOFILM
Key for the development & persistence of inf.
Aggregation of microbes enclosed with in an extracelluar
polysaccharide matrix [glycocalyx] that adheres to the surface
of the implants or devitalized bone.
59% of orthopaedic biomaterial related infections +ve
findings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectednonunion2-130423121623-phpapp01/85/Infected-nonunion2-9-320.jpg)

![MICROBIOLOGY
Staphylococcus aureas most common, [alone or in
combination in 65-70%].
Pseudomonas aeroginosa [20-37%]
Commonly polymicrobial [32-70%].
Atypical mycobacterium & fungi in immunocompromised
pts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectednonunion2-130423121623-phpapp01/85/Infected-nonunion2-11-320.jpg)

![ROSEN et al [AO manual]
Infected non-draining nonunion
Infected draining nonunion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectednonunion2-130423121623-phpapp01/85/Infected-nonunion2-13-320.jpg)





![INVESTIGATION
Elevated ESR & CRP,Normal WBC.
X RAY:
1] Quality of bone
2] Type of implant
3] Fracture healing status
4] Angular alignment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectednonunion2-130423121623-phpapp01/85/Infected-nonunion2-19-320.jpg)