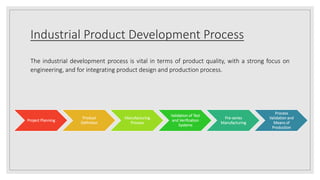
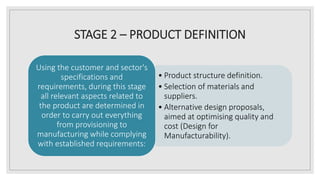
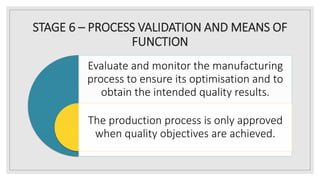
The document outlines the industrial product development process, emphasizing the differences between consumer and industrial goods, and detailing the stages of product planning, definition, manufacturing, testing, and validation. It describes how industrial products are reliant on consumer goods and includes steps for optimizing quality and cost. The process ensures that products meet specified quality standards before production is approved.