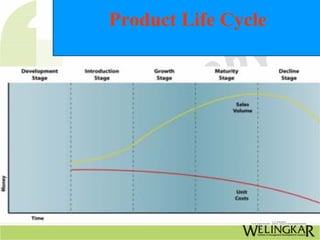
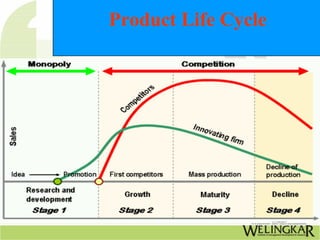
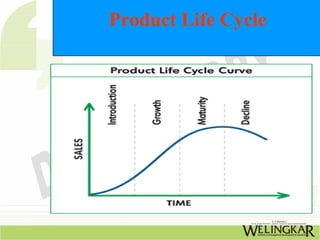
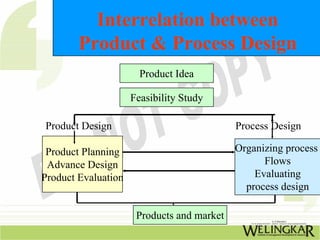
Product design involves conceptualizing and developing physical products and services through testing and implementation. It is a multifaceted role that combines aspects of marketing, product management, industrial design, and engineering. Effective product design follows a process from identifying needs to evaluation. Related process design delineates the manufacturing steps and ensures quality production. Together, product and process design are interrelated and dynamic activities that evolve based on factors like volume, quality, and available equipment over a product's lifecycle from development to maturity and decline.