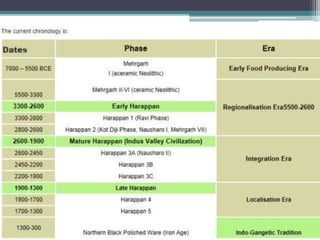
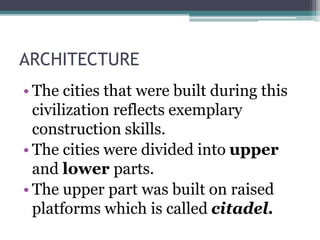
The Indus Valley Civilization developed between 3250-3000 BC along the Indus River valley. Major sites included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in modern-day Pakistan. The cities had advanced architecture, including citadels and lower towns divided by wide, planned streets. Harappan cities featured impressive public buildings and water supply systems. The civilization traded with Mesopotamia and Egypt and had a sophisticated culture, crafting artifacts out of materials like bronze, terracotta and stone. The Indus Valley Civilization was a highly developed ancient culture centered around the Indus River valley.