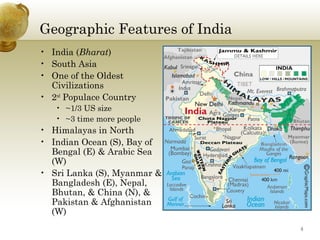
India has a population of over 1 billion people, with 70% living in rural areas. Rural villages remain culturally important despite urbanization. The country gained independence from Britain in 1947 and is a democratic republic with a federal government system. Major religions include Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Sikhism. Regional languages vary significantly across states. Traditional Indian culture emphasizes family and community over individualism.