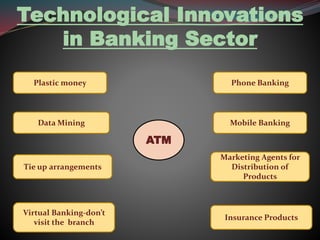
A bank is a financial institution that acts as an intermediary between borrowers and lenders by accepting deposits from customers and lending money. The first modern bank was established in Italy in 1406. The history of banking in India involves three phases - early banking before 1969, nationalization between 1969-1991, and recent reforms after 1991. The Reserve Bank of India, established in 1935, serves as India's central bank and regulates commercial banks. Technological innovations in Indian banking include ATMs, online and mobile banking, and distribution of insurance products through various agents and partnerships. Indian banking offers career opportunities, leadership development, competitive salaries, and personal growth.