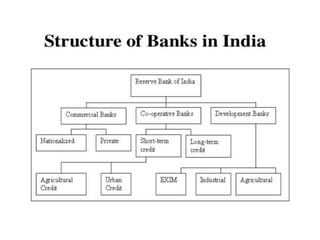
This document provides an overview of the banking sector in India. It discusses the definition of a bank according to Indian law and the history of banking in India in phases from the 18th century to present day. It also classifies the different types of banks in India including the Reserve Bank of India, public sector banks, private sector banks, cooperative banks, and development banks. The roles of commercial banks and investment banks are explained. Finally, it discusses modern modes of banking transactions such as e-banking, ATMs, debit cards, and credit cards.