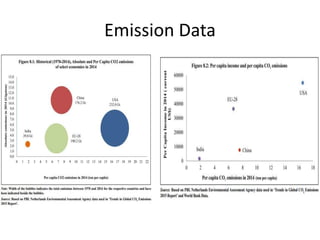
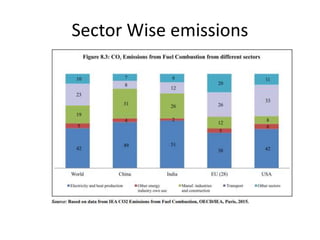
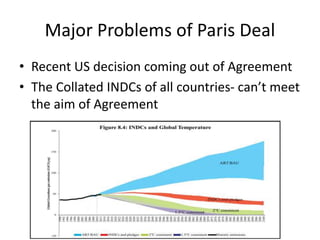
The document discusses the Paris Agreement and India's role in addressing climate change, highlighting its impact on global temperatures and emissions. It details India's Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) and various domestic actions, including the establishment of missions under the National Action Plan and renewable energy targets. Major challenges faced by the agreement include the lack of compliance and recent US withdrawal from the accord.