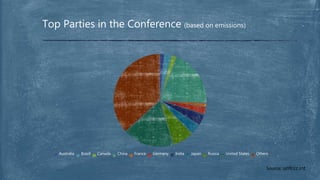
The Paris Agreement is an agreement within the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change dealing with greenhouse gas emissions mitigation, adaptation and finance starting in 2020. 194 countries have signed it, with 127 ratifying it, and it went into effect in November 2016. The agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C by reducing emissions through nationally determined contributions that are reported every 5 years. However, the contributions are not legally binding and there is no enforcement if countries do not meet their targets.