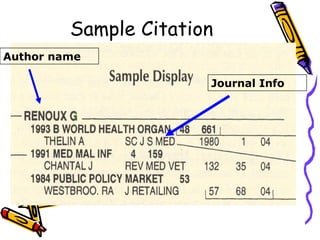
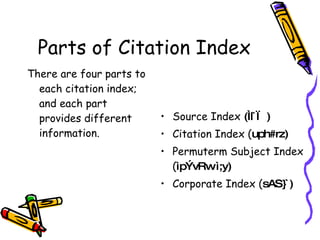
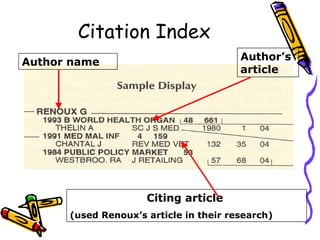
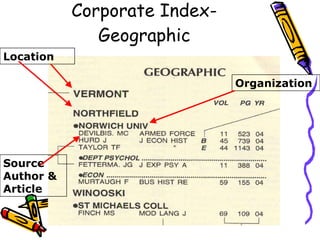
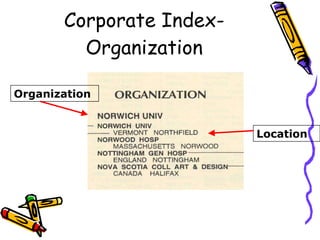
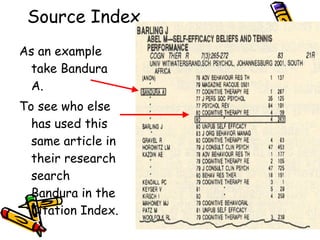
Indexes and abstracts organize information from documents in a systematic way to facilitate searching. Indexes contain records for articles that include fields like authors, titles, sources, and abstracts. Citation indexes allow users to trace interconnections between authors on a topic and determine an article's importance by how often it is cited. They contain four parts: a source index, citation index, permuterm subject index, and corporate index. Users can search these indexes in different ways to locate relevant articles on a topic.