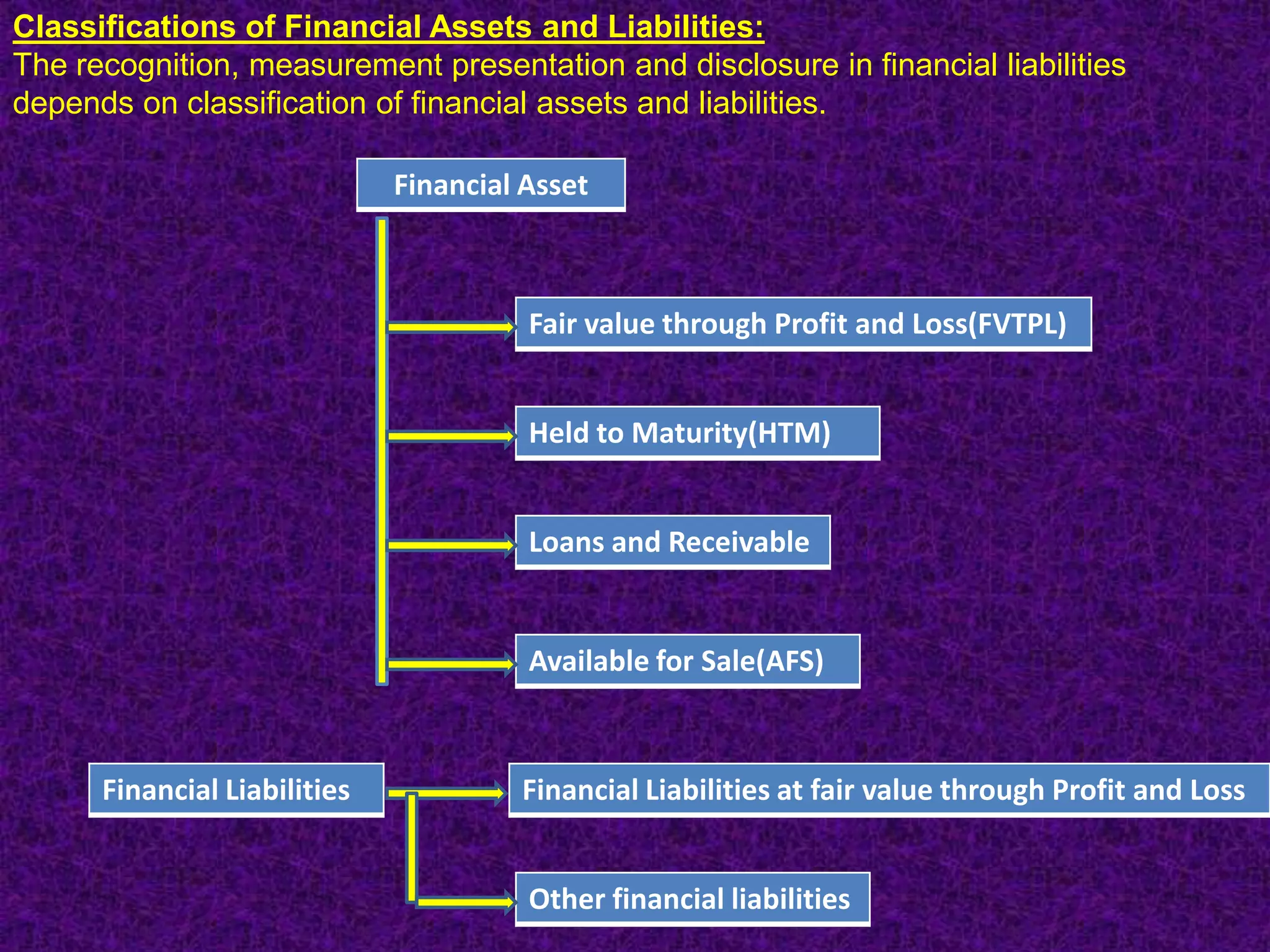
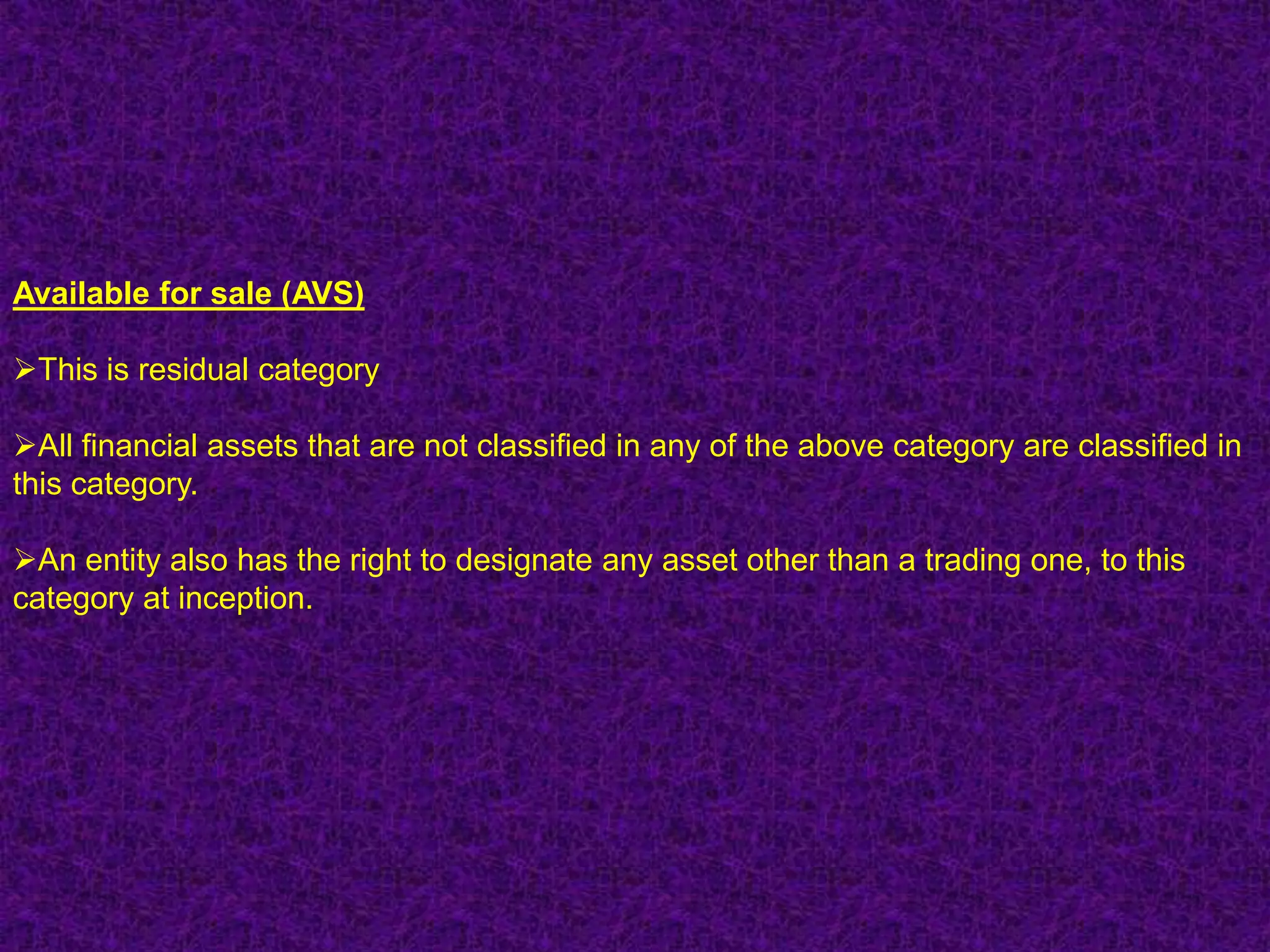
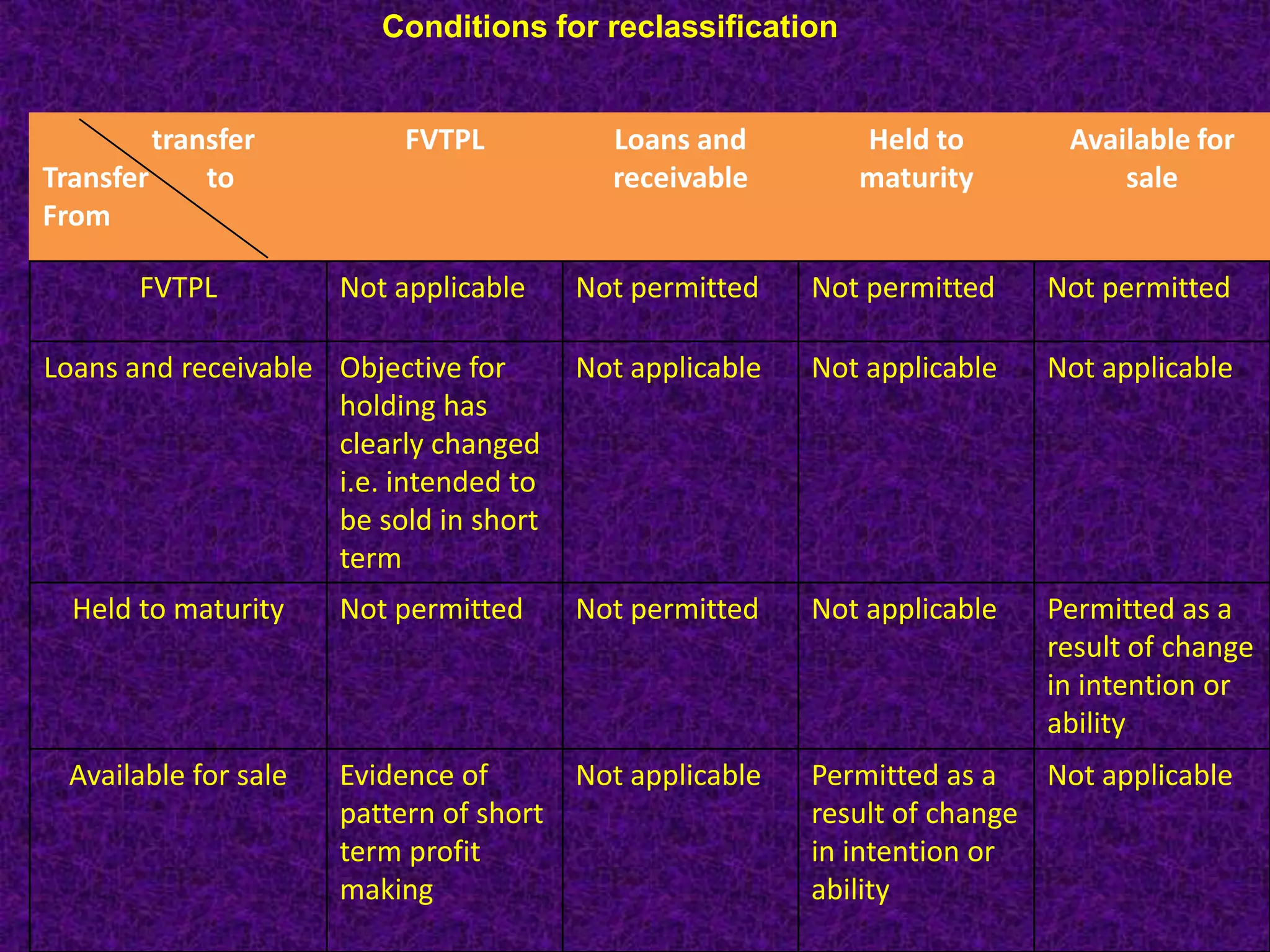
Financial instruments are contracts that give rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity. There are several types of financial instruments including cash, receivables, payables, loans, bonds, derivatives, and equity instruments. Financial instruments are classified and accounted for differently depending on whether they are assets, liabilities, or equity. Financial assets are classified as financial assets at fair value through profit or loss, held-to-maturity, loans and receivables, or available-for-sale. Financial liabilities are classified as either financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss or other financial liabilities. The classification of financial instruments affects how they are measured and presented in financial statements





![Compound financial instrument
• It is instrument which contain elements of debt as well as equity. Eg convertible debenture
• It must be split into liability and equity component for accounting purpose.
• The liability element is determined by fair valuing cash flows excluding any equity
component and balance is assigned to equity.
Example: 200, 5% convertible debentures issued @ Rs100 per debenture. Option of conversion
can be exercised at end of four year. Prevailing market rate for similar debt without
conversion option is 7%(assumed for calculation purpose)
Calculation carrying amount of liability portion Rs
Present value of principal[ 20000* DF(7%, 4th year)] 15260
Present value of interest[1000*AF(7%, 4 year)] 3387
18647
Proceeds of issue 20000
Less: liability portion 18647
Equity portion 1353](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/as30part-i-120422202500-phpapp02/75/AS-30-Part-I-6-2048.jpg)