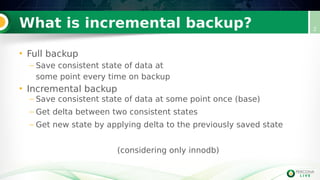
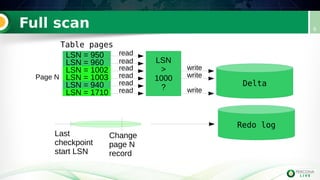
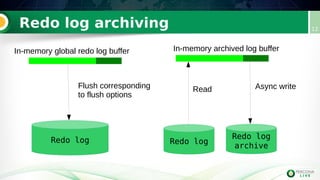
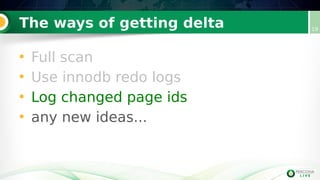
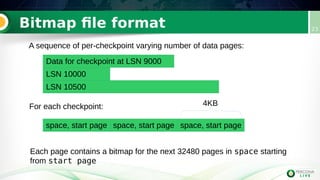
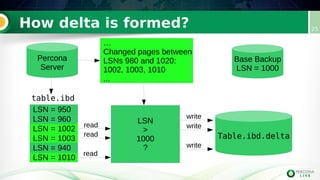
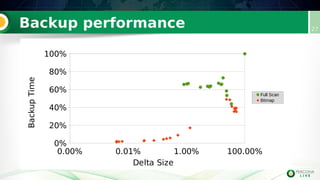
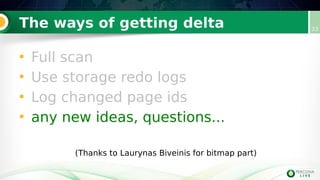
Incremental backups can be performed by tracking changed database pages since the last backup. This can be done through three main methods: full table scan, using redo logs, or logging changed page IDs. Logging changed page IDs avoids the overhead of a full scan and redo log archiving. The server tracks page modifications in a bitmap file. For incremental backups, only pages marked as changed since the last backup need to be read, reducing backup time and storage needs compared to a full backup or redo log approach. This page ID tracking provides an efficient alternative to full table scans or redo log archiving for incremental backups.