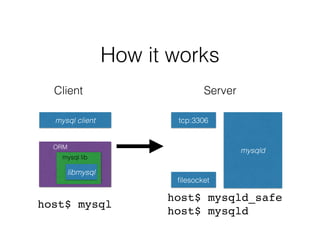
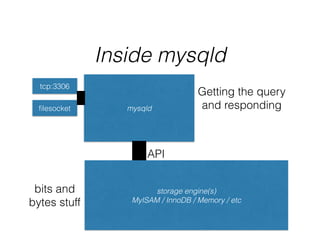
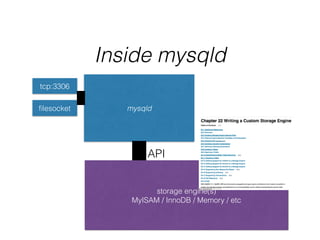
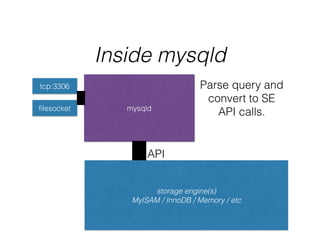
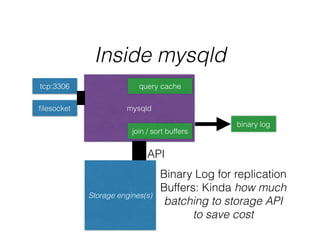
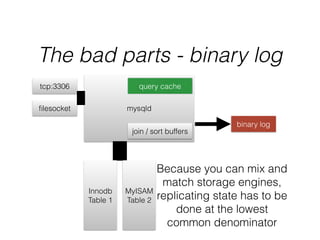
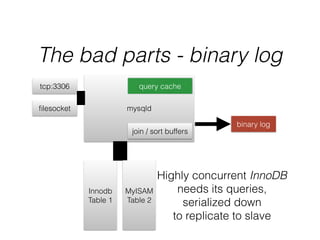
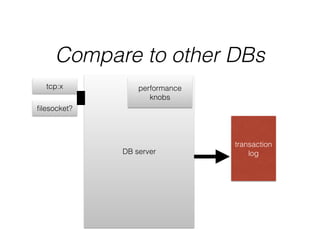
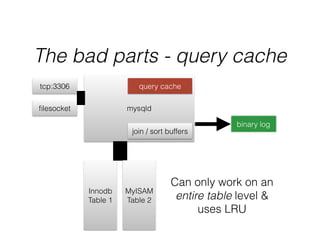
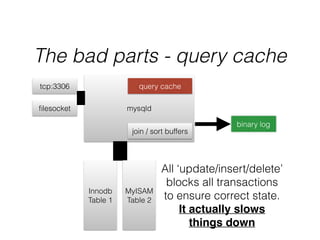
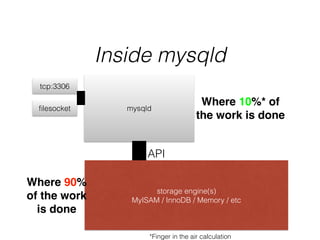
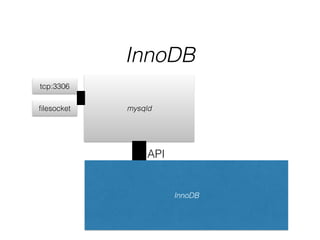
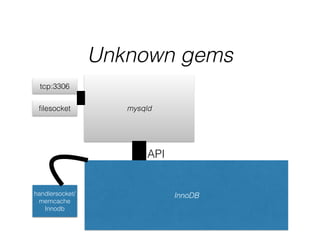
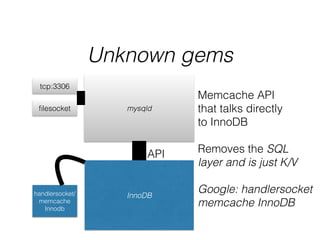
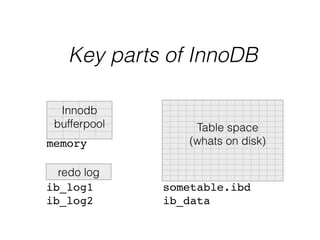
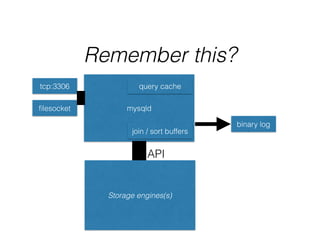
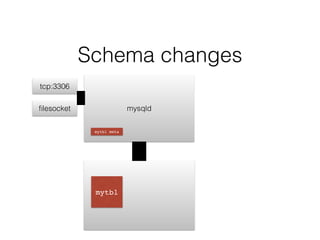
- The document provides an overview of MySQL and how it works internally. It discusses the key components of MySQL including the MySQL daemon (mysqld), storage engines like InnoDB and MyISAM, and the buffer pool.
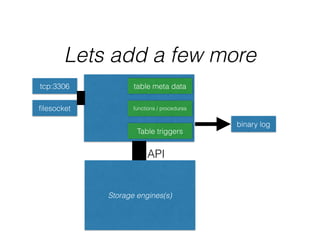
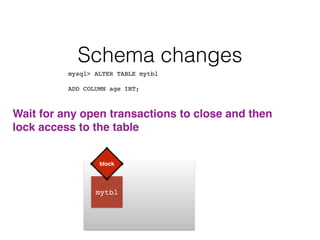
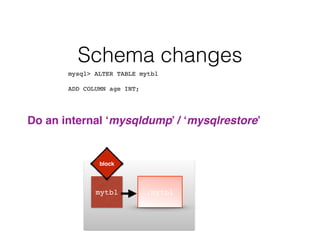
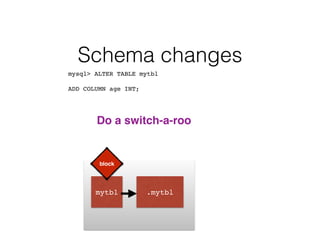
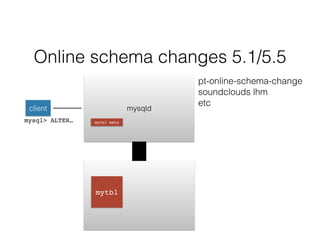
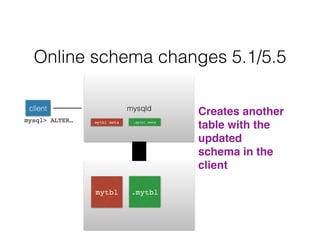
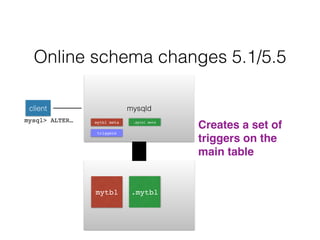
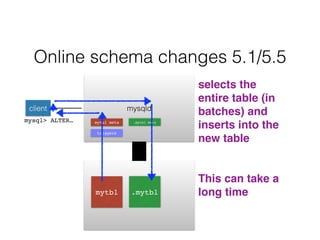
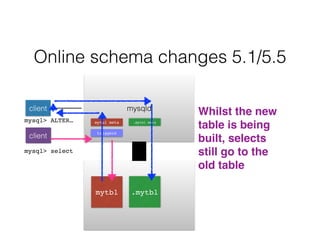
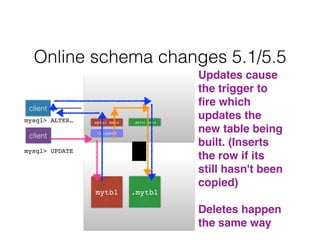
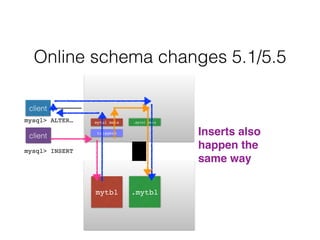
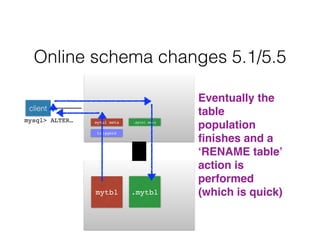
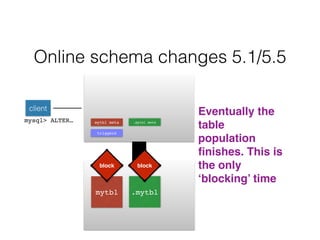
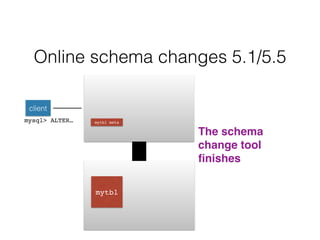
- Schema changes in earlier versions of MySQL were blocking and required table locks. More recent versions support online schema changes using triggers to copy data to a new table in the background.
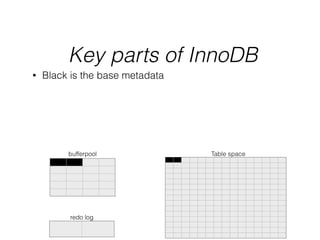
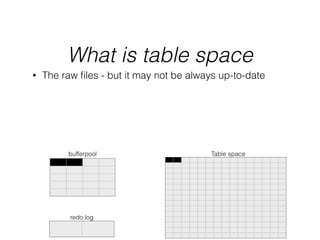
- InnoDB performs queries by loading relevant pages from the tablespace into the buffer pool in memory for fast random access, then writing changes to the redo log and periodically to the tablespace on disk.