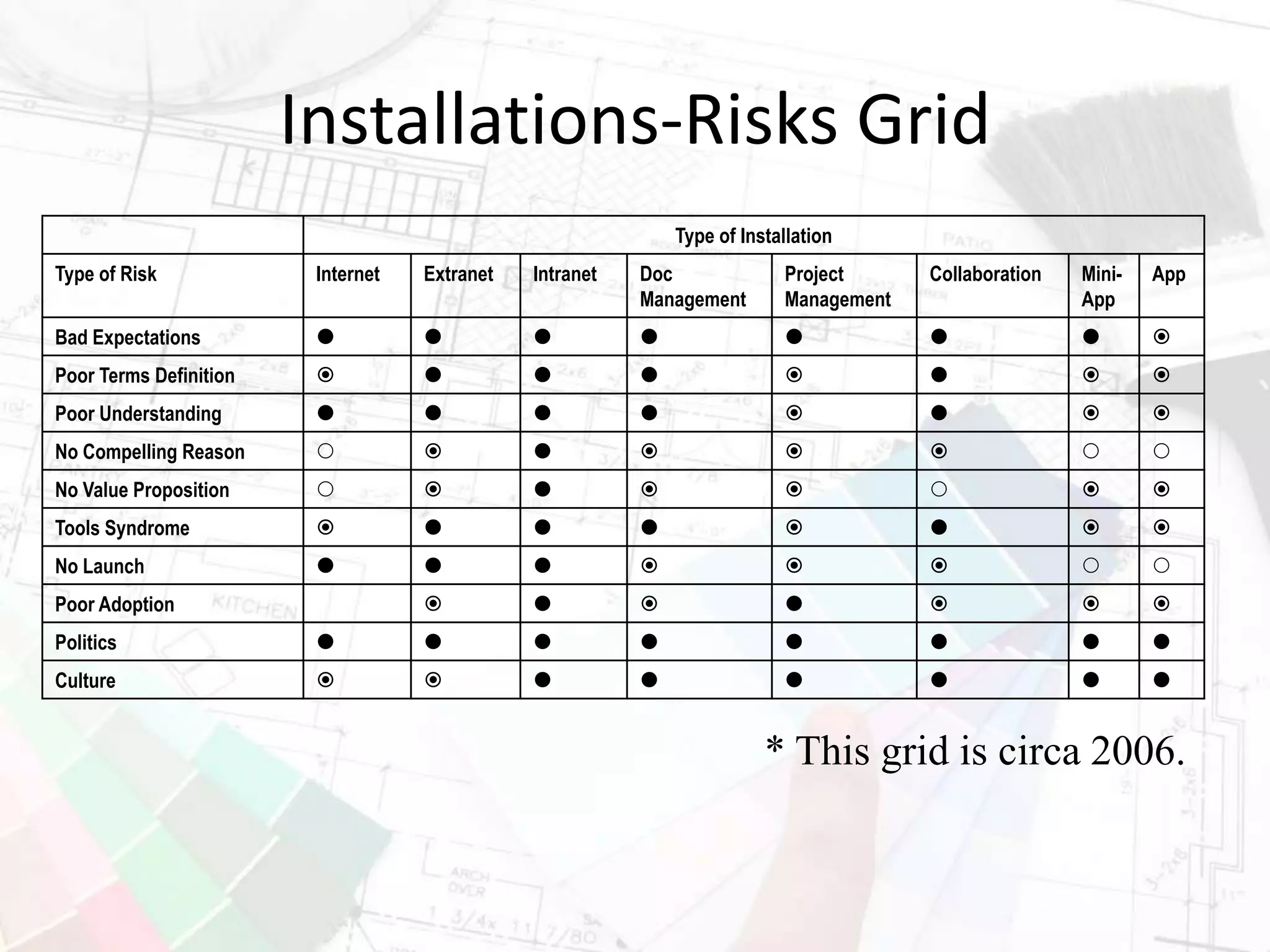
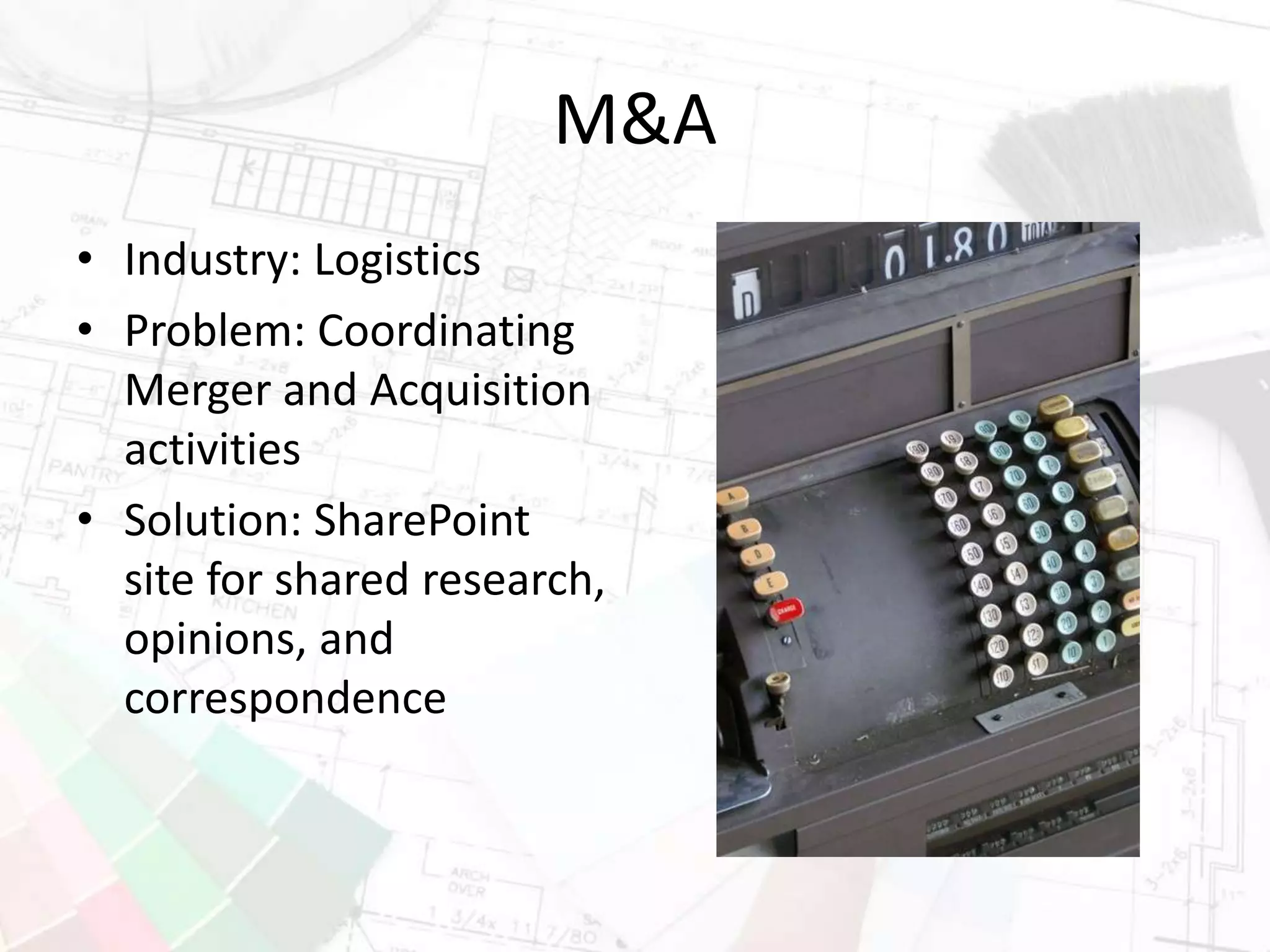
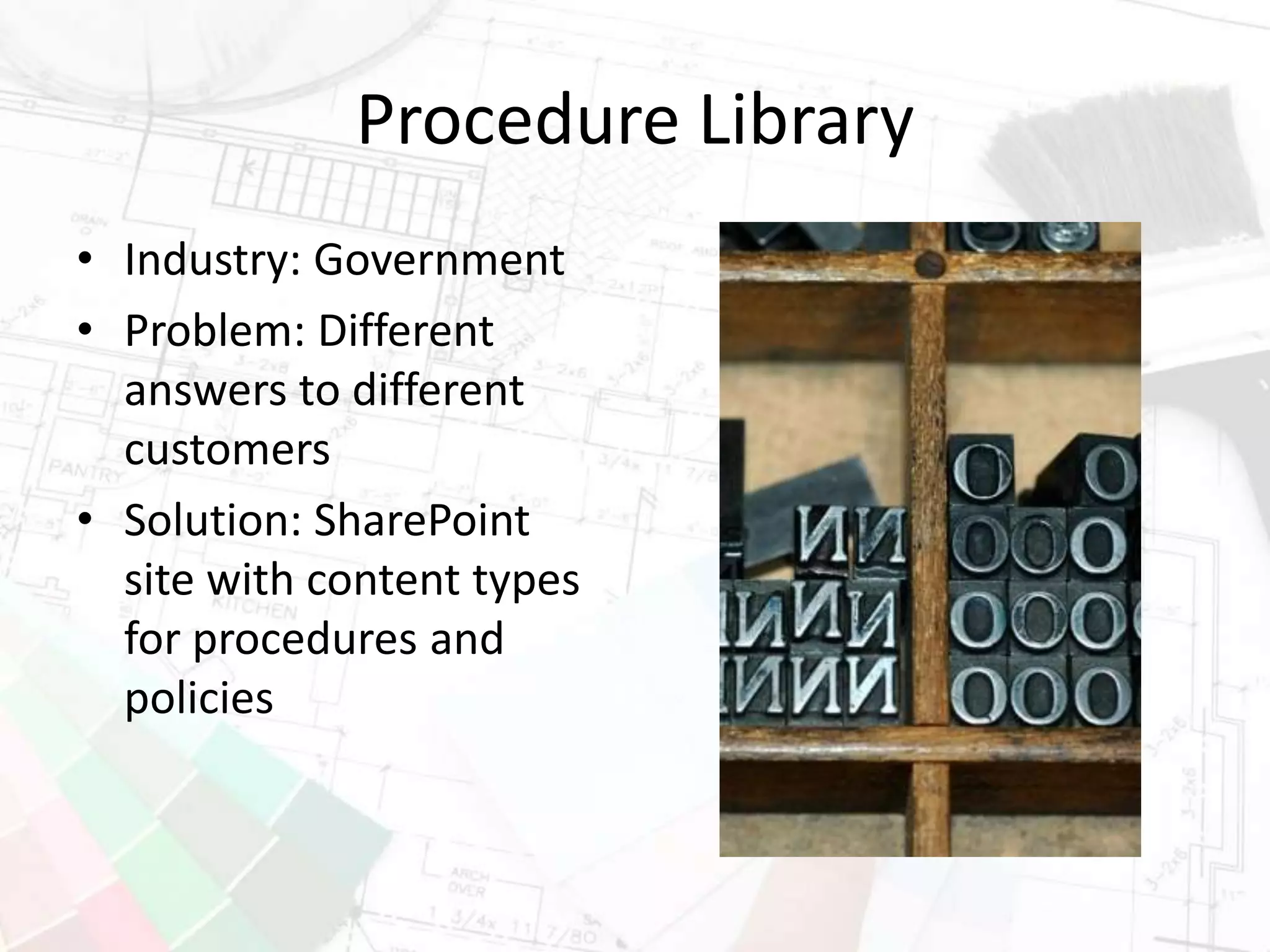
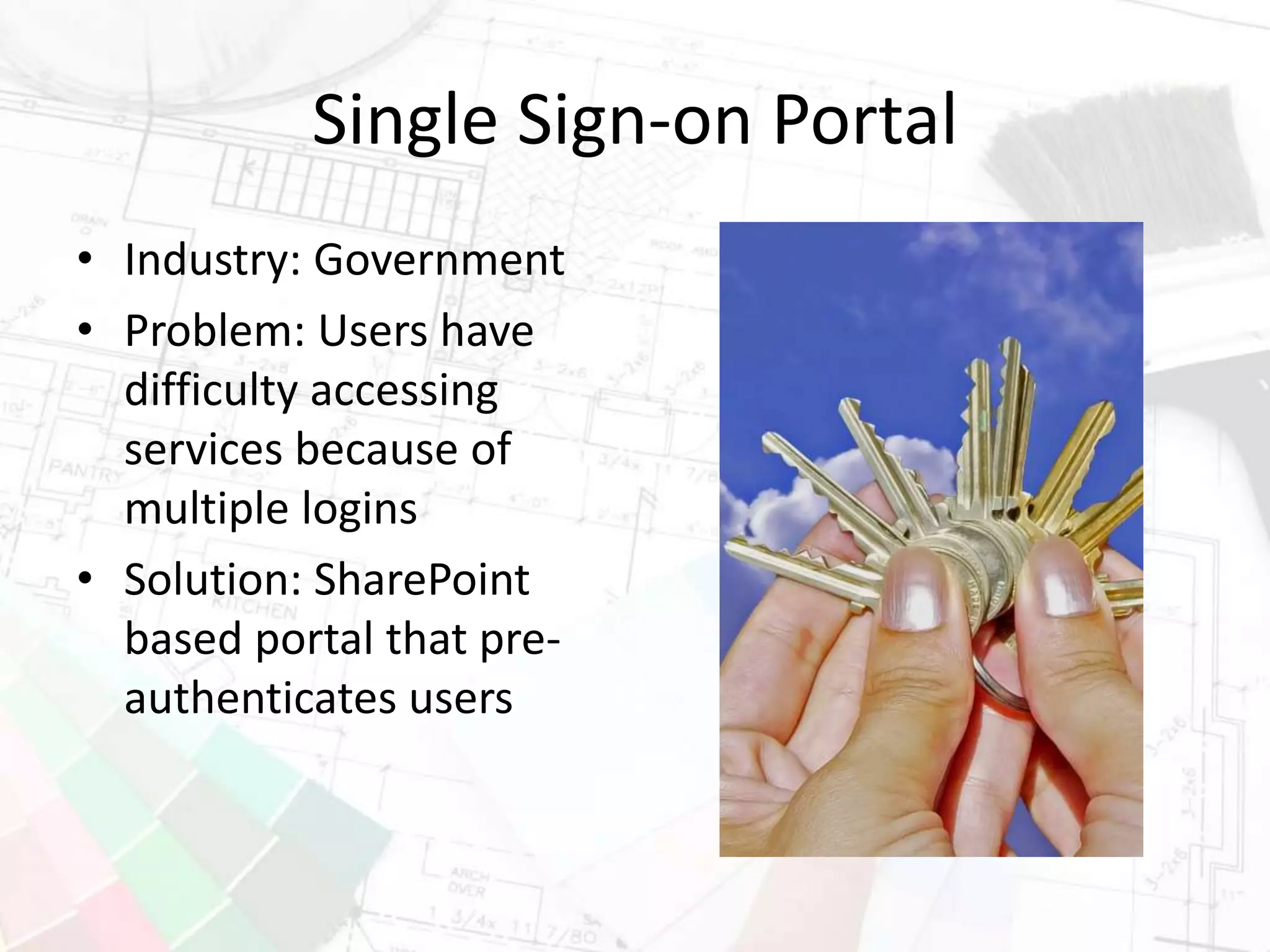
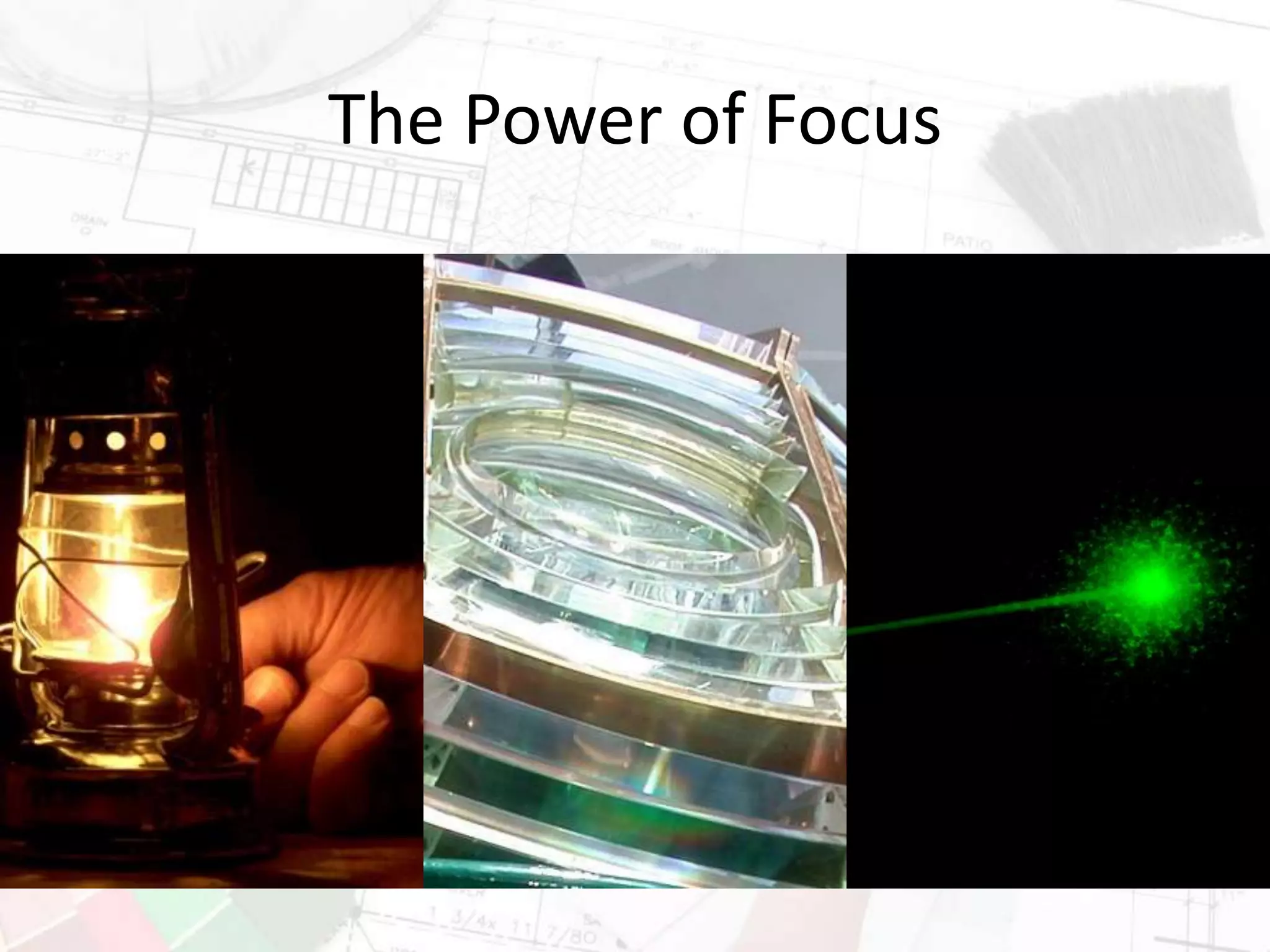
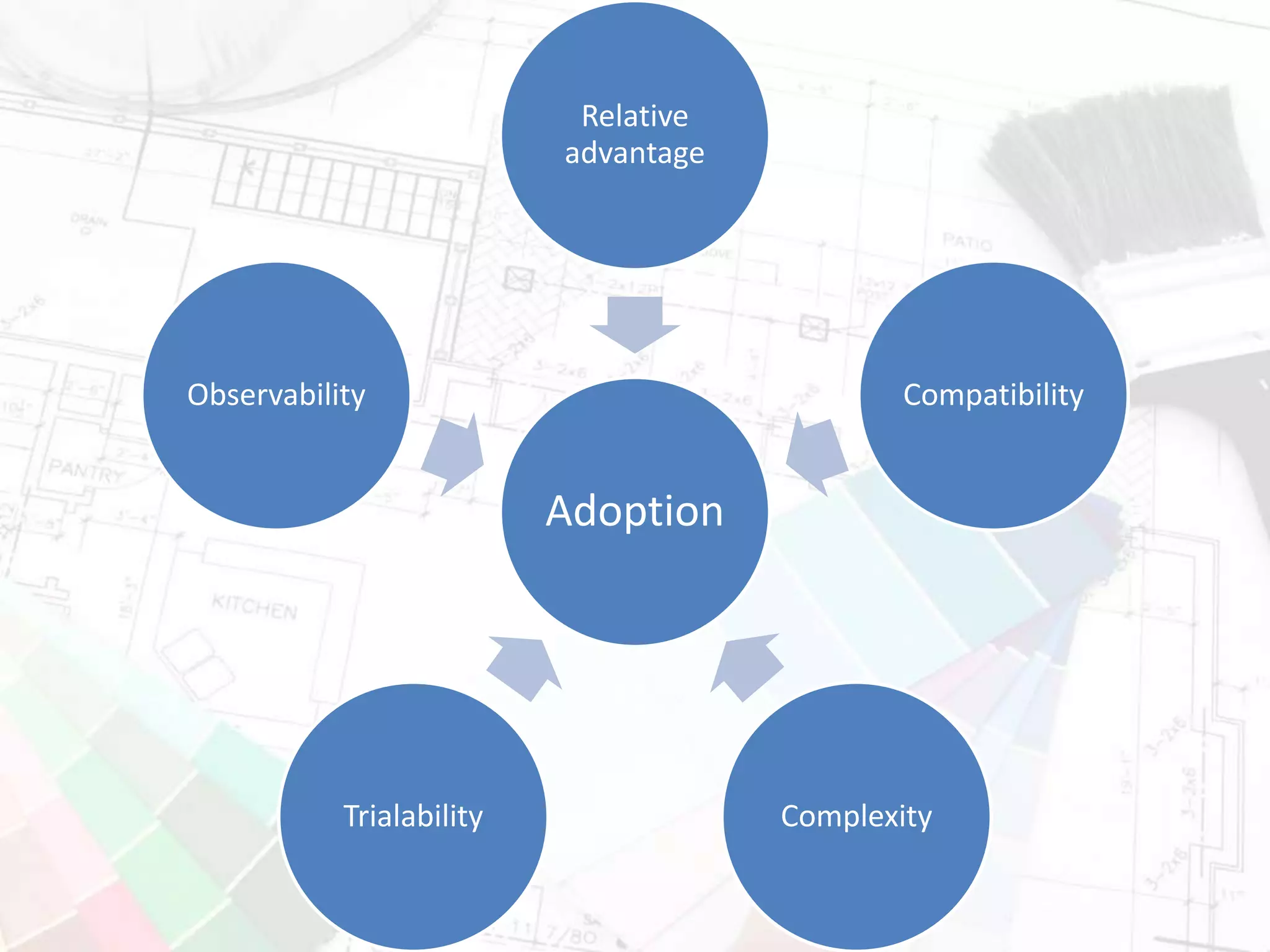
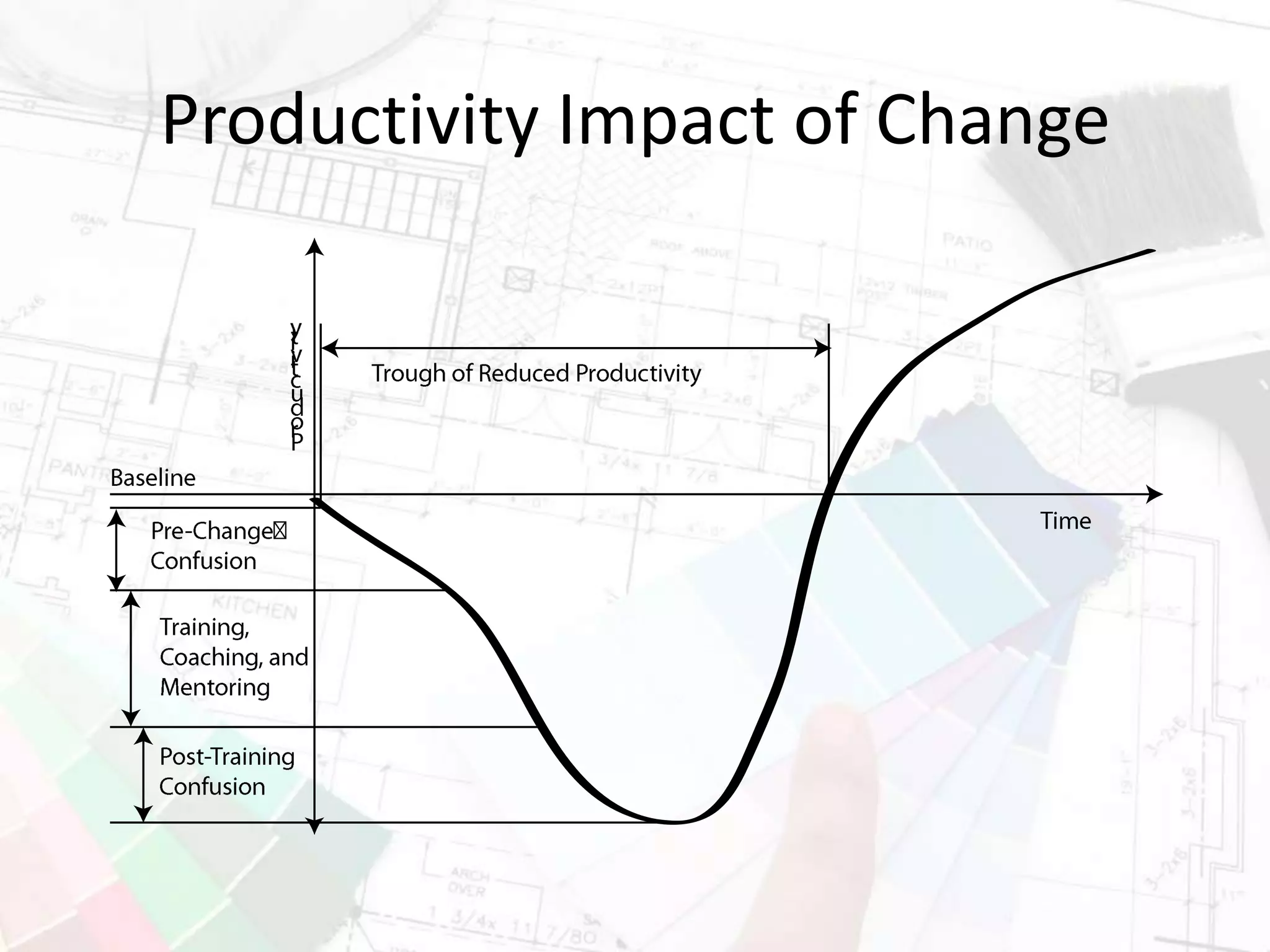
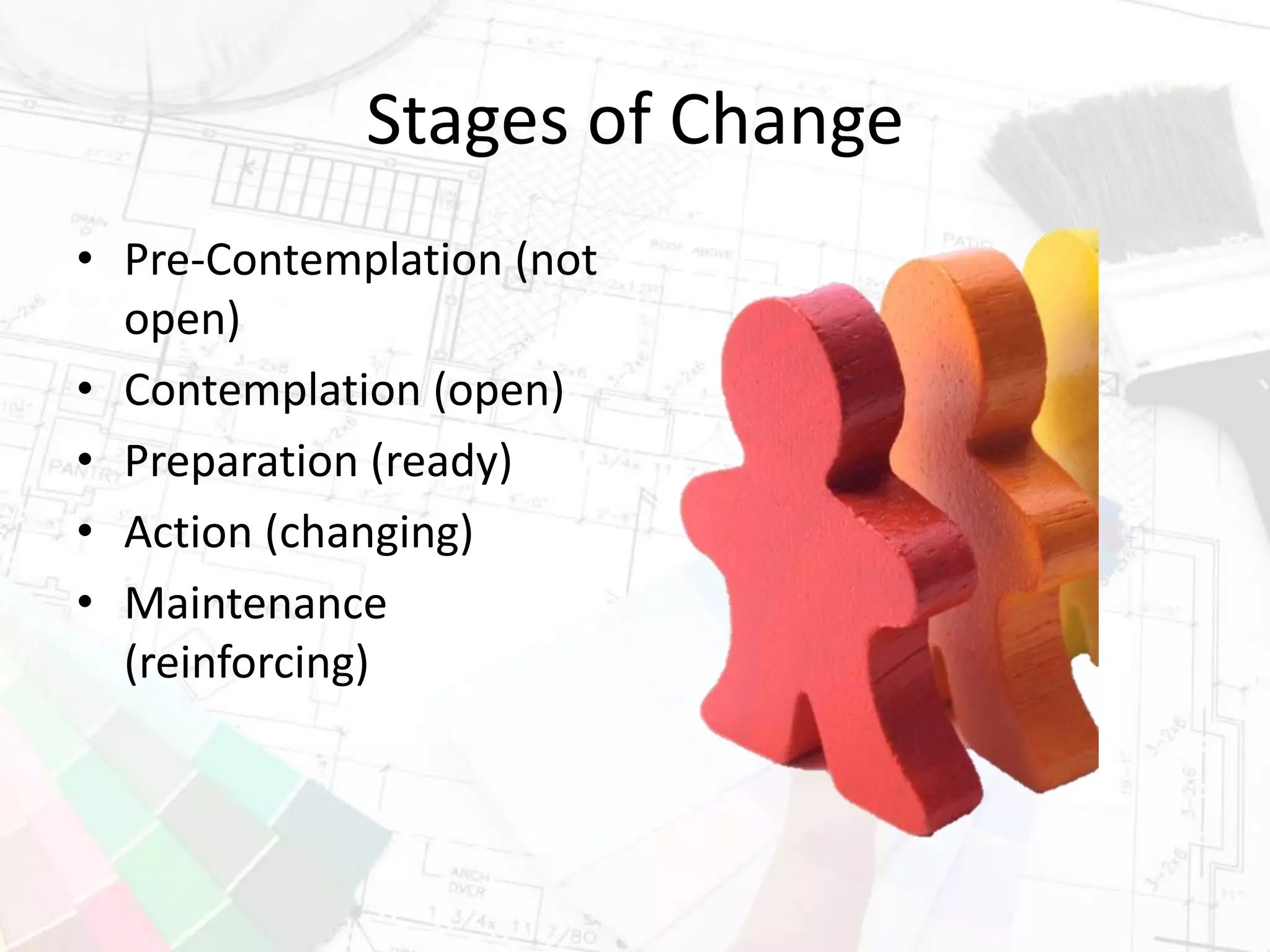
The document presents insights on increasing SharePoint engagement by Robert Bogue, a Microsoft MVP and author, emphasizing the importance of understanding adoption and emotional factors in organizational change. It outlines key strategies for successful SharePoint implementation, including establishing a shared vision and planning for ongoing engagement and training. The document also discusses the complexities of user adoption, presenting case studies and practical recommendations for various industries.





![What is Engagement?
• Engagement (noun) –
the act of engaging or
the state of being
engaged.
– Dictionary.com
• Engaged – busy or
[fully] occupied;
involved
– Dictionary.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/increasingsharepointengagementv2-130813181948-phpapp01/75/Increasing-SharePoint-Engagement-6-2048.jpg)



















![Right Defaults
• Behavior is a function of
the person and the
environment [B=f(P, E)-
Kurt Lewin]
• Establish the default
behavior and people
will follow (mindlessly)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/increasingsharepointengagementv2-130813181948-phpapp01/75/Increasing-SharePoint-Engagement-33-2048.jpg)