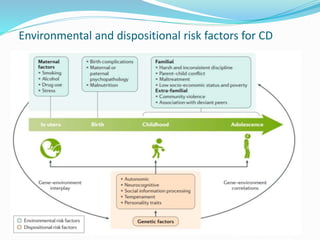
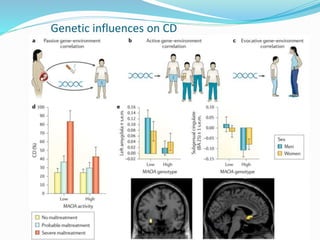
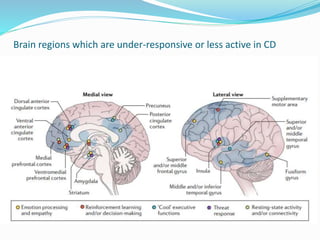
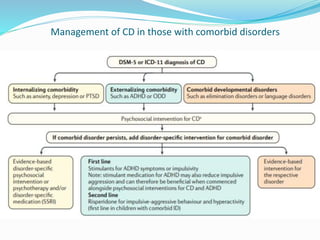
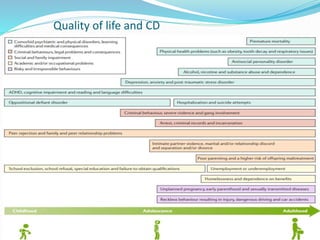
Impulse control disorders (ICDs) include oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder, intermittent explosive disorder, pyromania, and kleptomania. They are characterized by the inability to control impulsive behaviors that violate the rights of others or societal norms. The etiology is multifactorial involving genetics, family environment, social factors, and biological disturbances in the prefrontal cortex. Treatment involves parenting skills training, cognitive behavioral therapy, and sometimes medication, while differential diagnosis considers disorders with similar impulsive or oppositional symptoms like ADHD, mood disorders, and personality disorders that may co-occur.