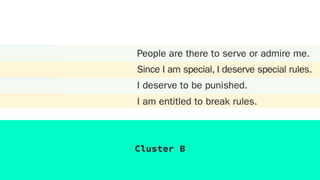
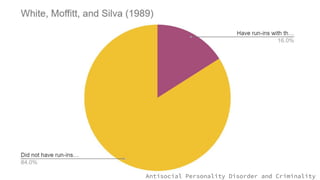
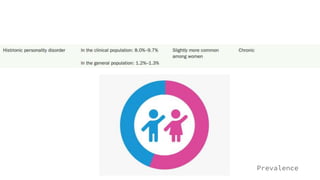
The document discusses Cluster B personality disorders, including antisocial, borderline, histrionic, and narcissistic personality disorders, highlighting their characteristics, causes, prevalence, and intervention strategies. It emphasizes the role of genetics, environment, and early life experiences in the development of these disorders, as well as the challenges in treating individuals with these conditions. Overall, it outlines the clinical descriptions, diagnostic criteria, and the interplay of genetic and environmental factors contributing to these complex psychological issues.