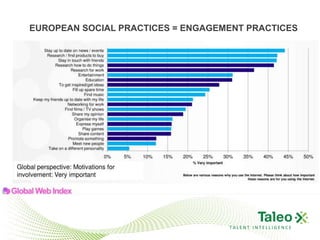
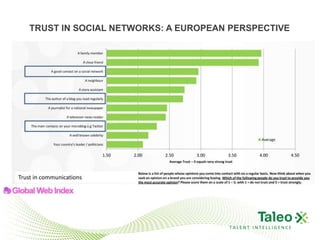
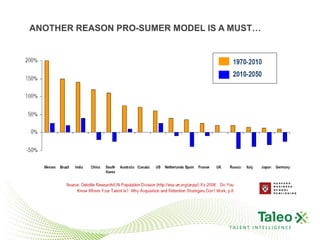
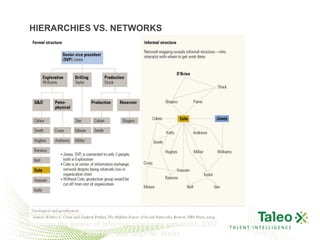
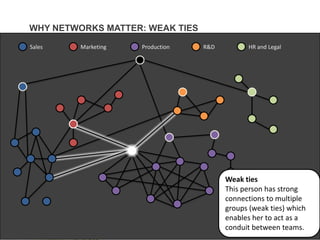
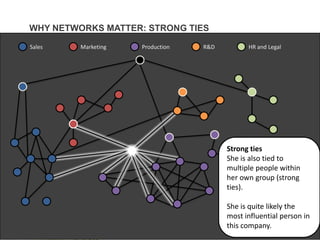
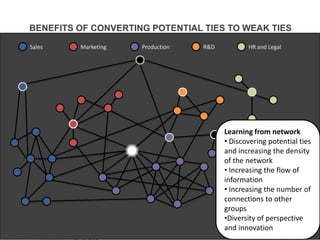
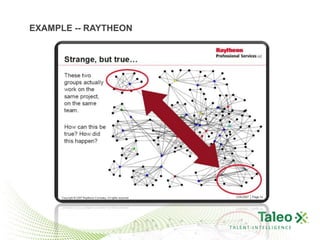
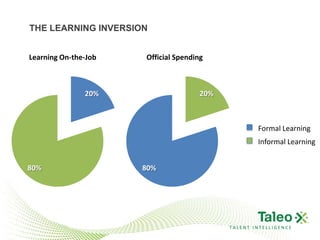
This document discusses improving employee engagement through social learning. It argues that social learning enables the key drivers of engagement by allowing employees to share knowledge, network with peers, and collaborate in shared spaces. It provides examples of how organizations have used social tools like discussion forums, blogs, and expertise networks to create learning communities and drive better business outcomes through increased engagement. The presentation recommends that companies develop a pro-sumer learning model, employee social networks, and shared learning spaces to harness the power of social learning for engagement.