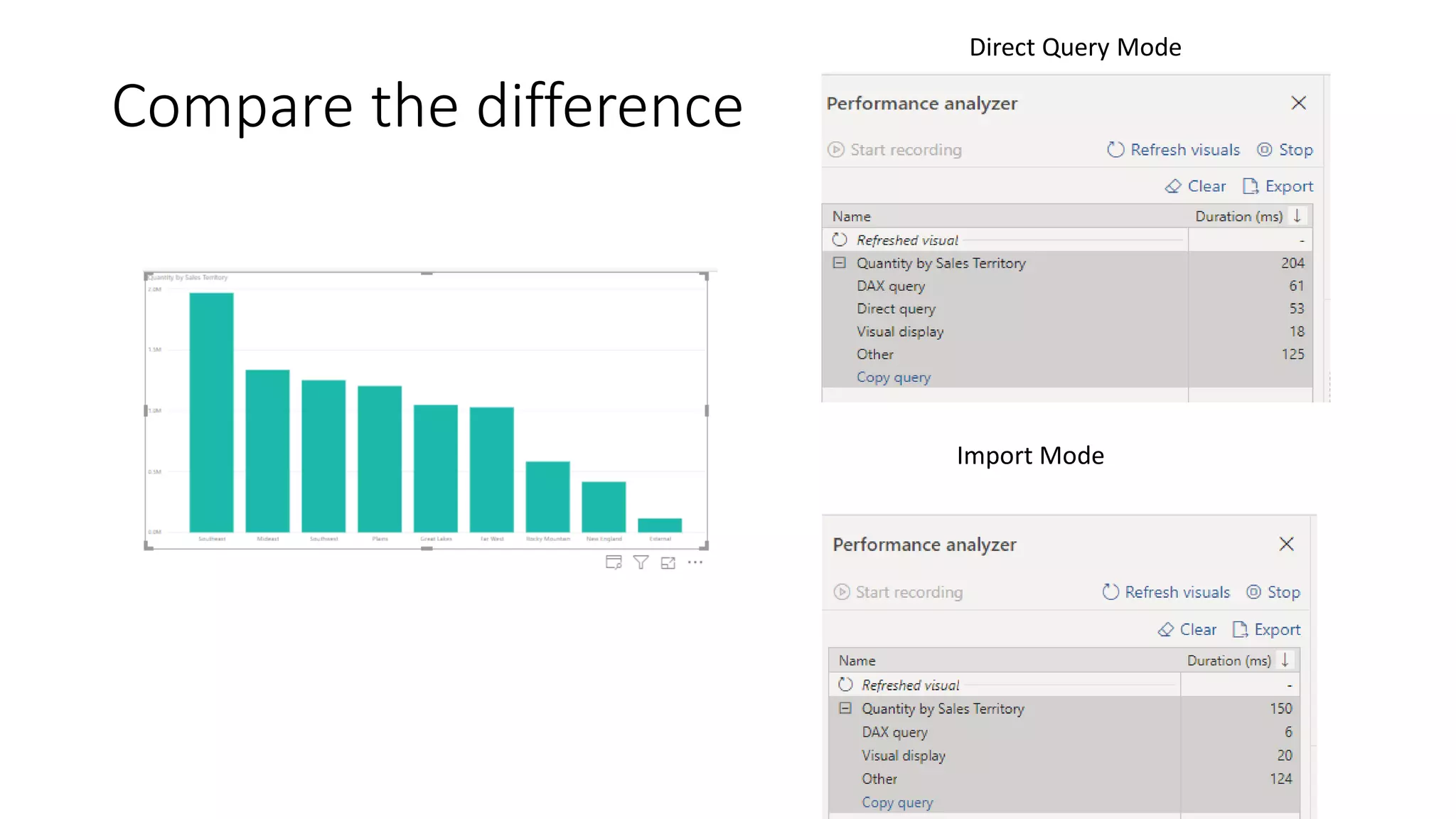
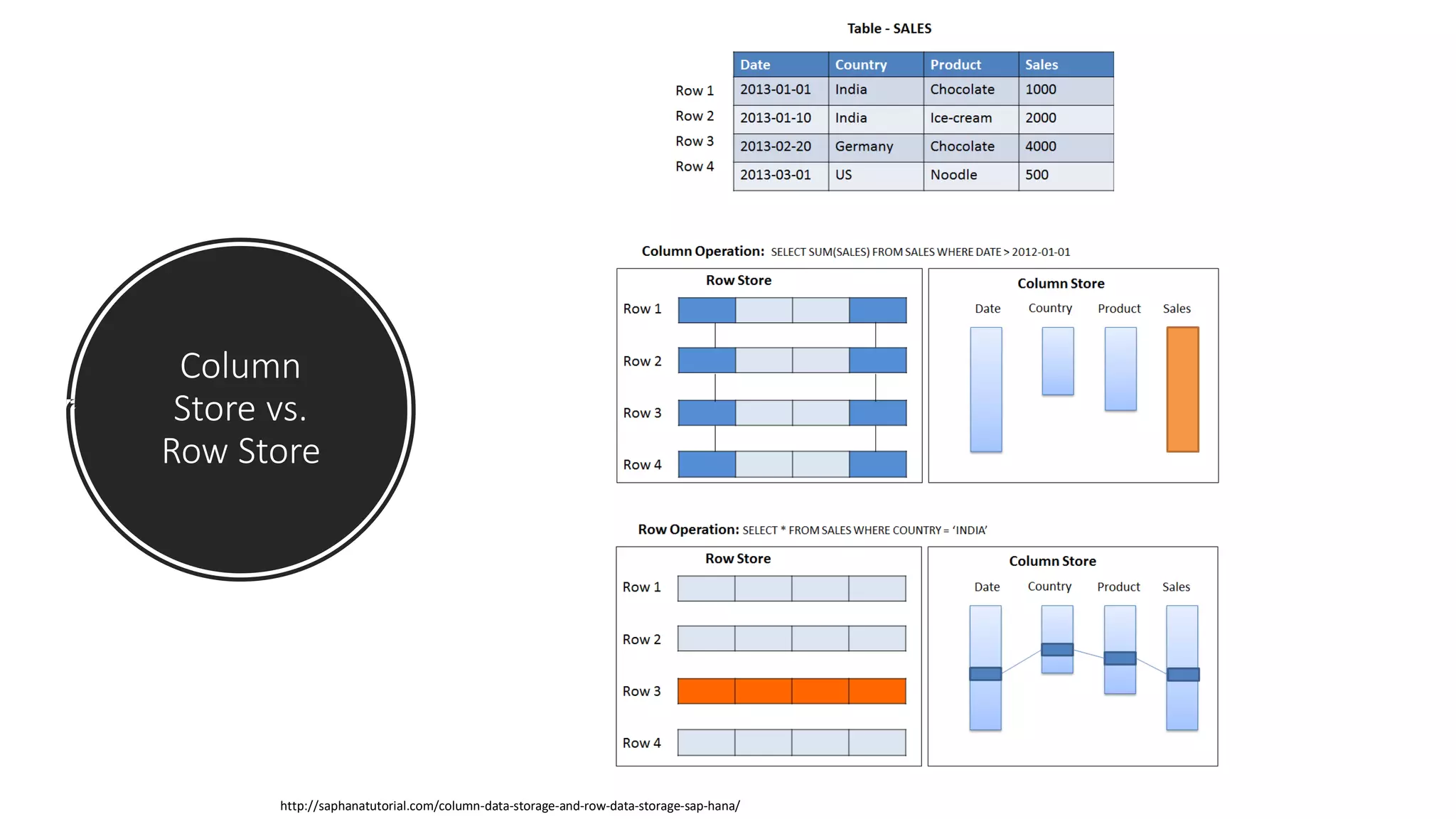
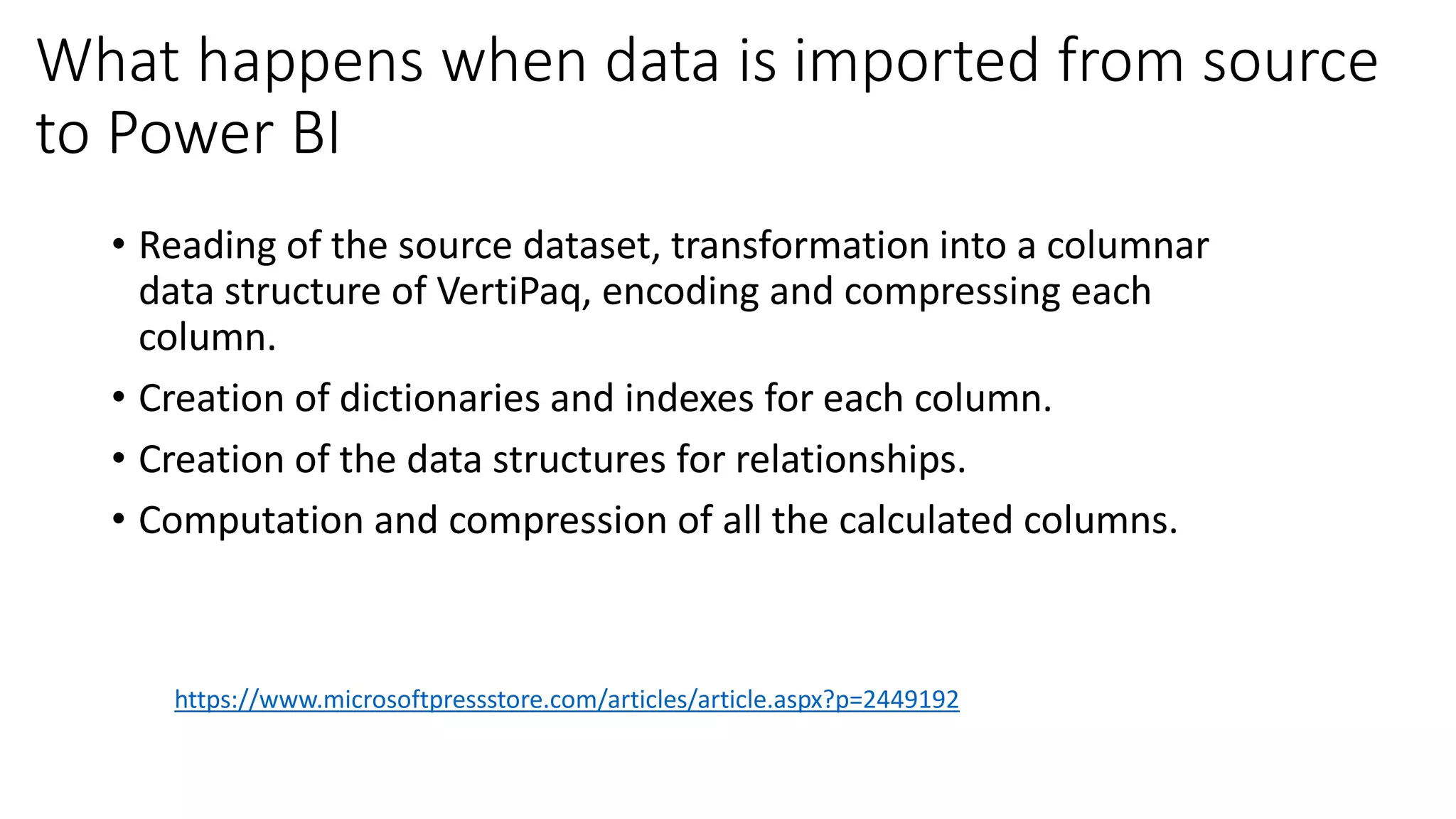
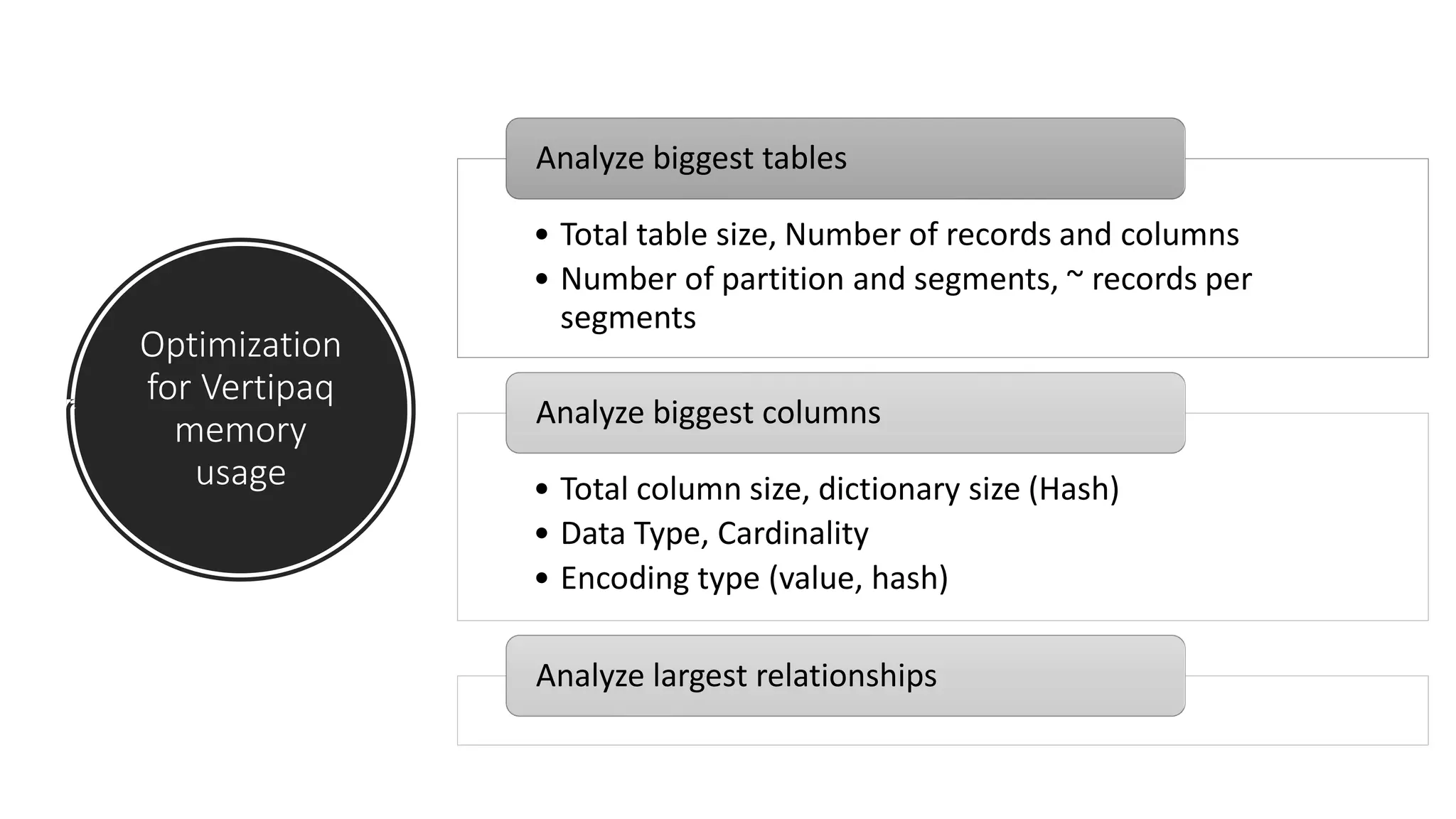
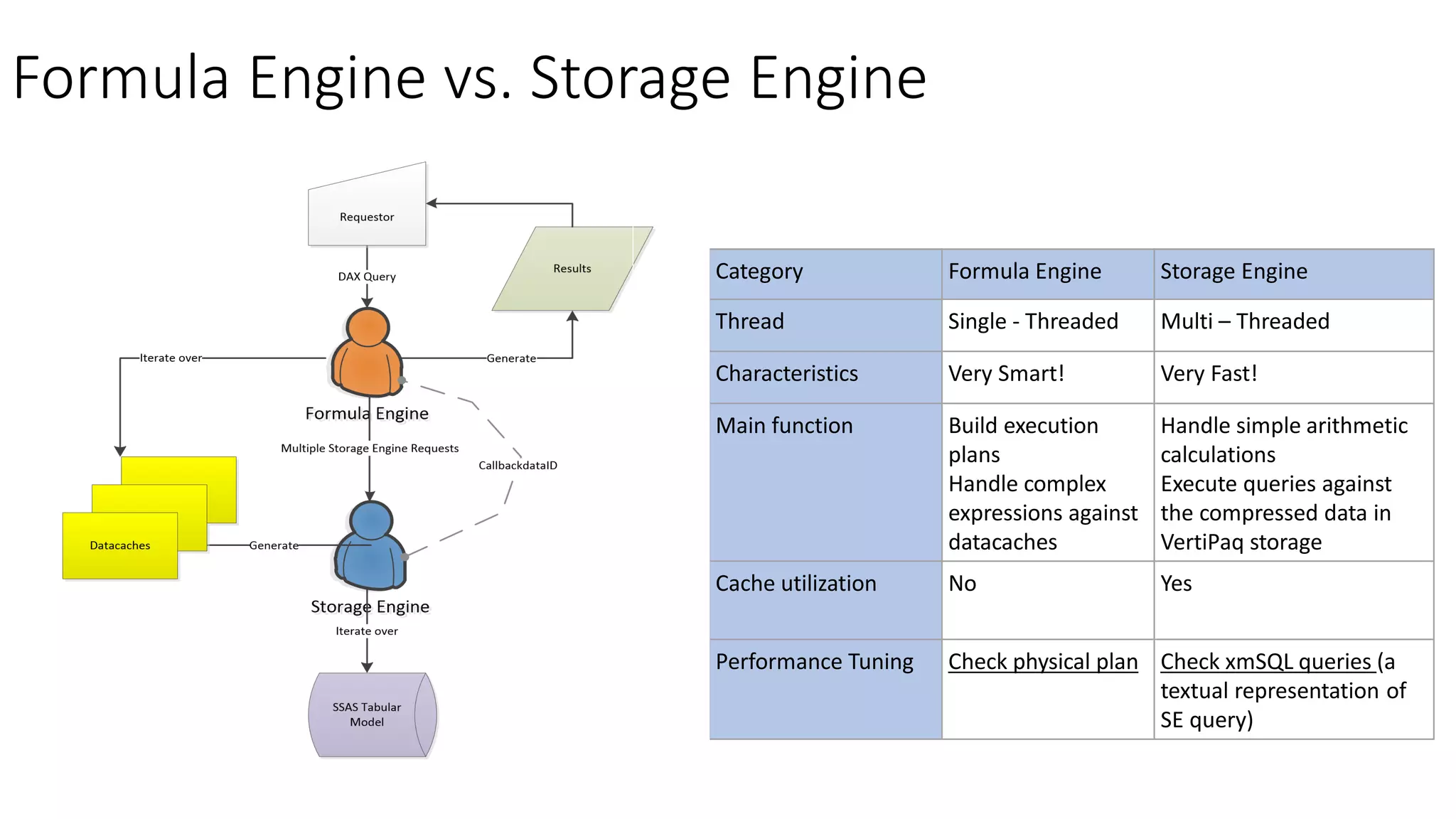
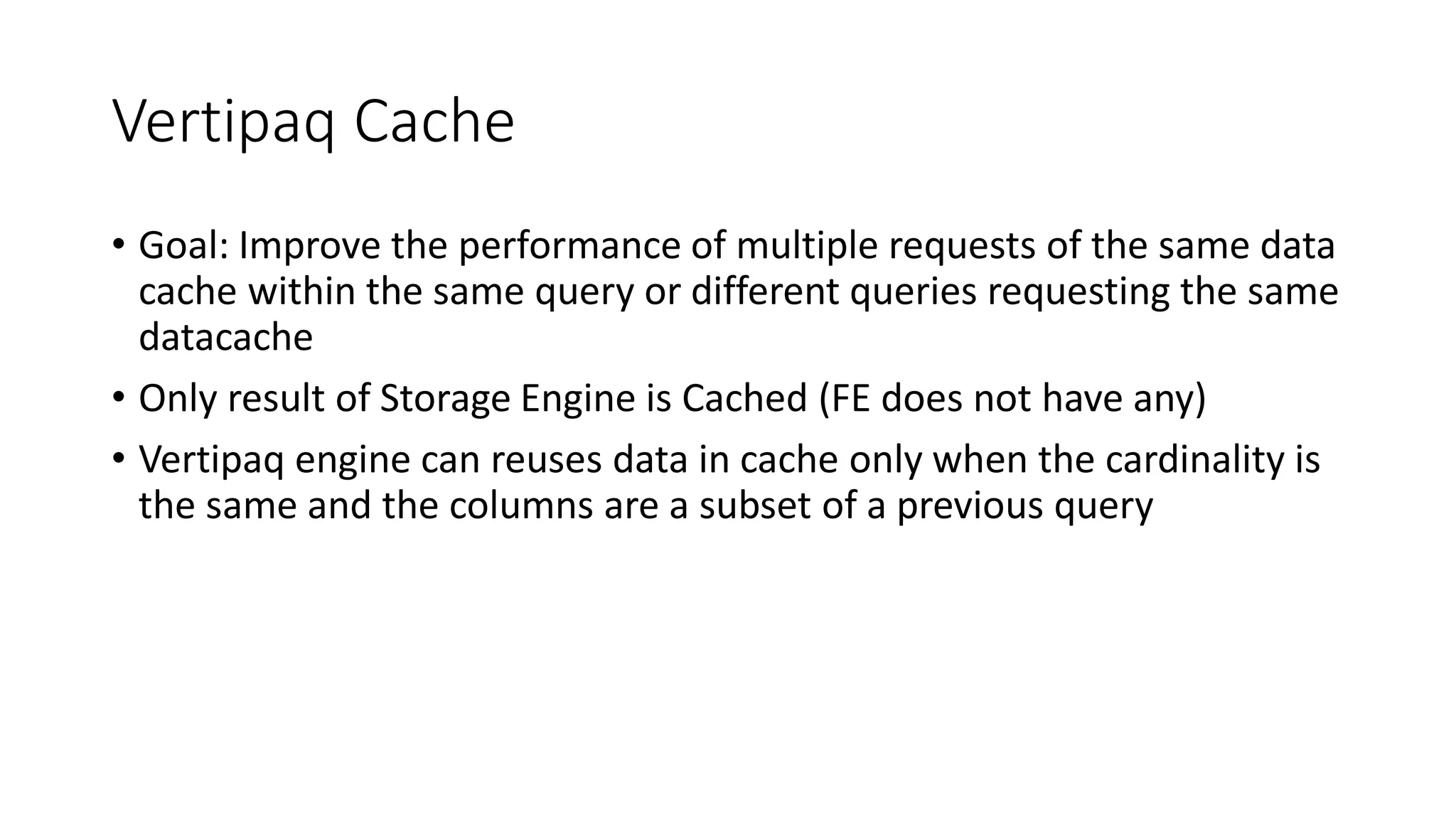
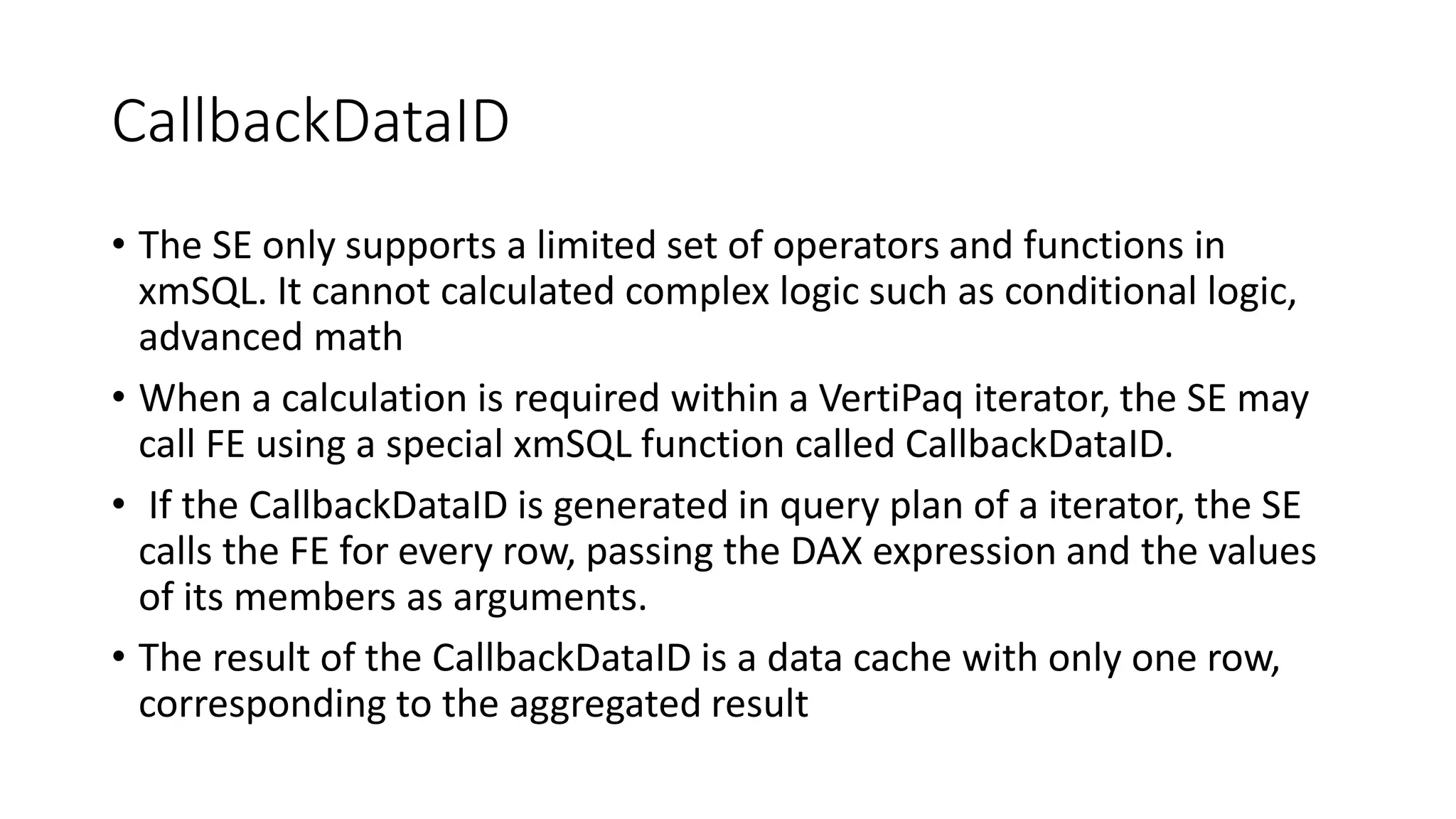
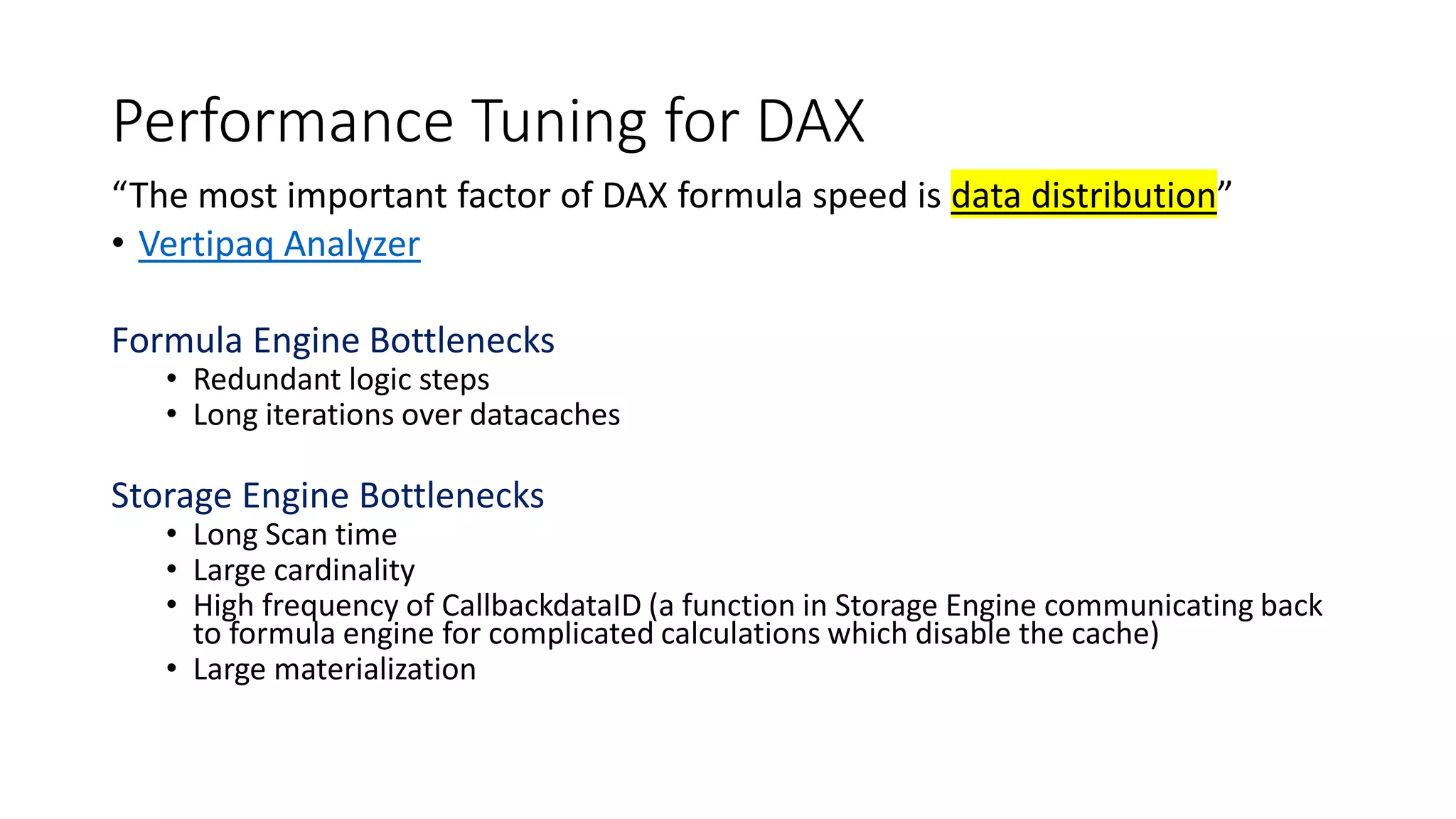
The document provides an overview of optimizing performance in Power BI, focusing on the VertiPaq engine, query architecture, and best practices for data modeling. Key strategies include understanding the differences between import and direct query modes, and utilizing tools like the VertiPaq Analyzer and DAX Studio for performance analysis. It emphasizes the importance of model design and offers various performance tuning techniques to enhance query execution and memory usage.