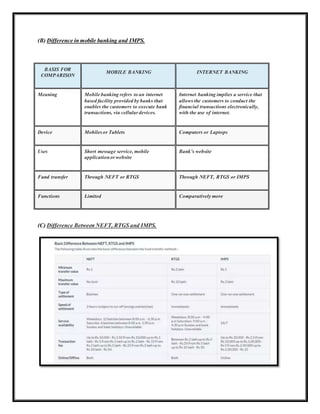
The document provides a comprehensive list of important banking terminology, including definitions of terms like ATM, bancassurance, bank rate, and mortgage among others. It also discusses differences between mobile banking and internet banking, as well as various fund transfer methods such as NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS. Overall, it serves as a guide for understanding key banking concepts and services.