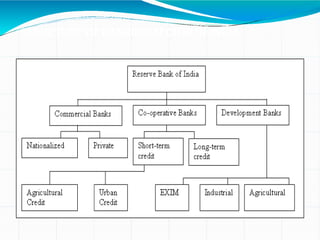
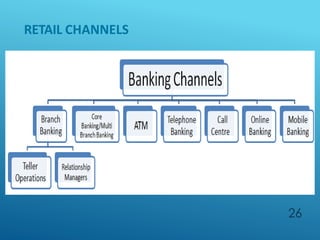
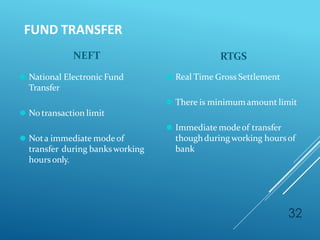
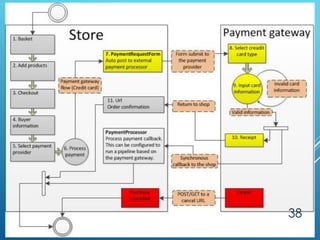
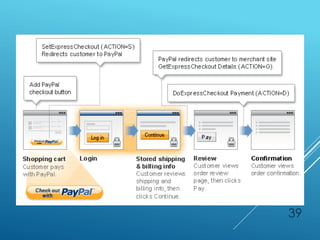
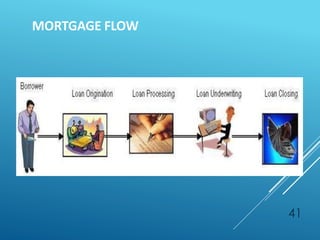
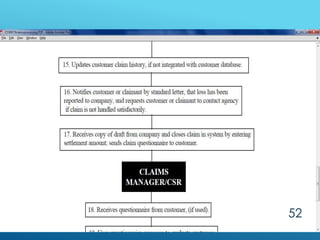
The document provides an overview of key concepts in banking and finance. It covers topics such as money, financial instruments, banking, retail banking services, mortgages, insurance, and the role of information technology in banking. The document aims to help technology professionals understand financial terms and the operations of the banking sector.